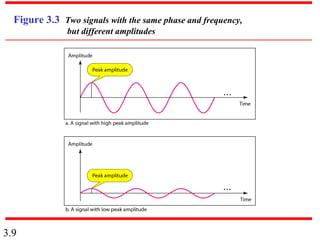
This document discusses analog and digital data and signals. It defines analog data as continuous and taking on continuous values, while digital data is discrete and takes on discrete values. Signals can also be analog or digital. Periodic signals that repeat over time can be decomposed into simpler sine waves using Fourier analysis. This represents the signal in the frequency domain. Nonperiodic signals have a continuous range of frequencies. The bandwidth of a signal is the range between its highest and lowest frequencies. Examples are given of various signal types and their Fourier representations.