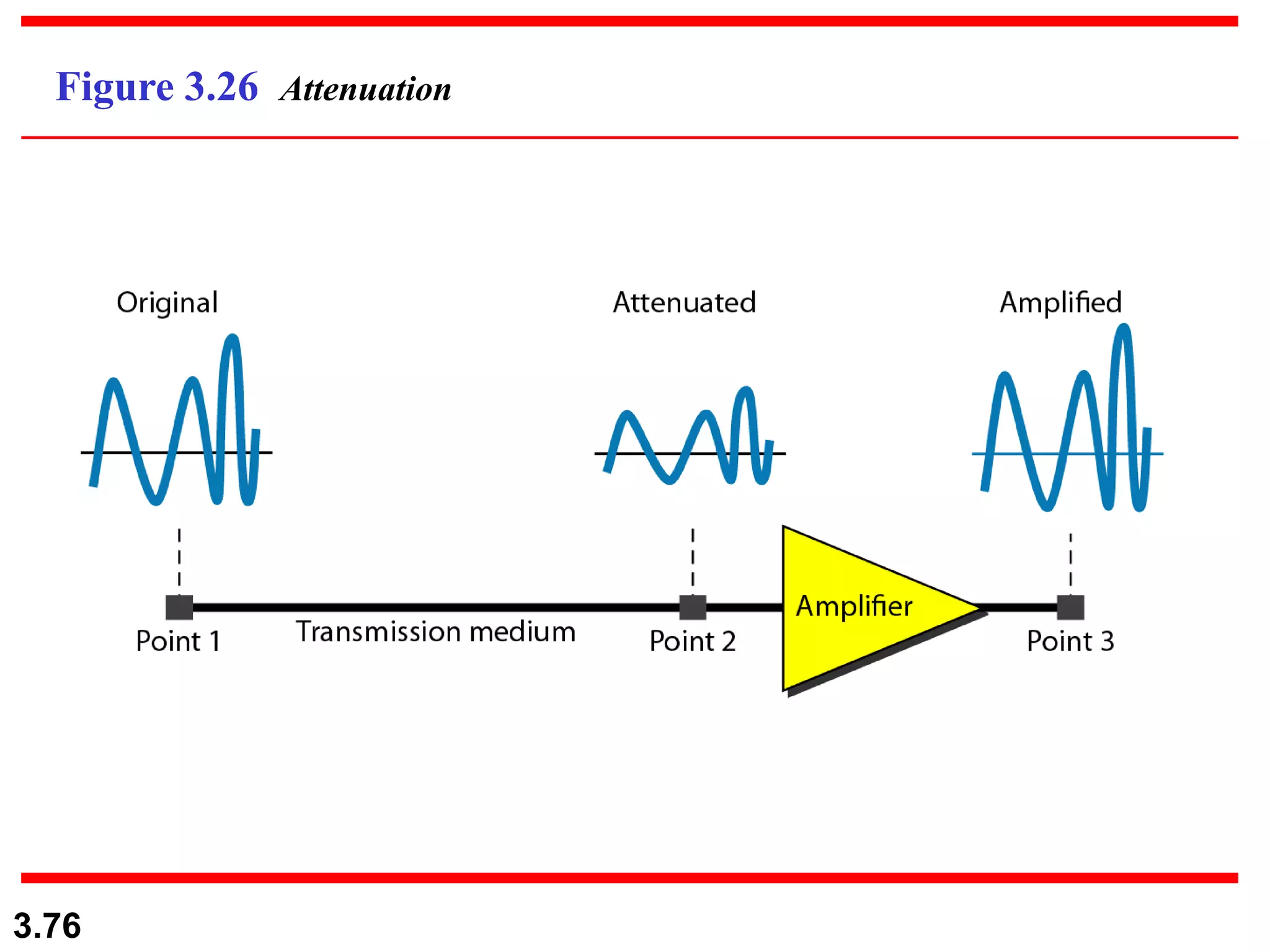
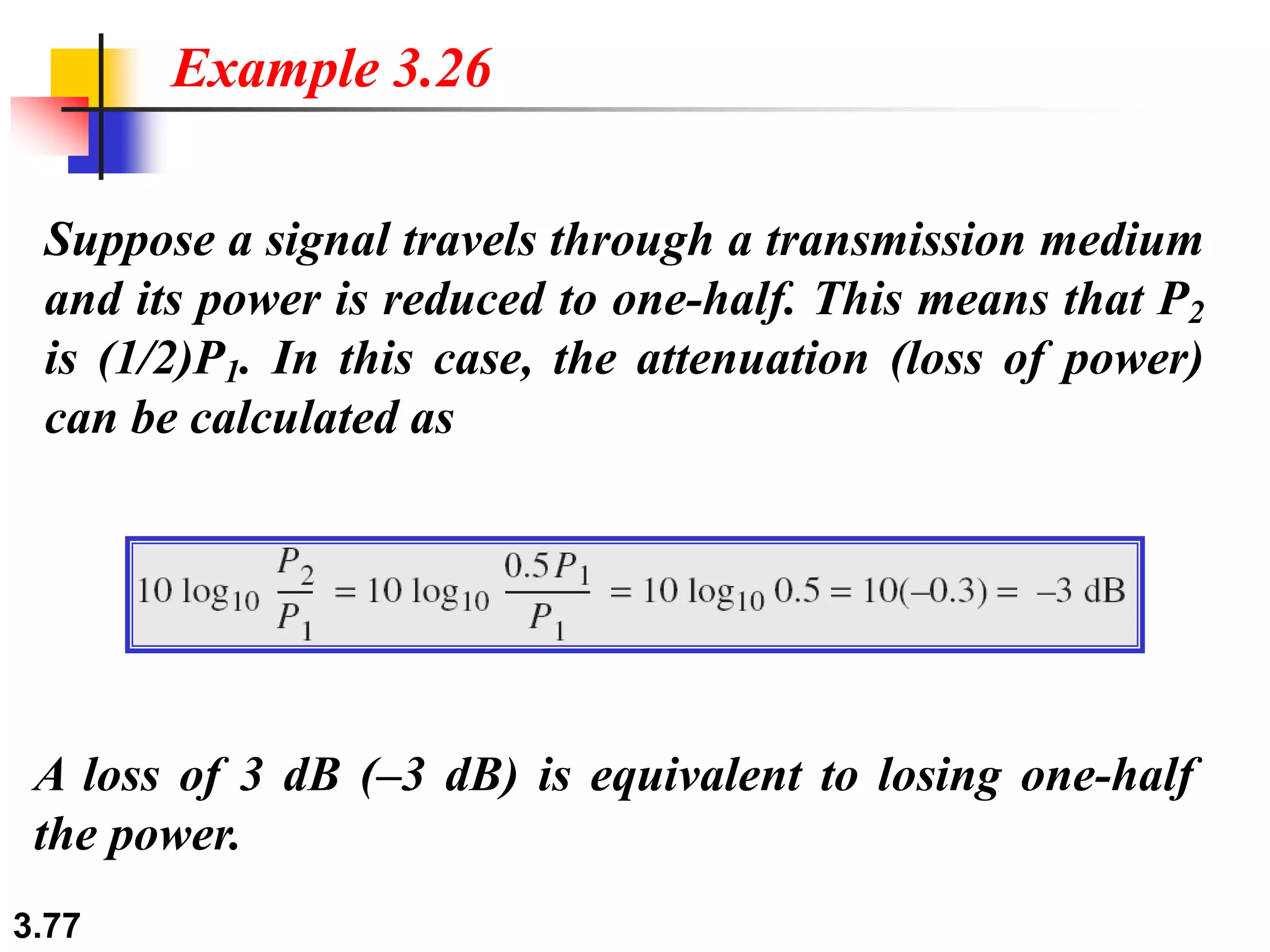
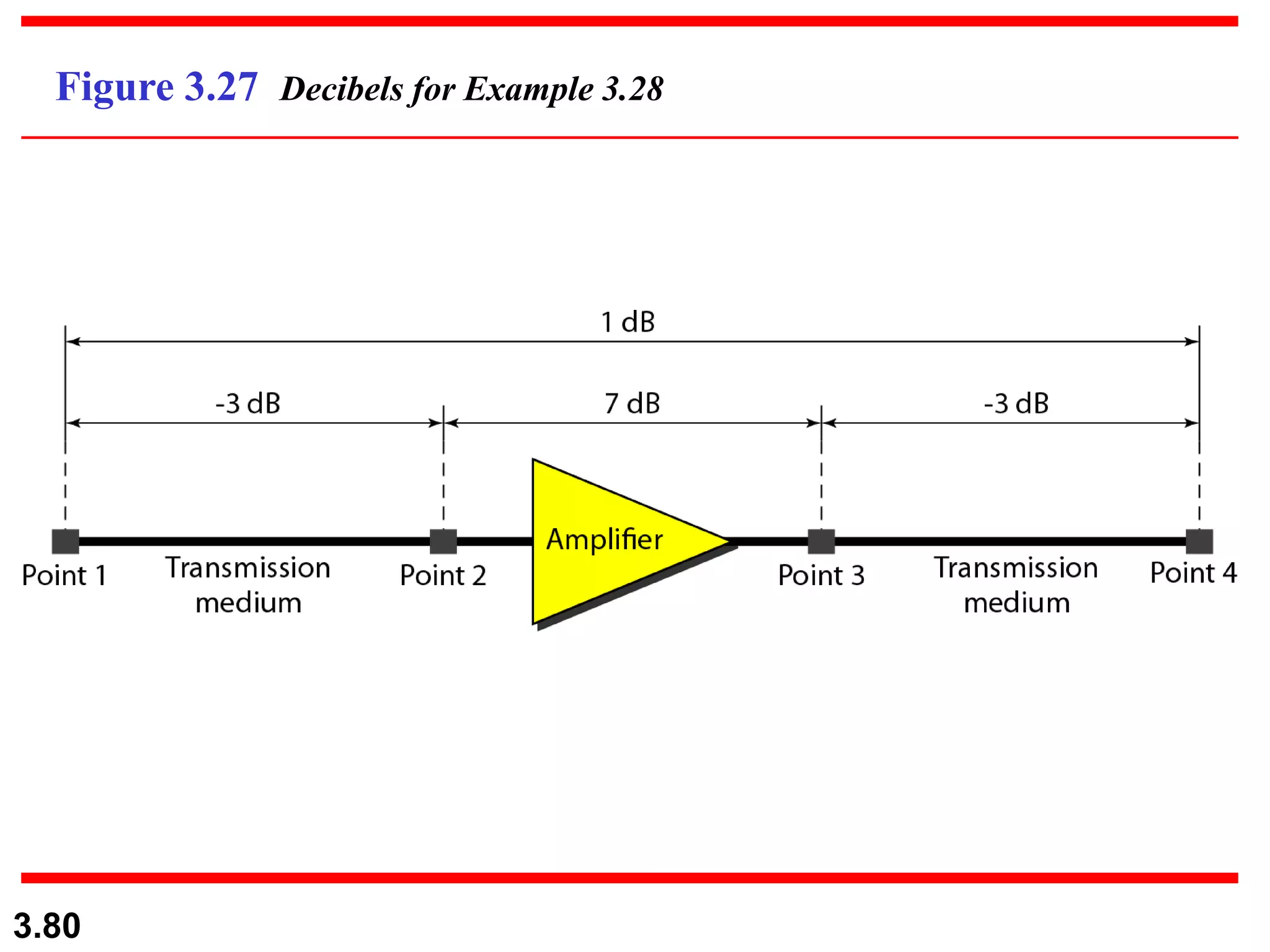
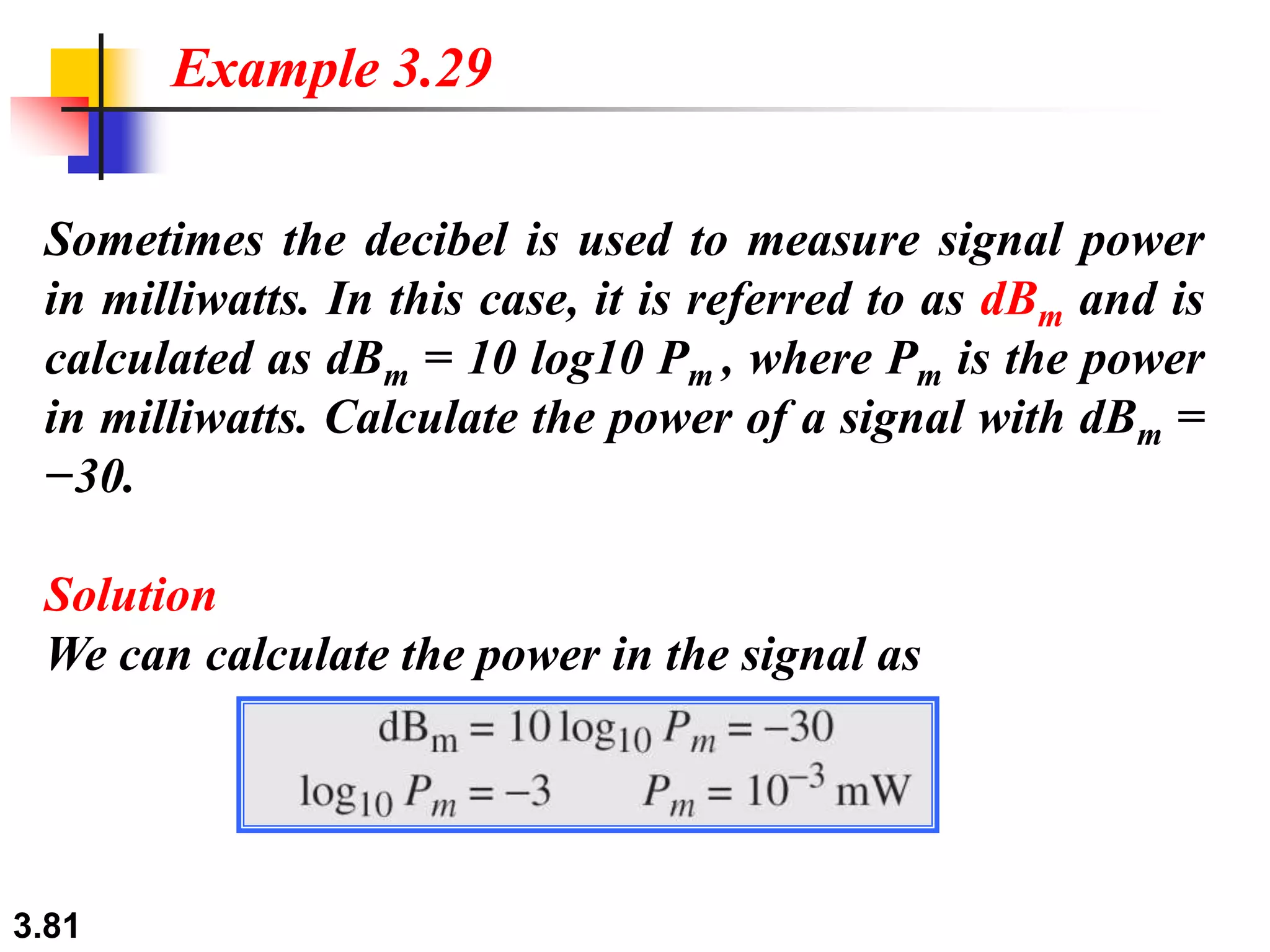
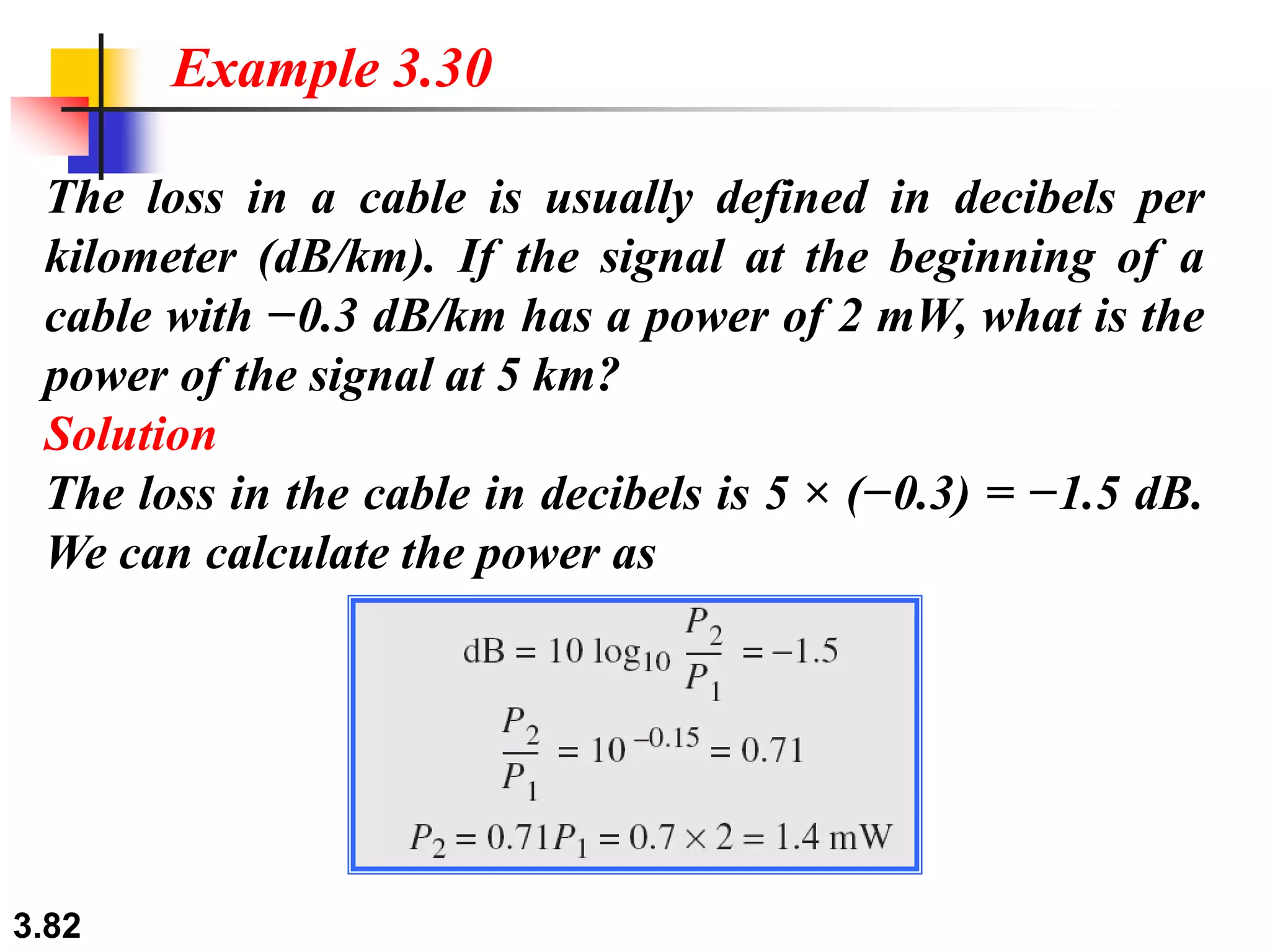
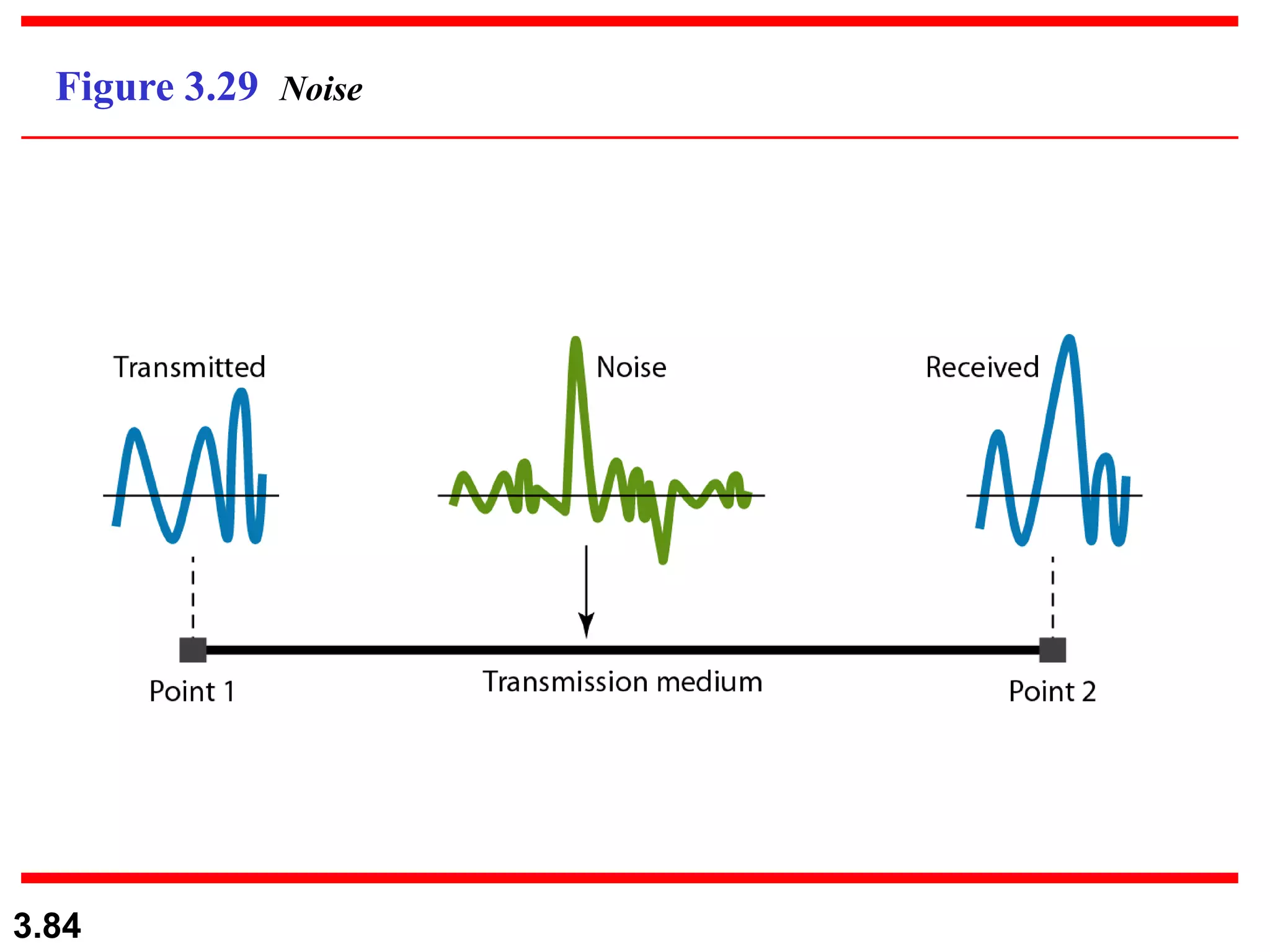
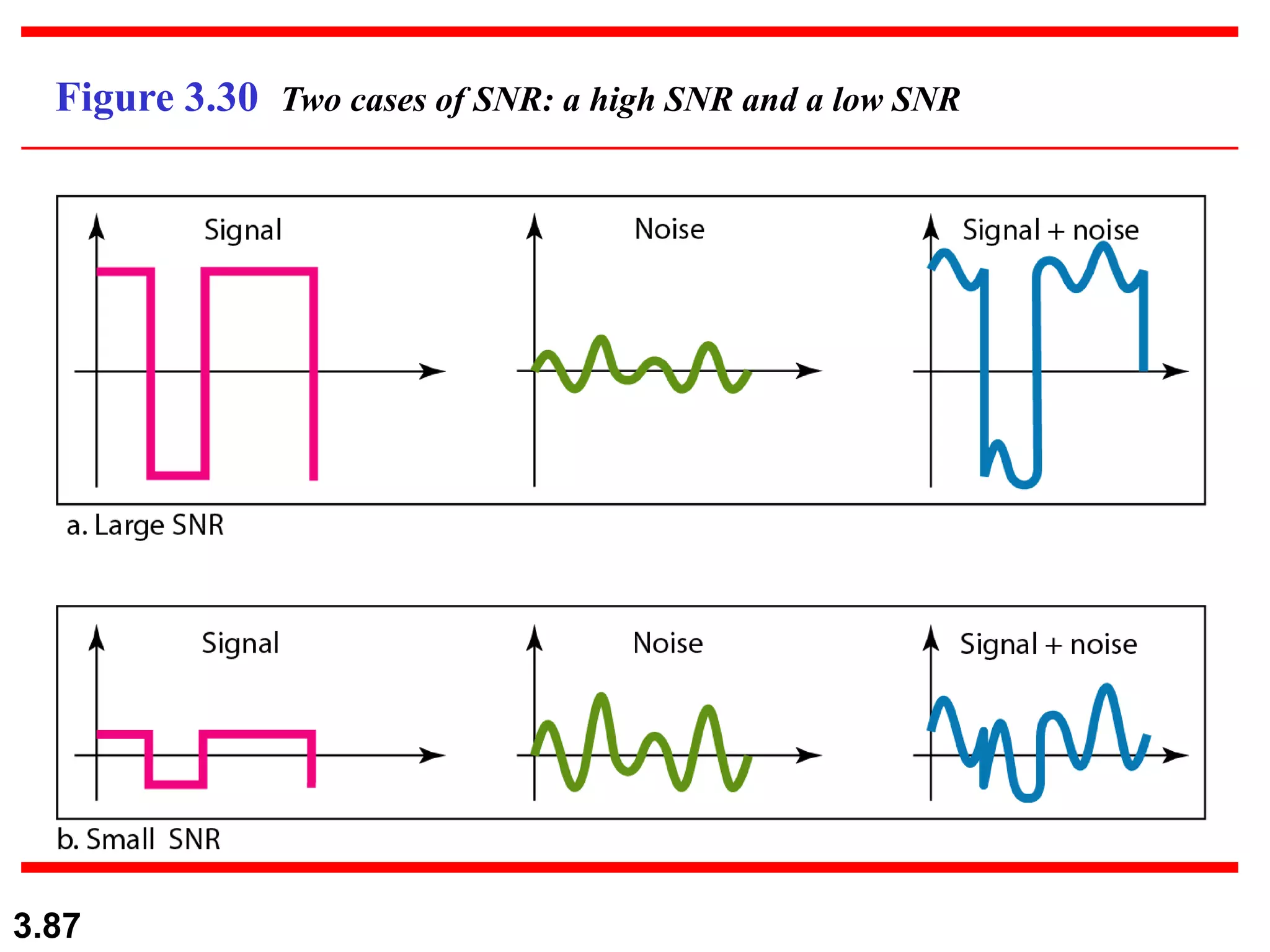
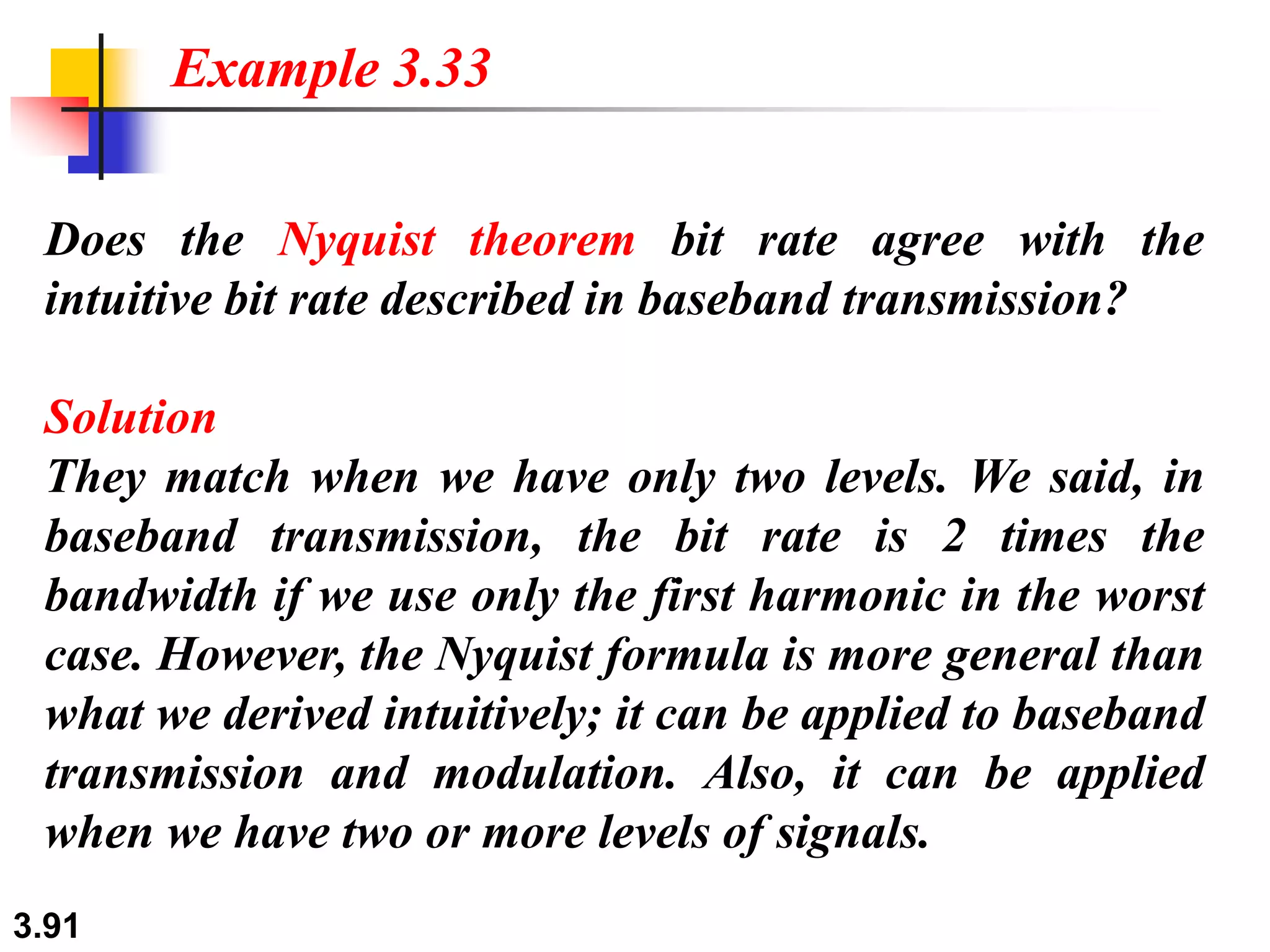
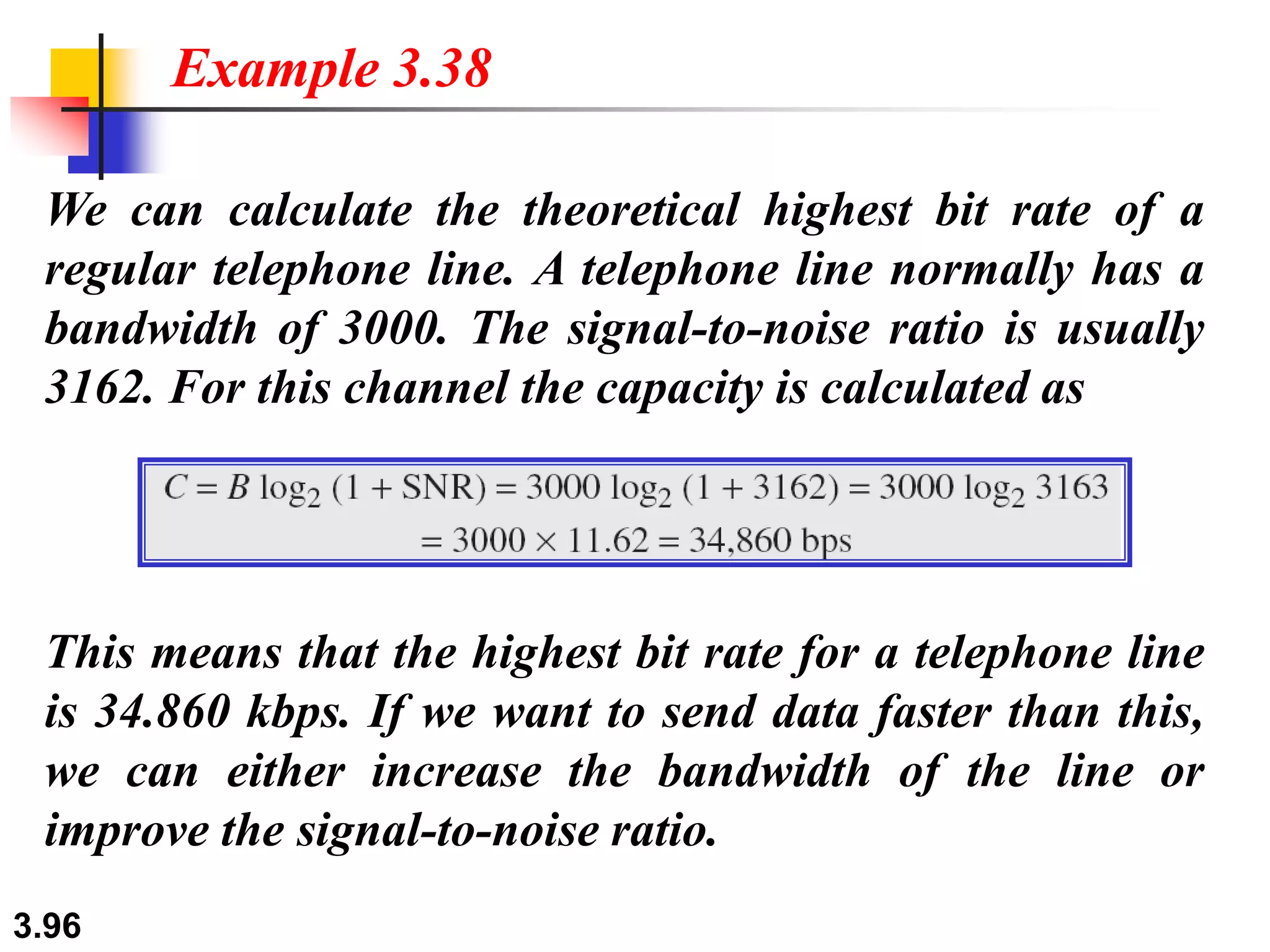
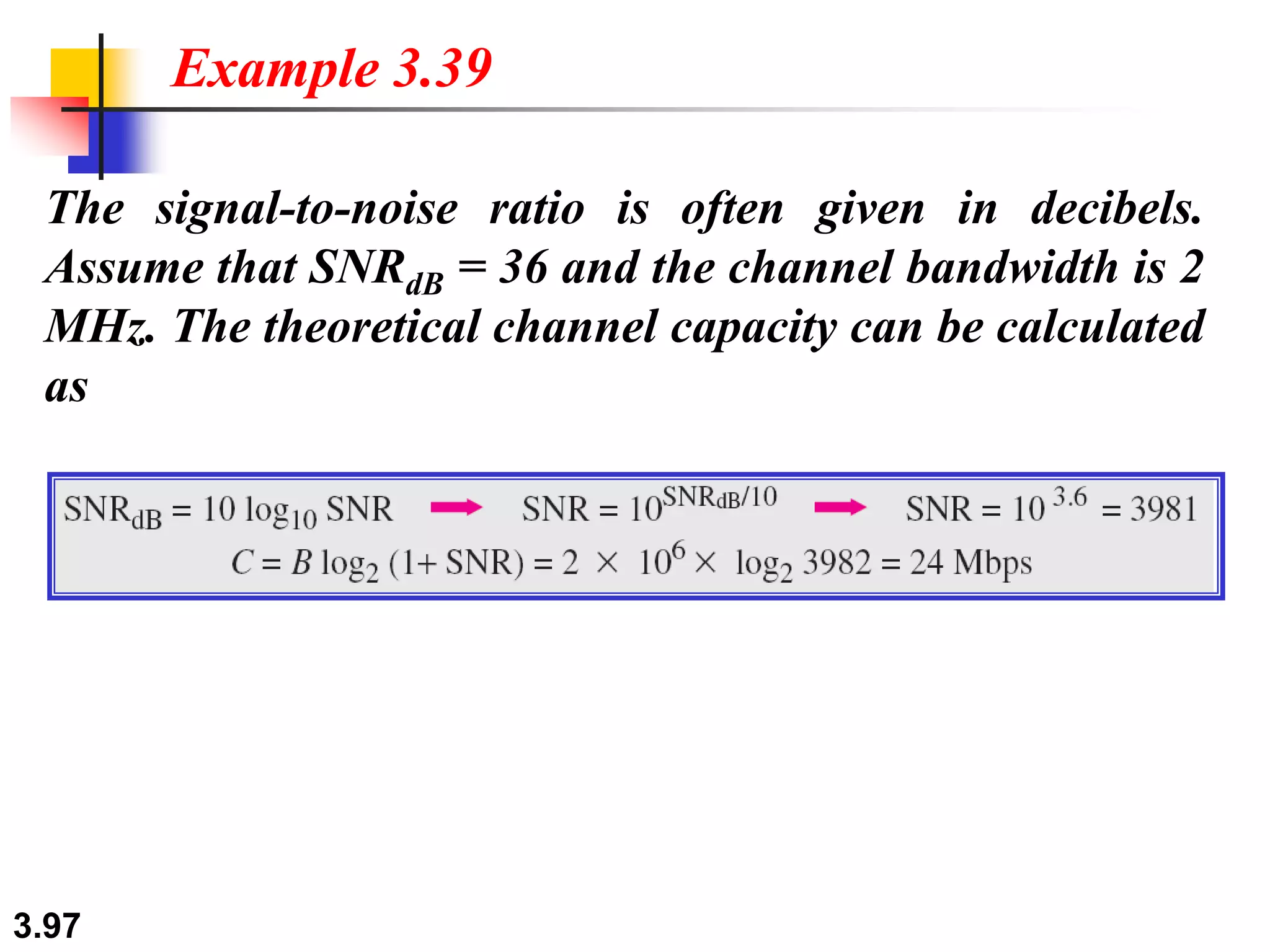
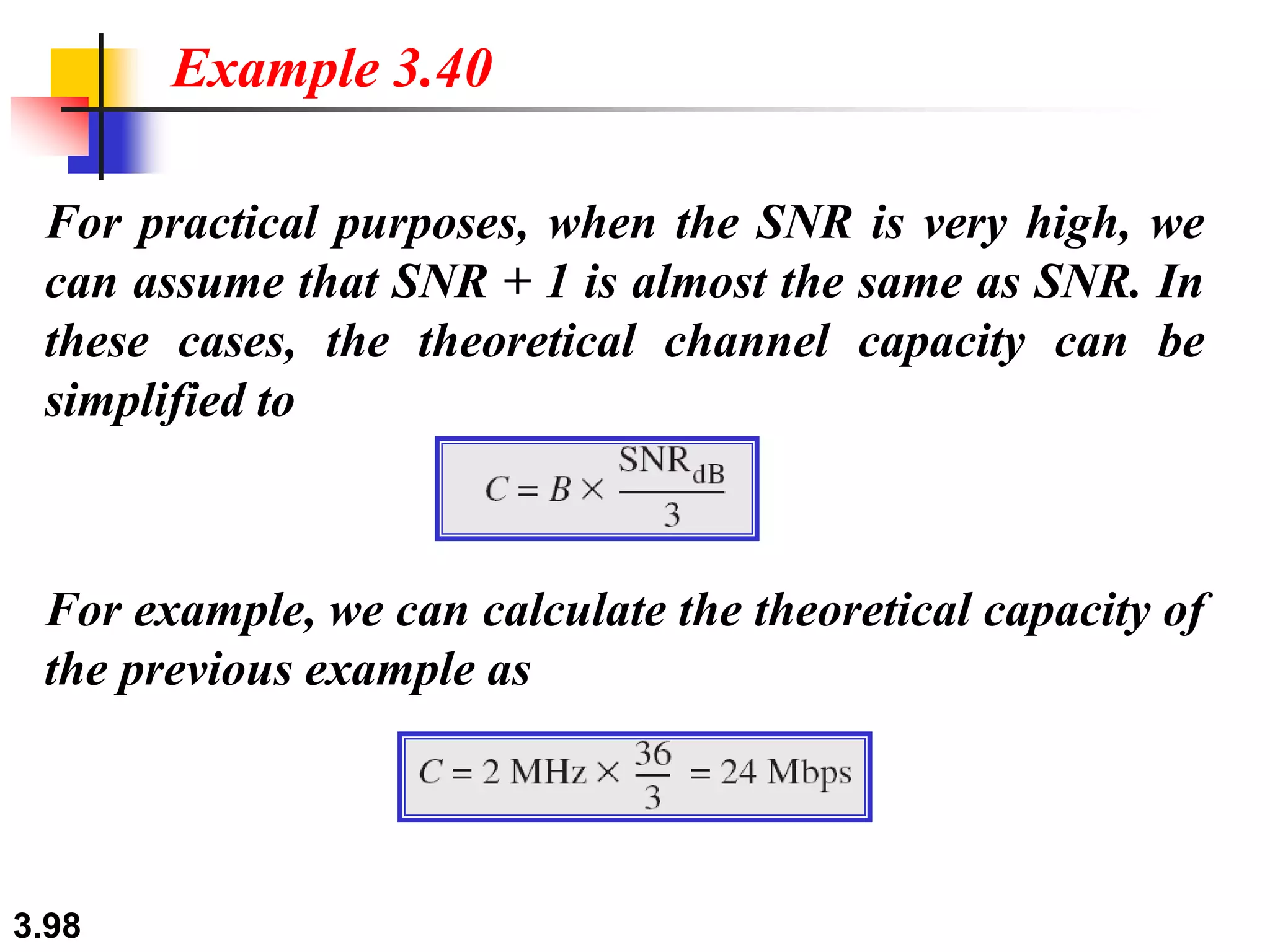
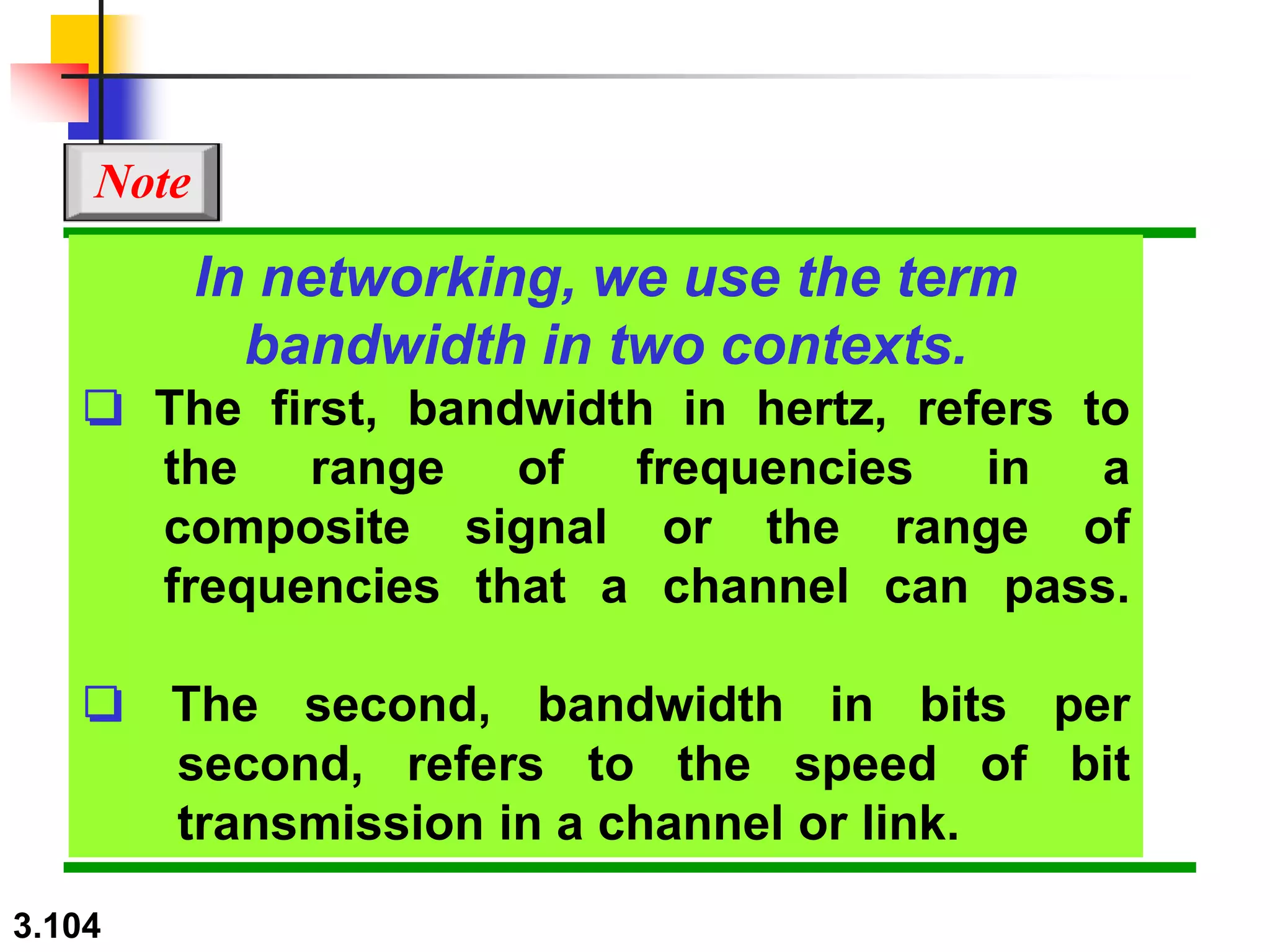
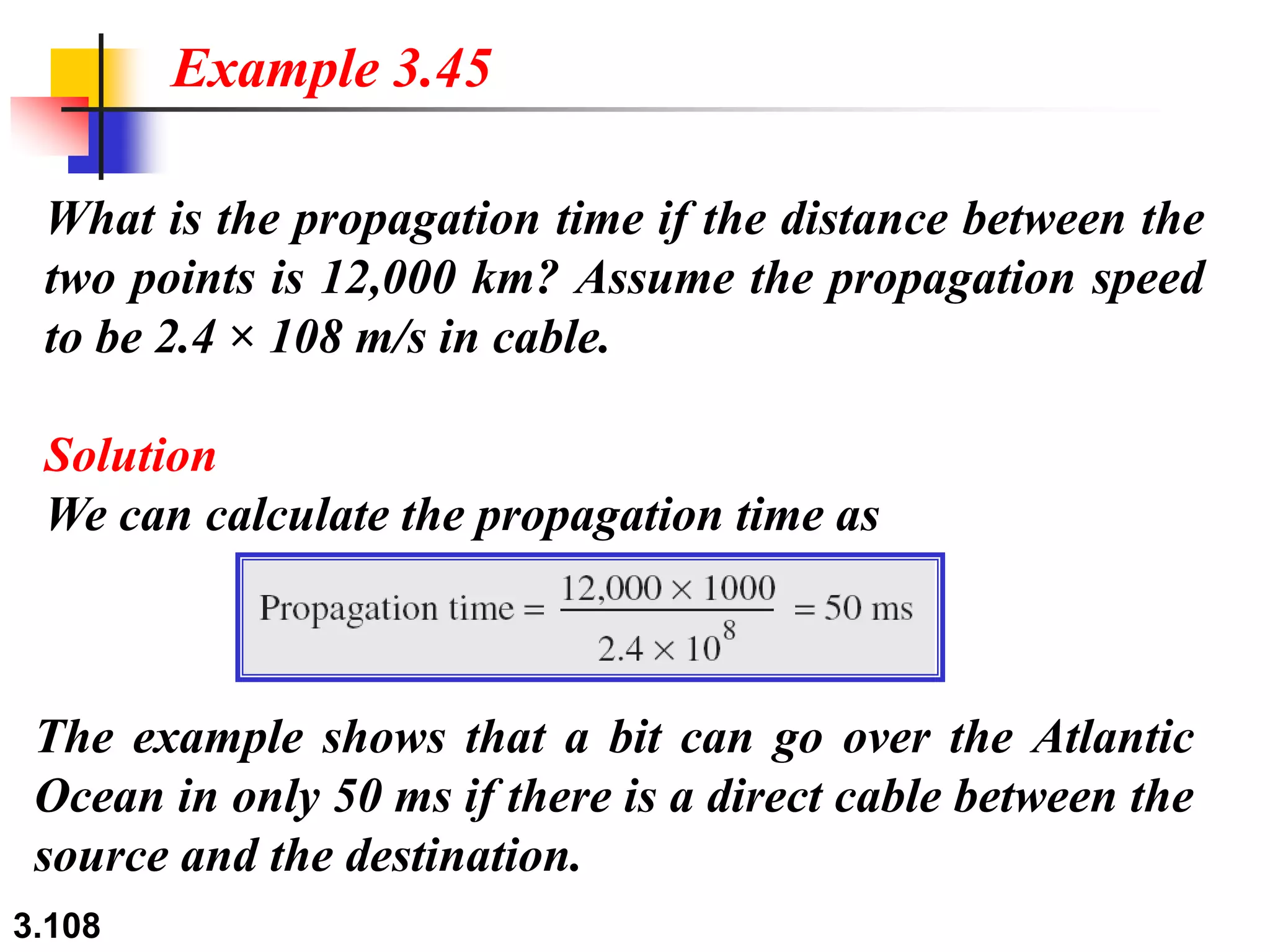
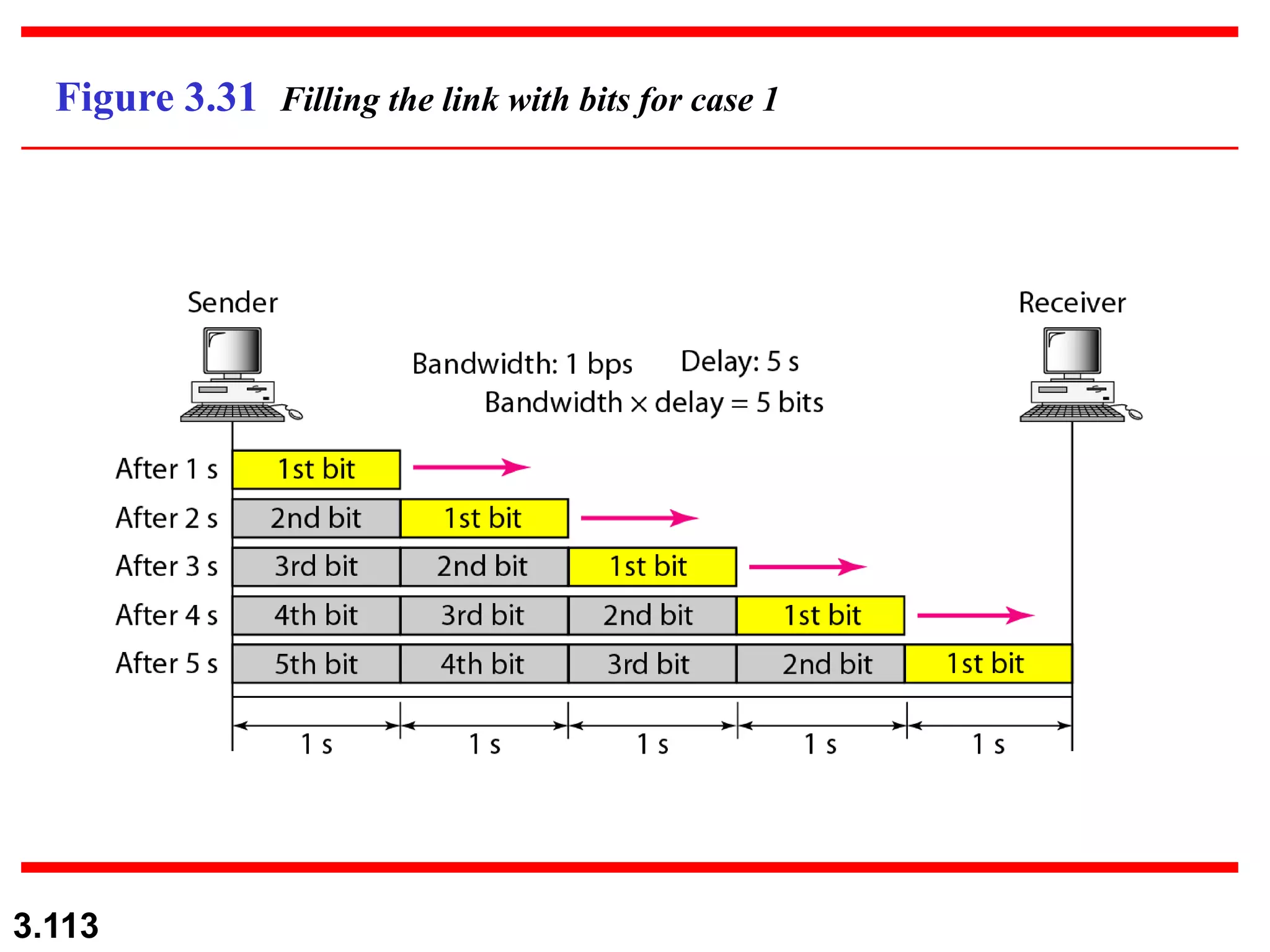
This document discusses analog and digital data and signals. It explains that:
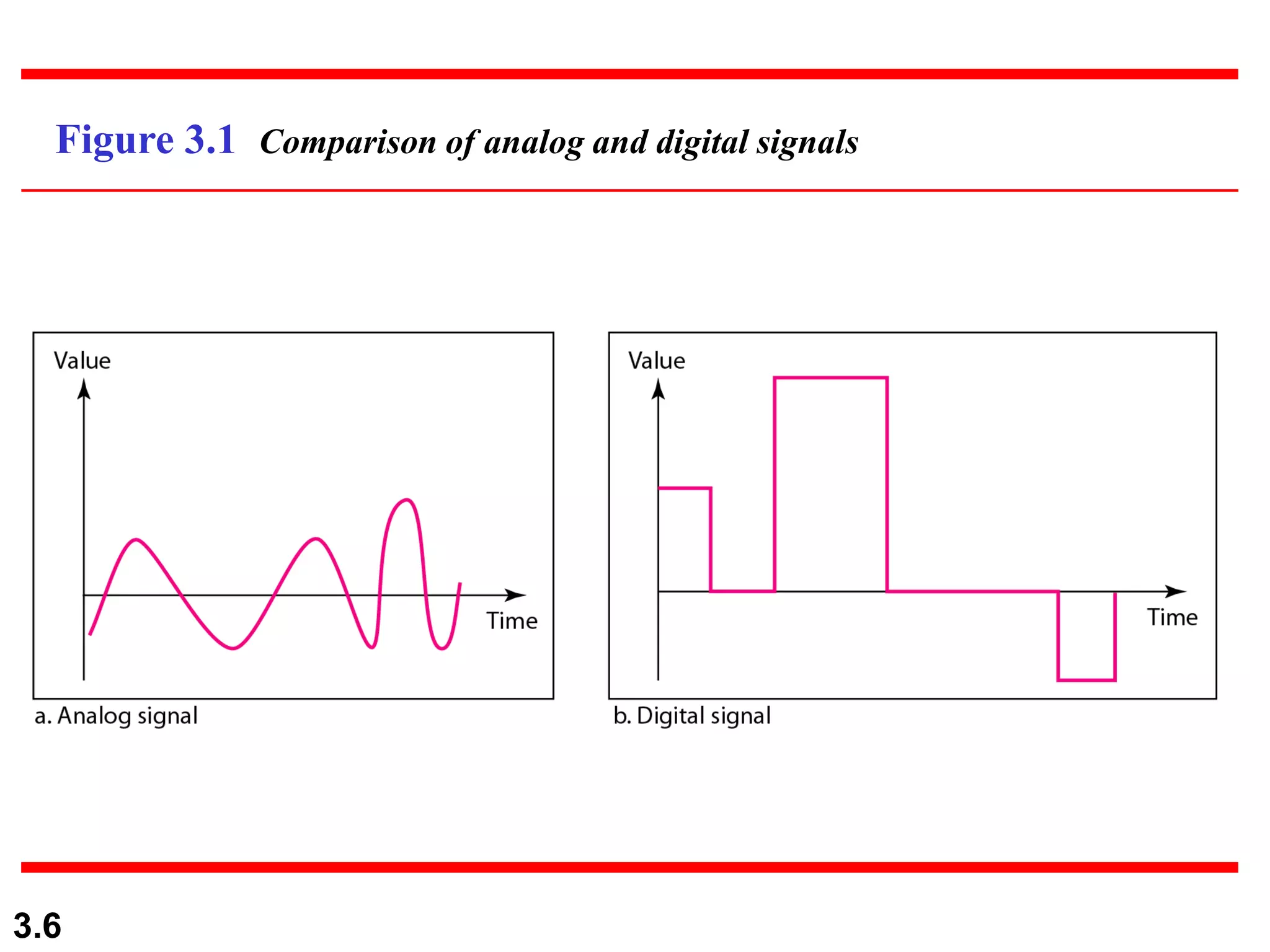
- Data can be analog (continuous) or digital (discrete). Analog signals can have an infinite number of values, while digital signals have a limited number of values.
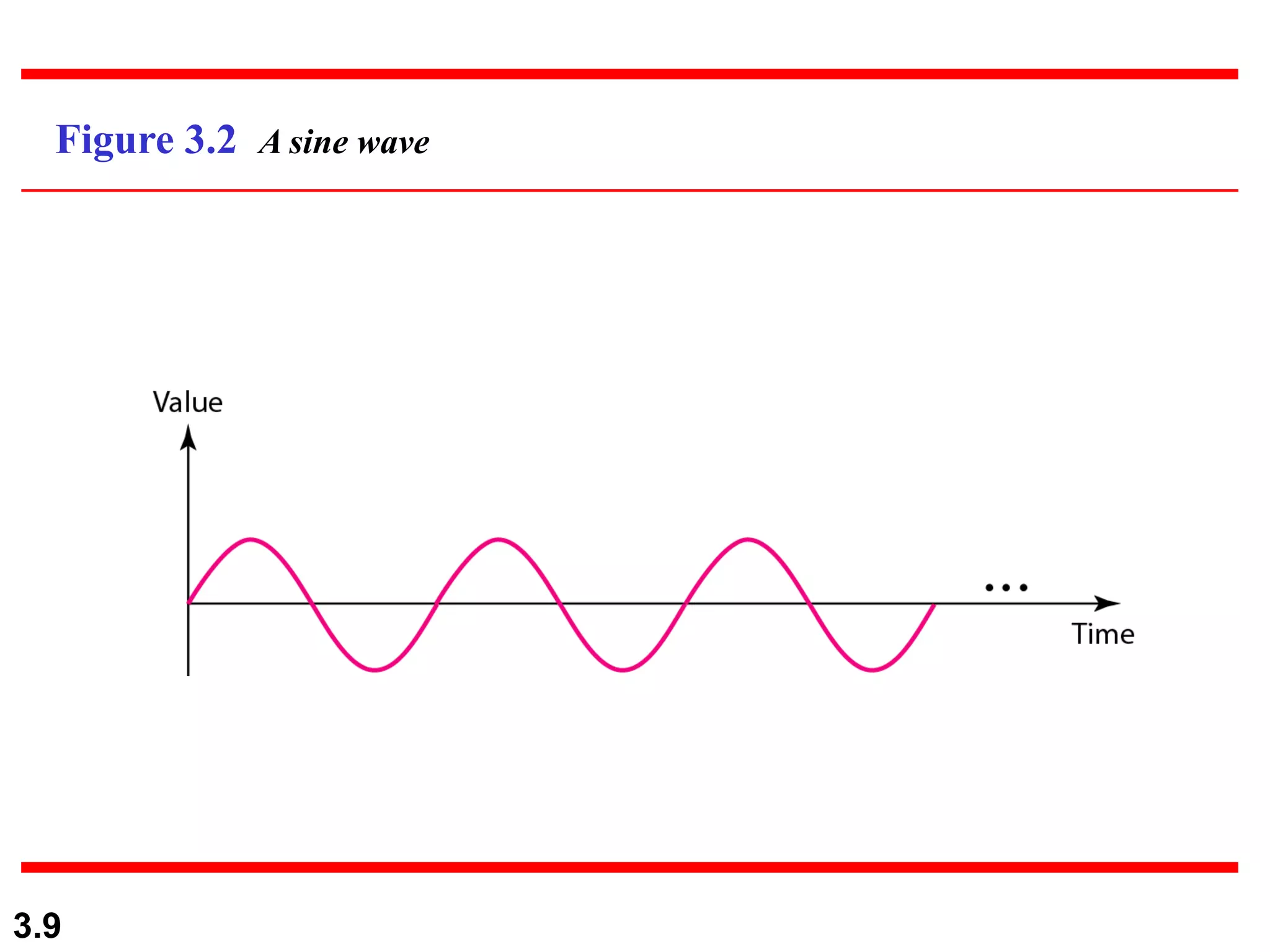
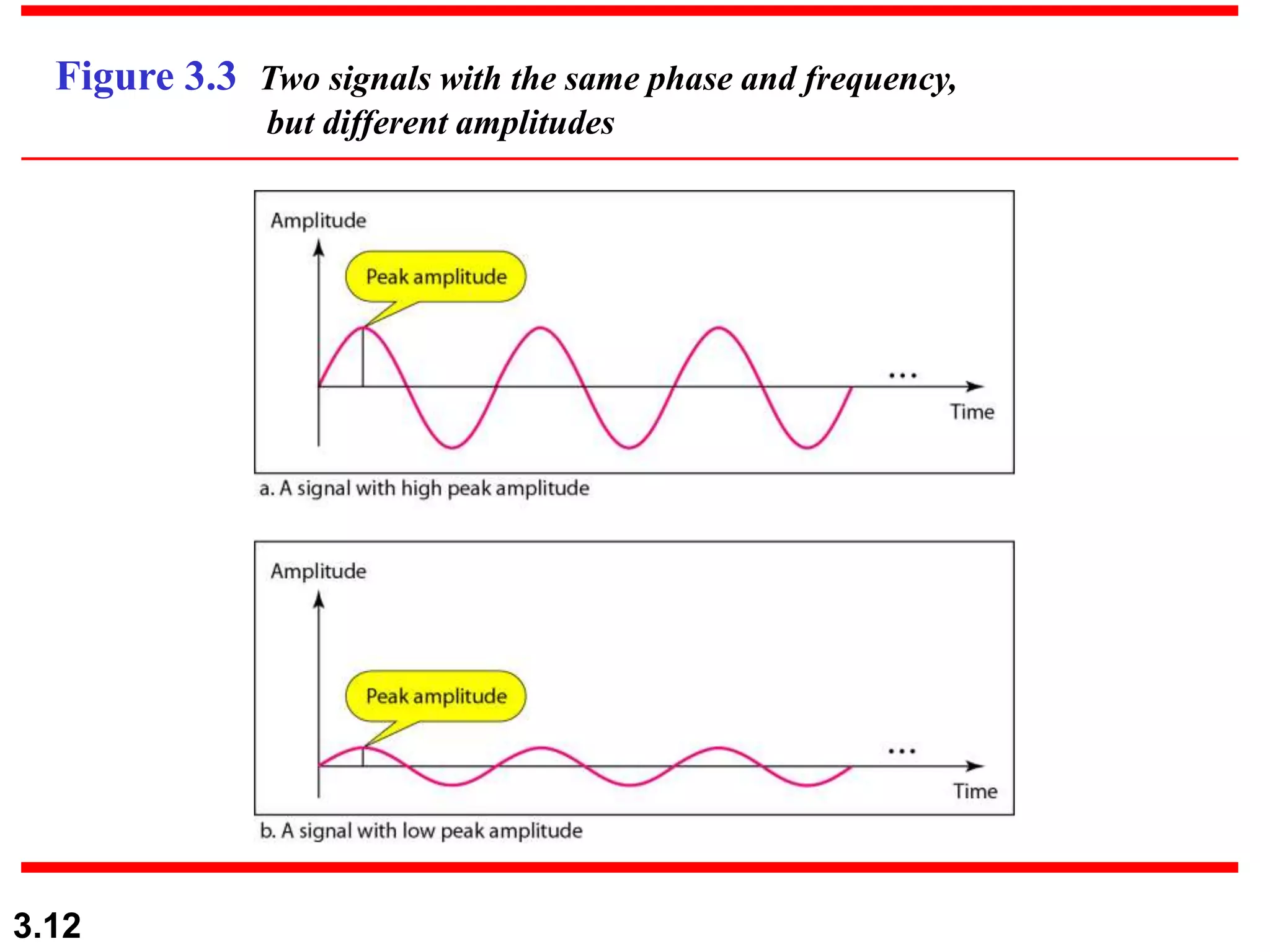
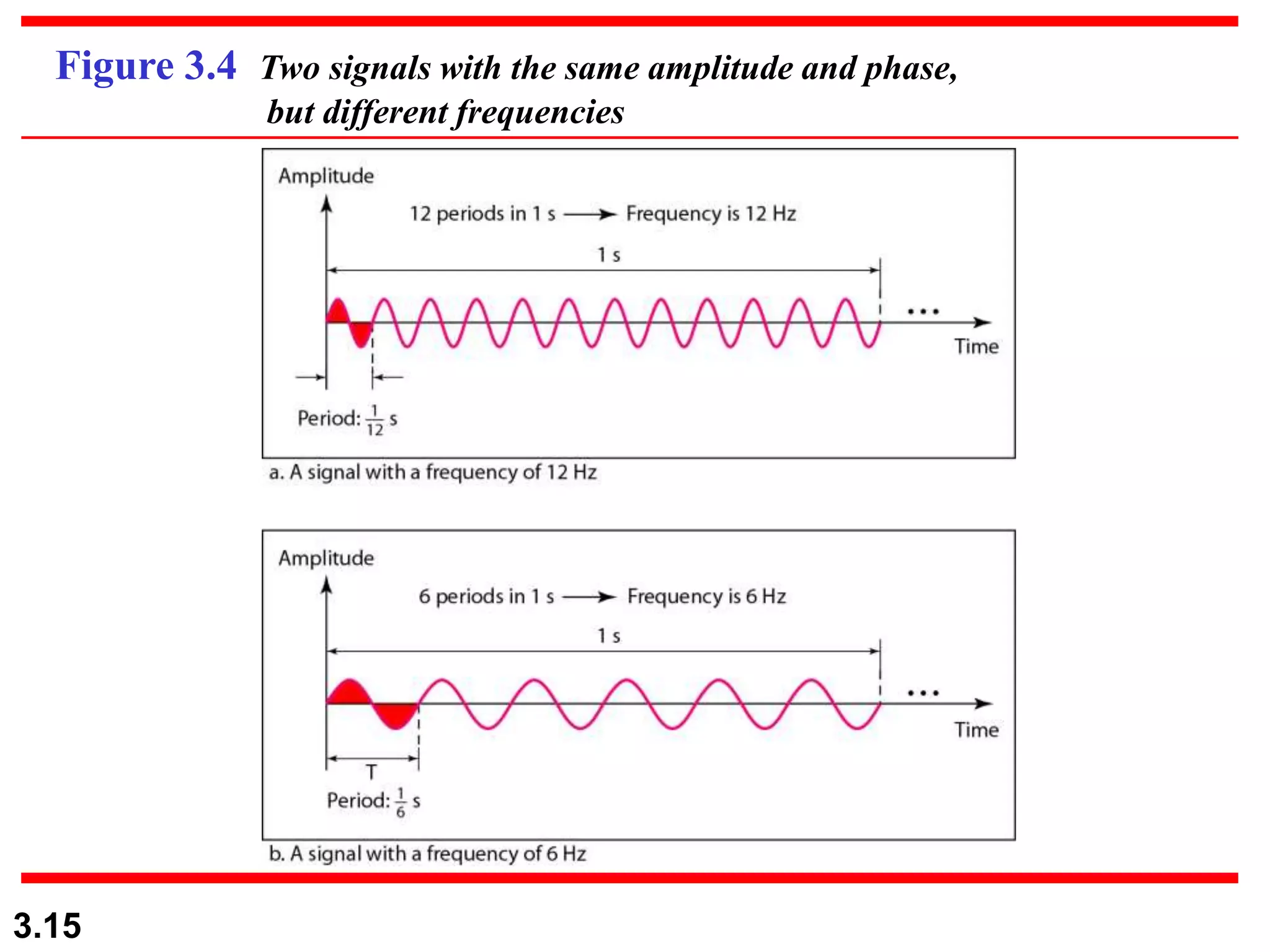
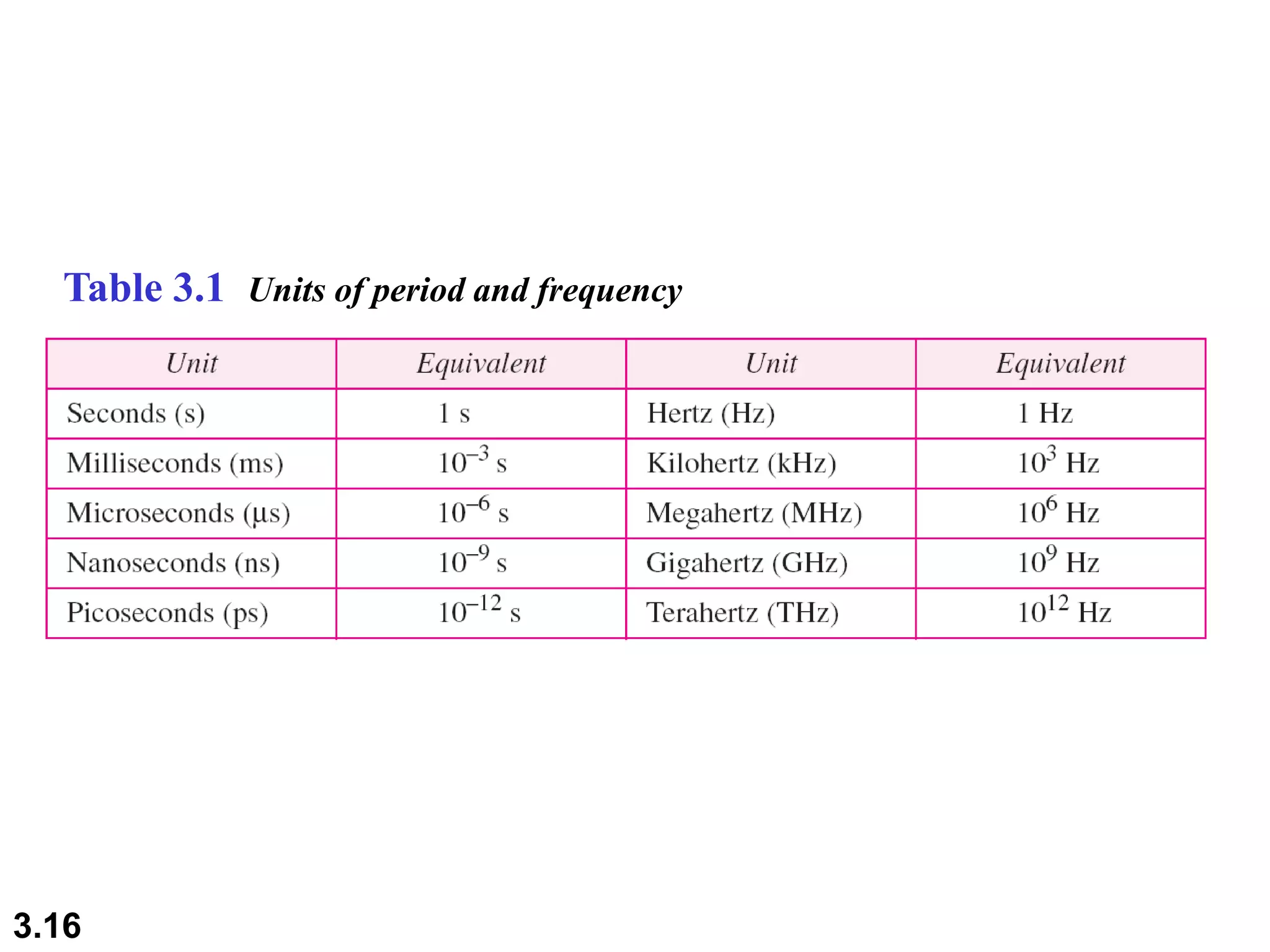
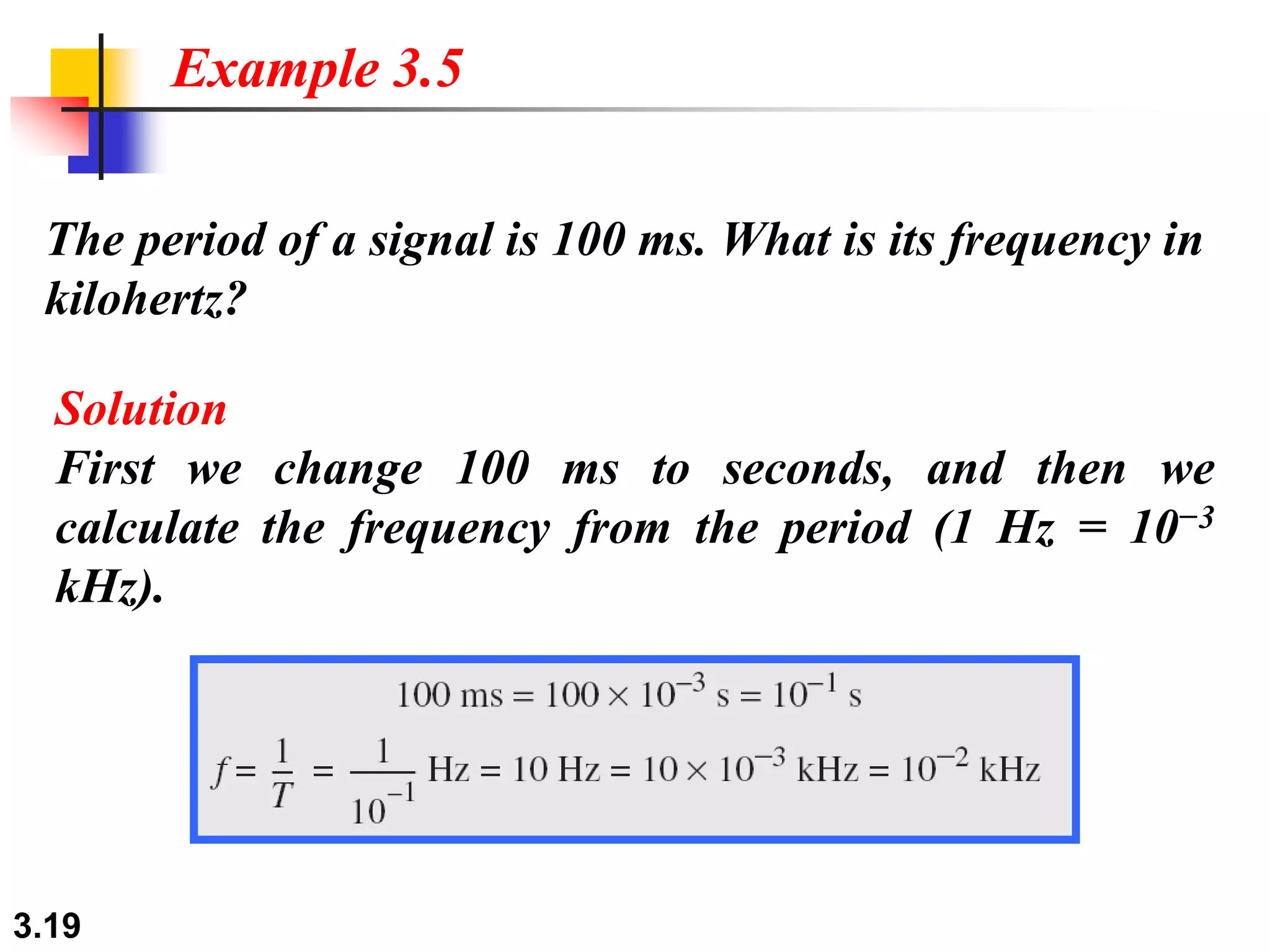
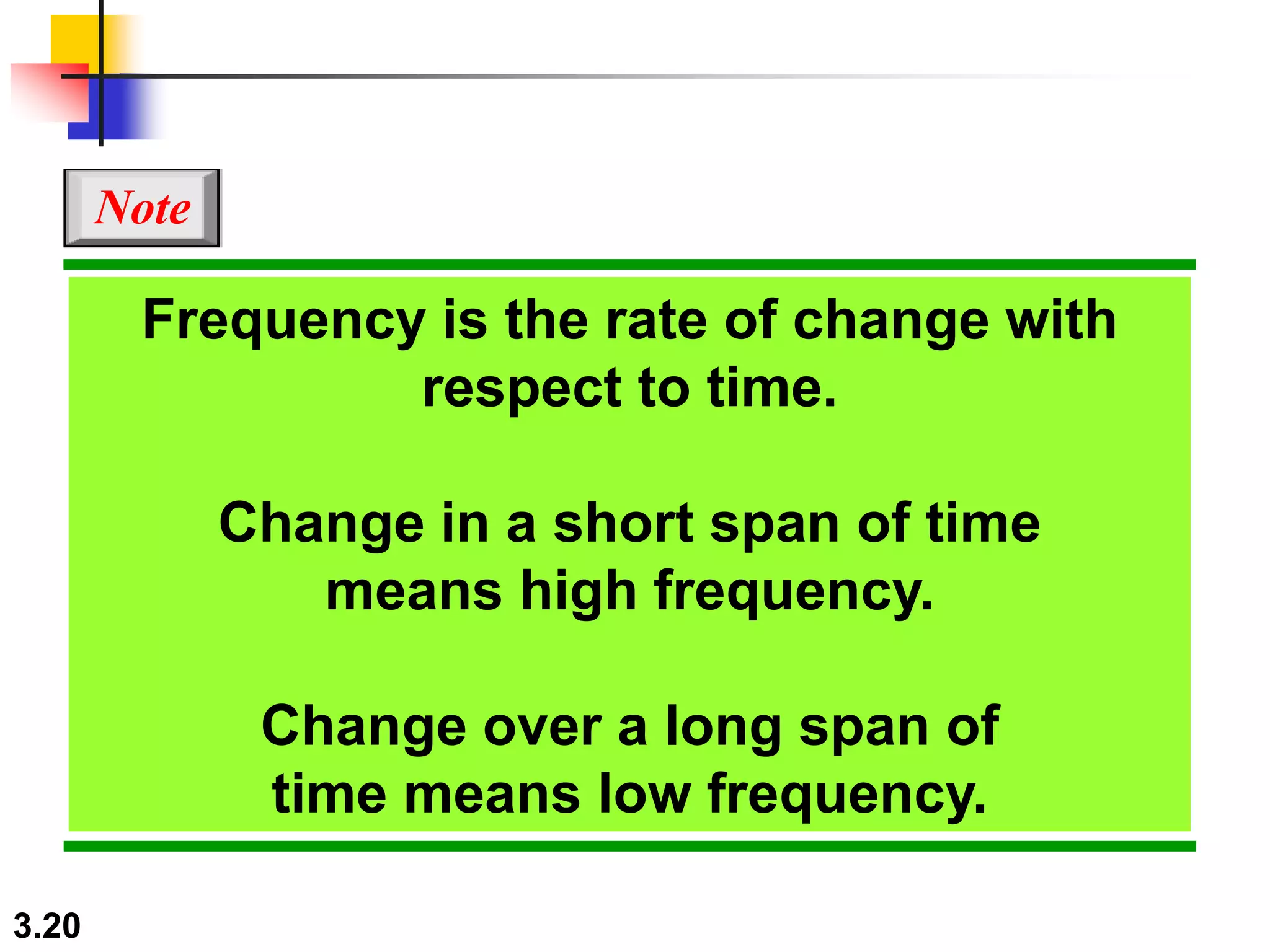
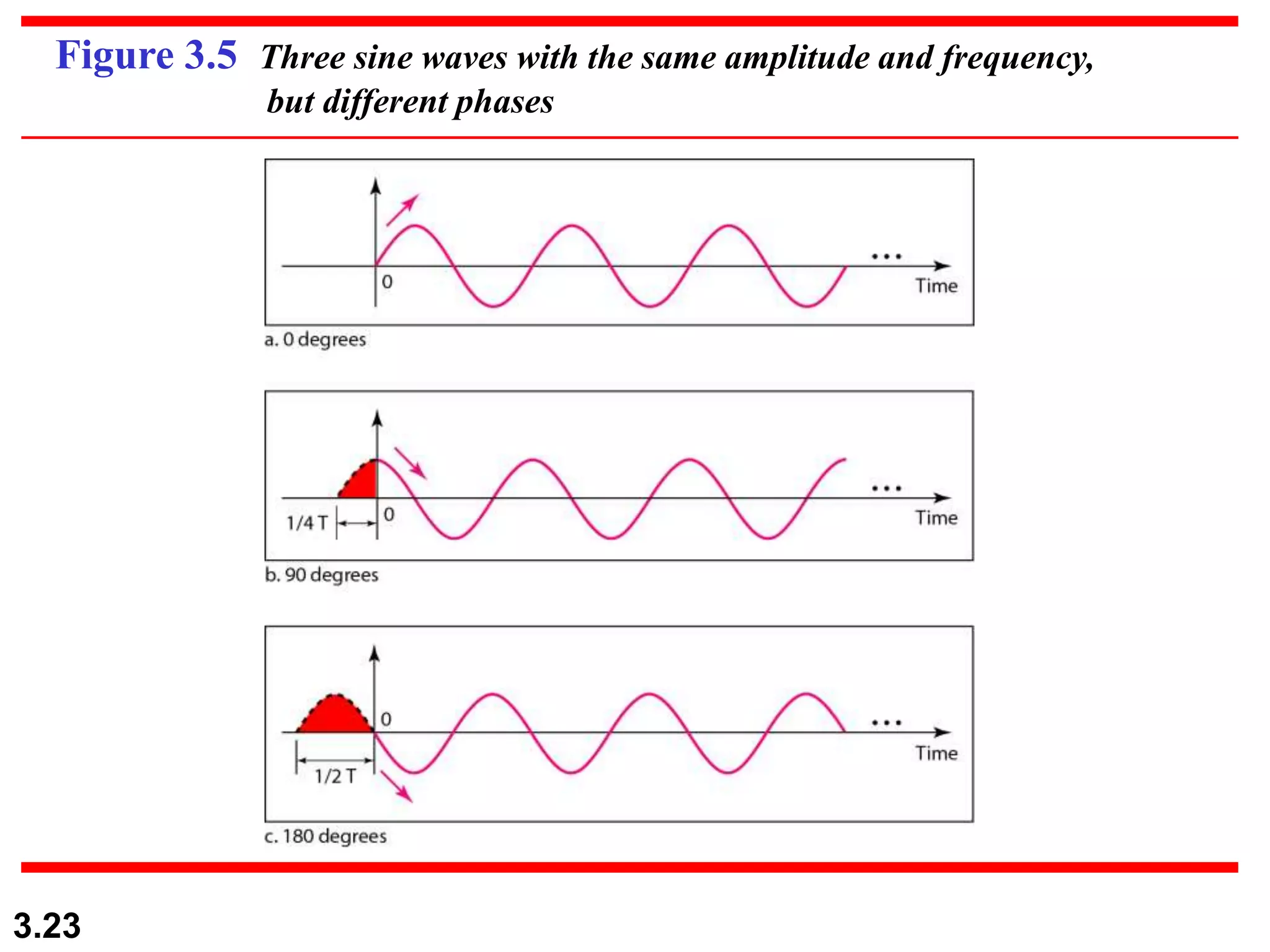
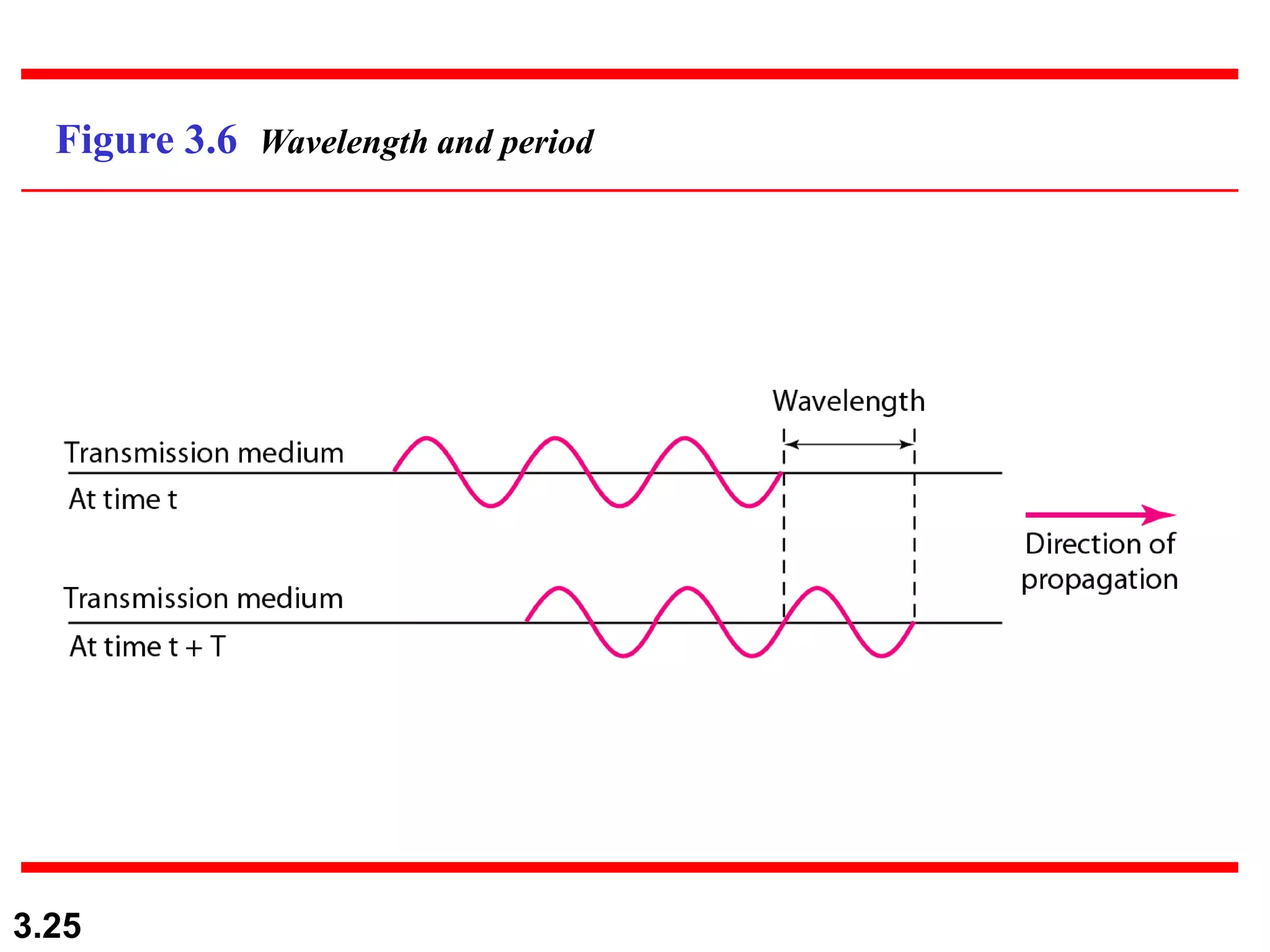
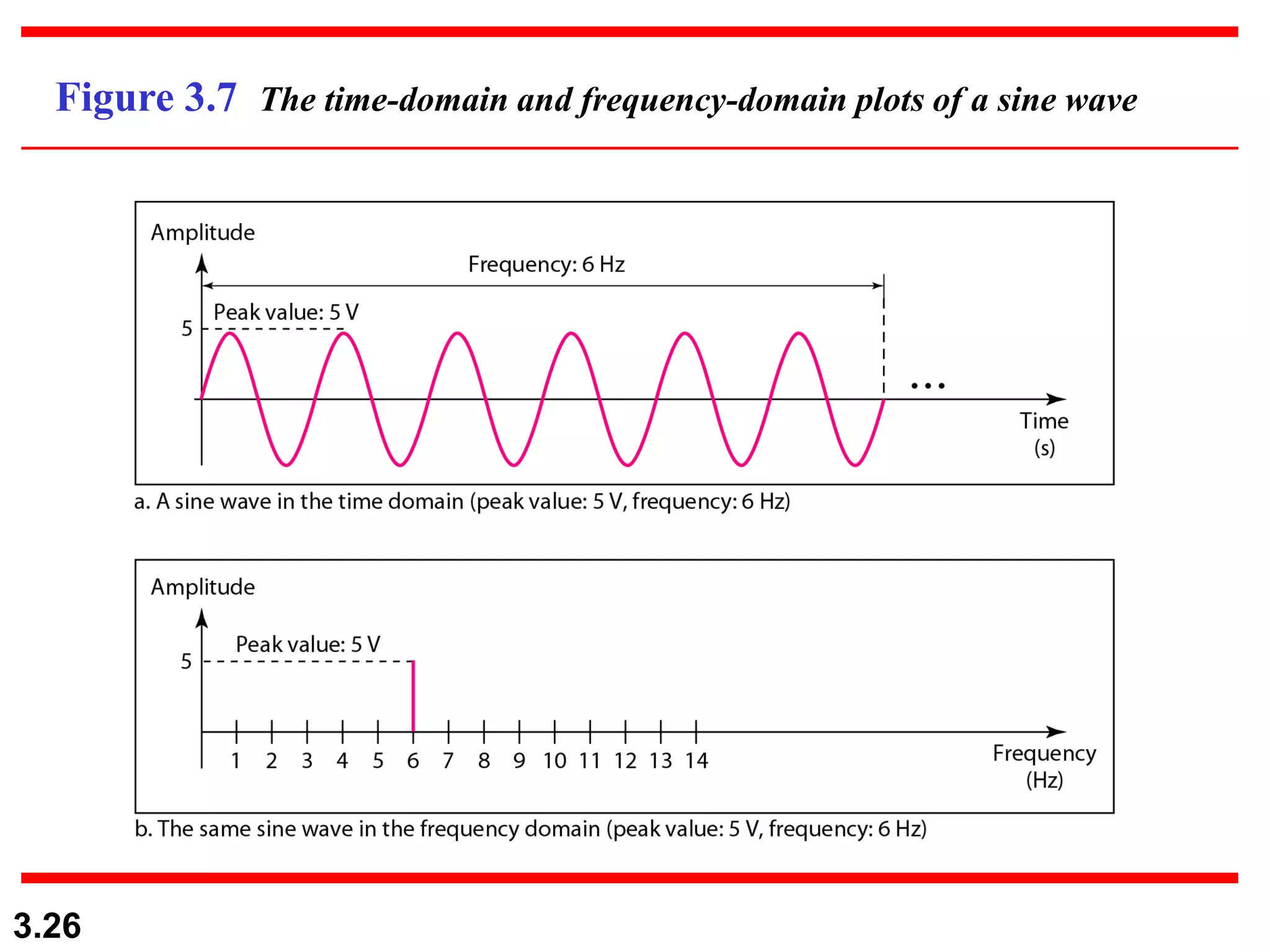
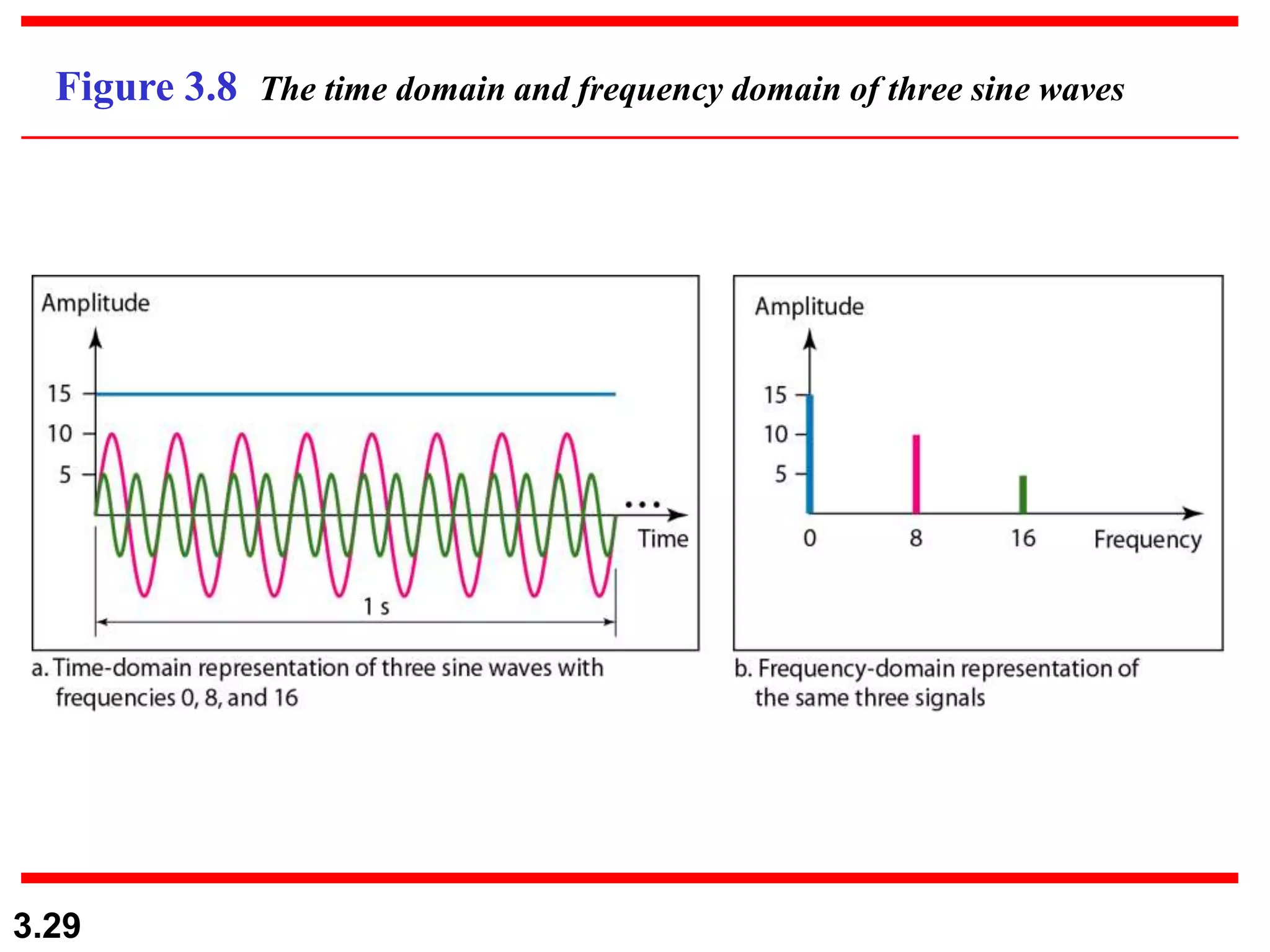
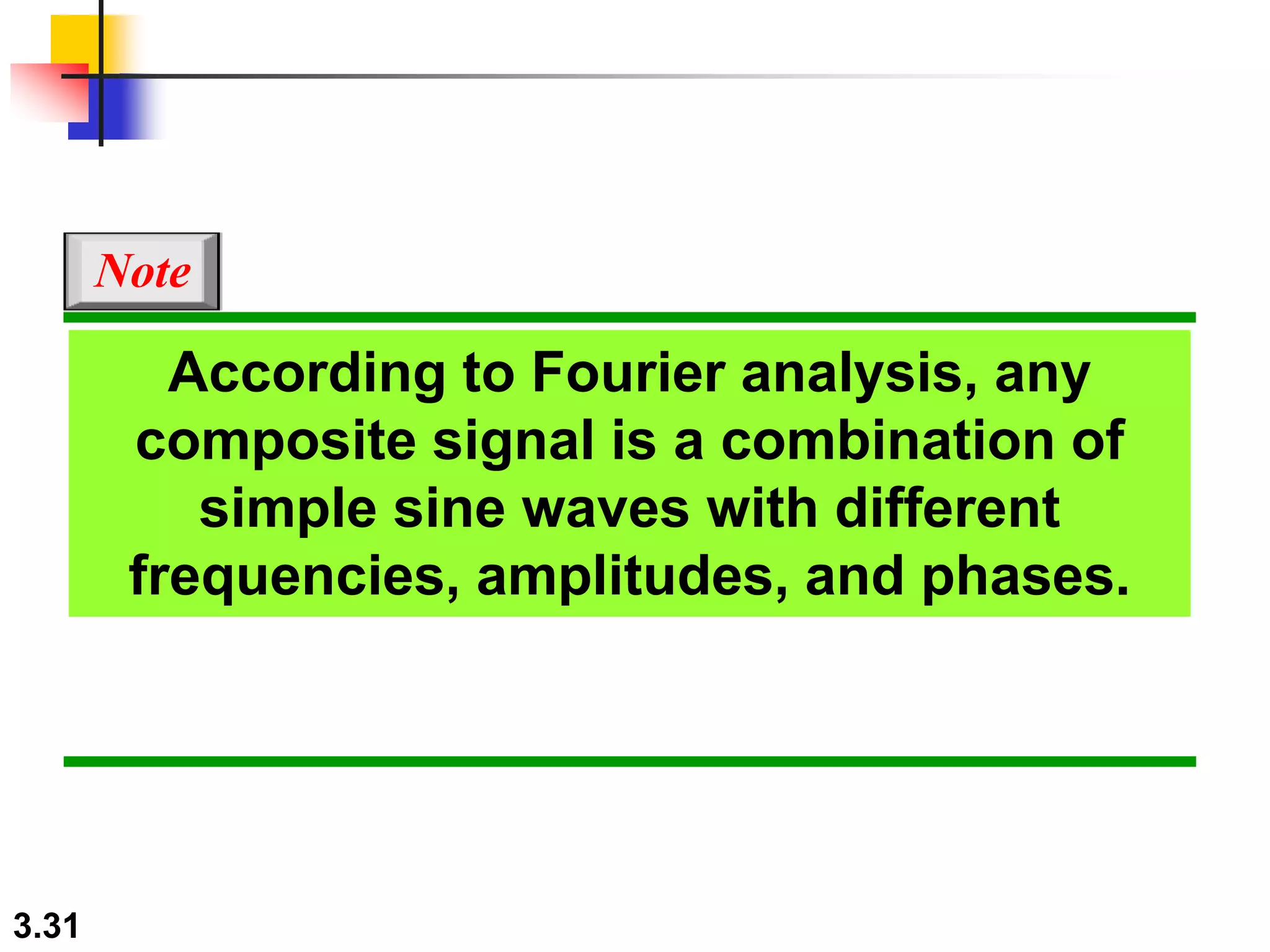
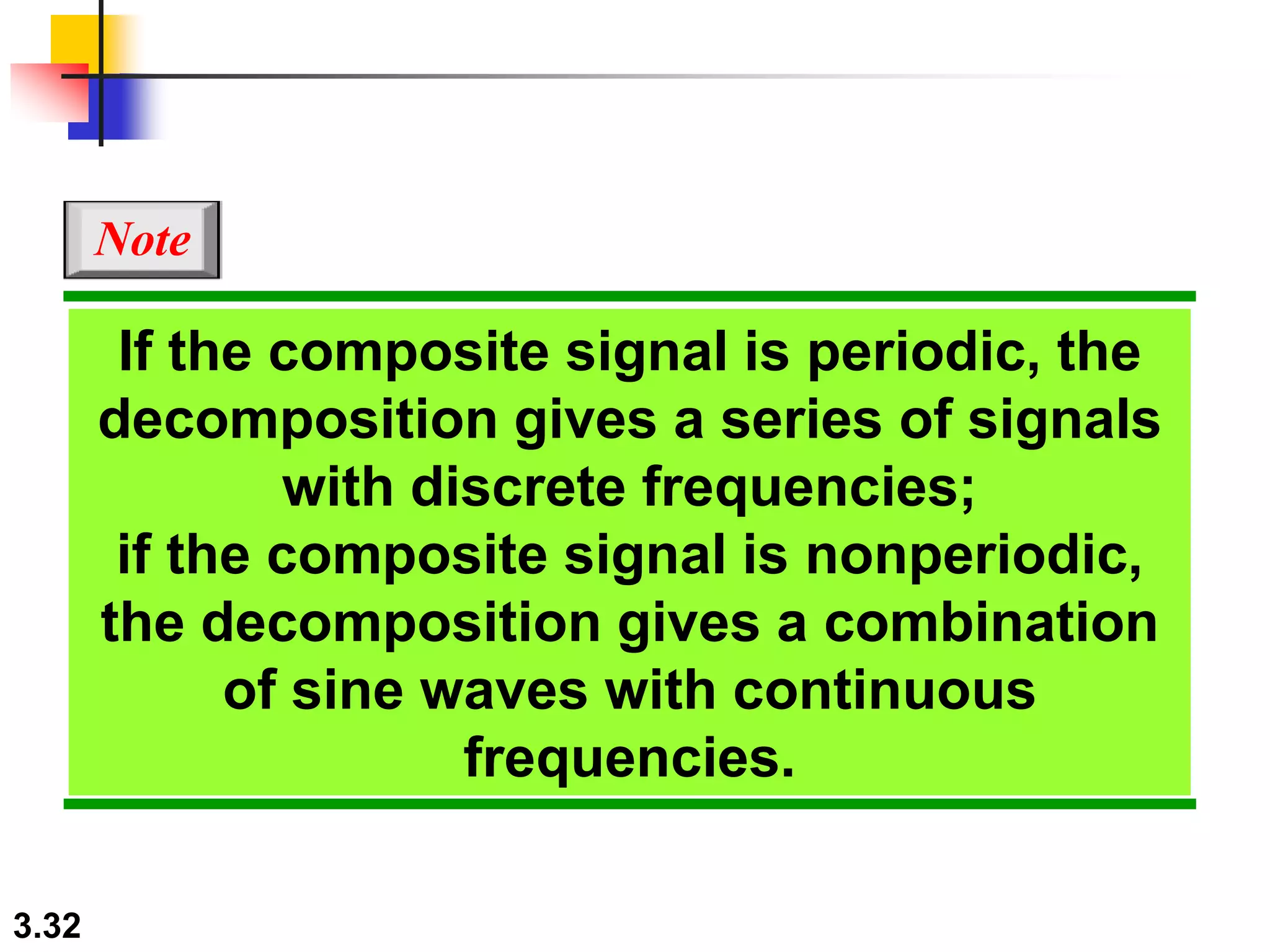
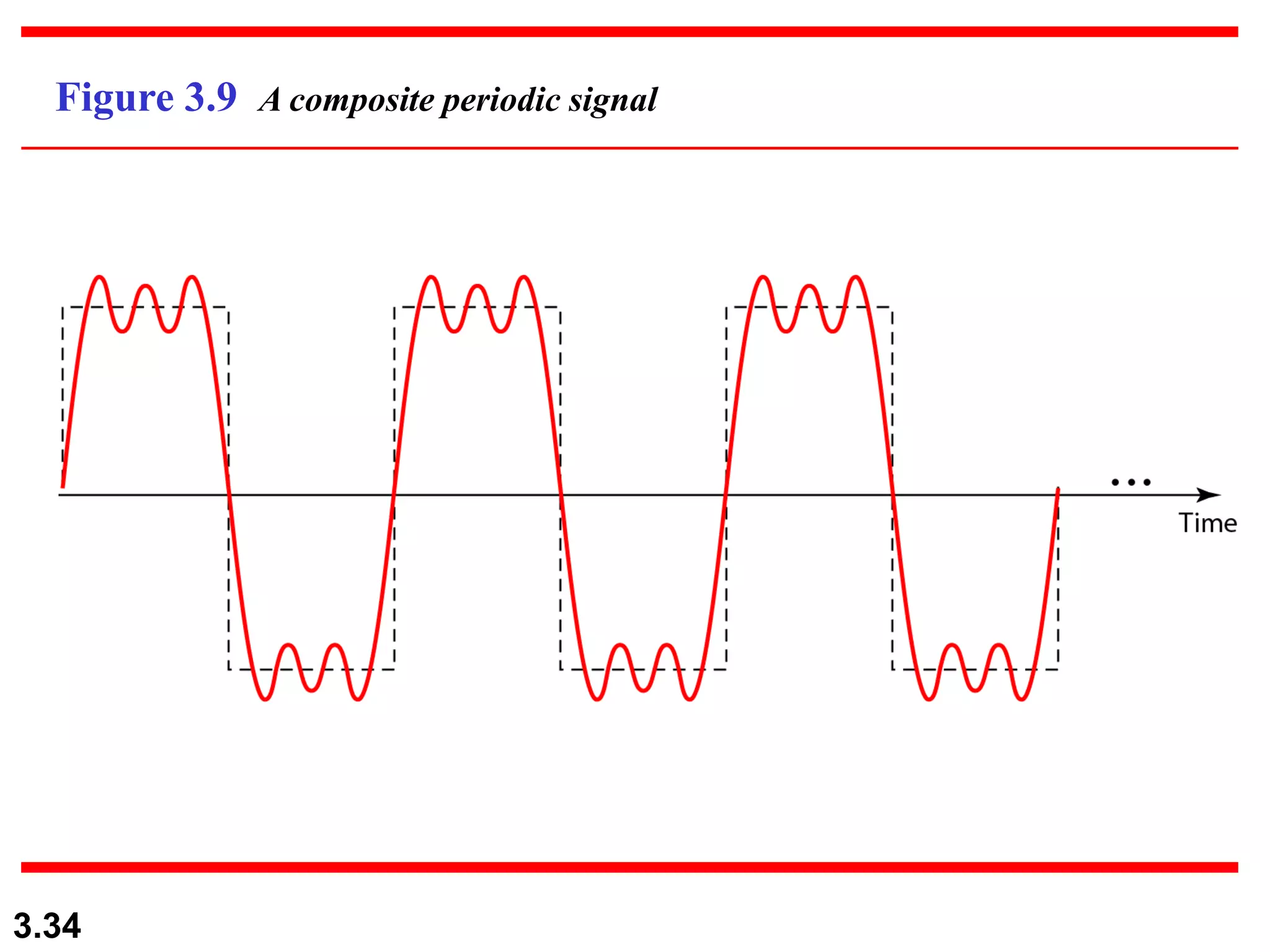
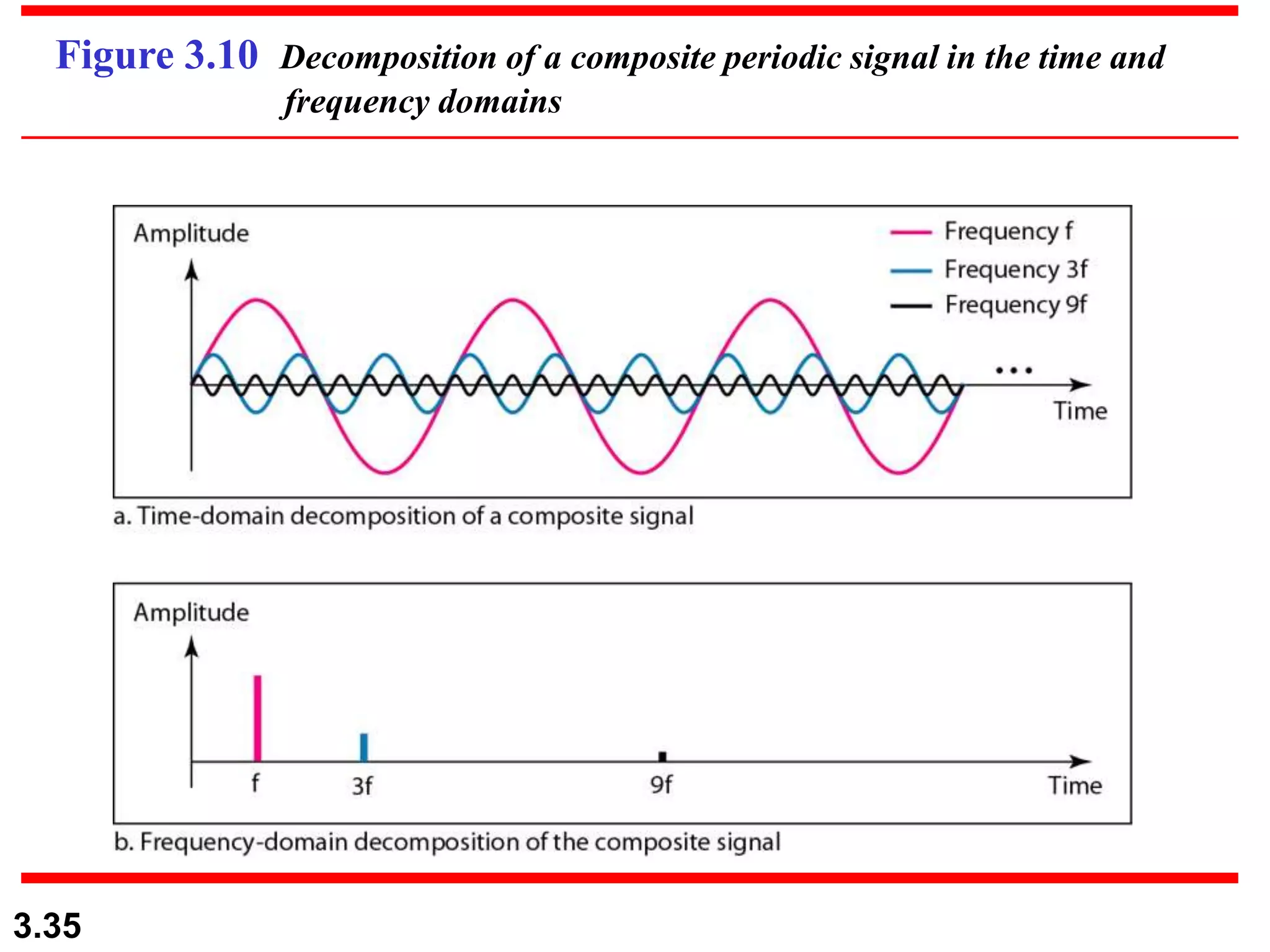
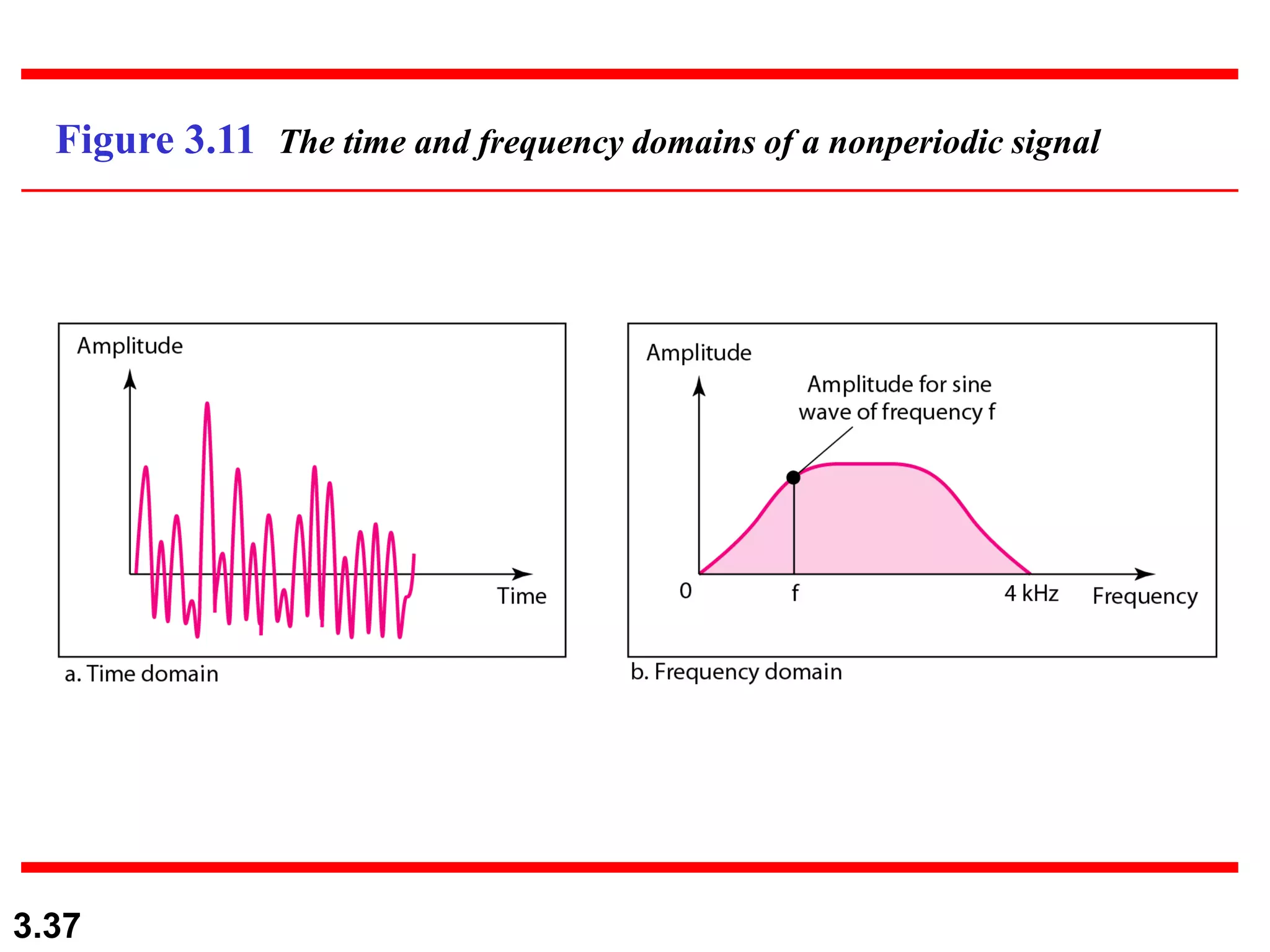
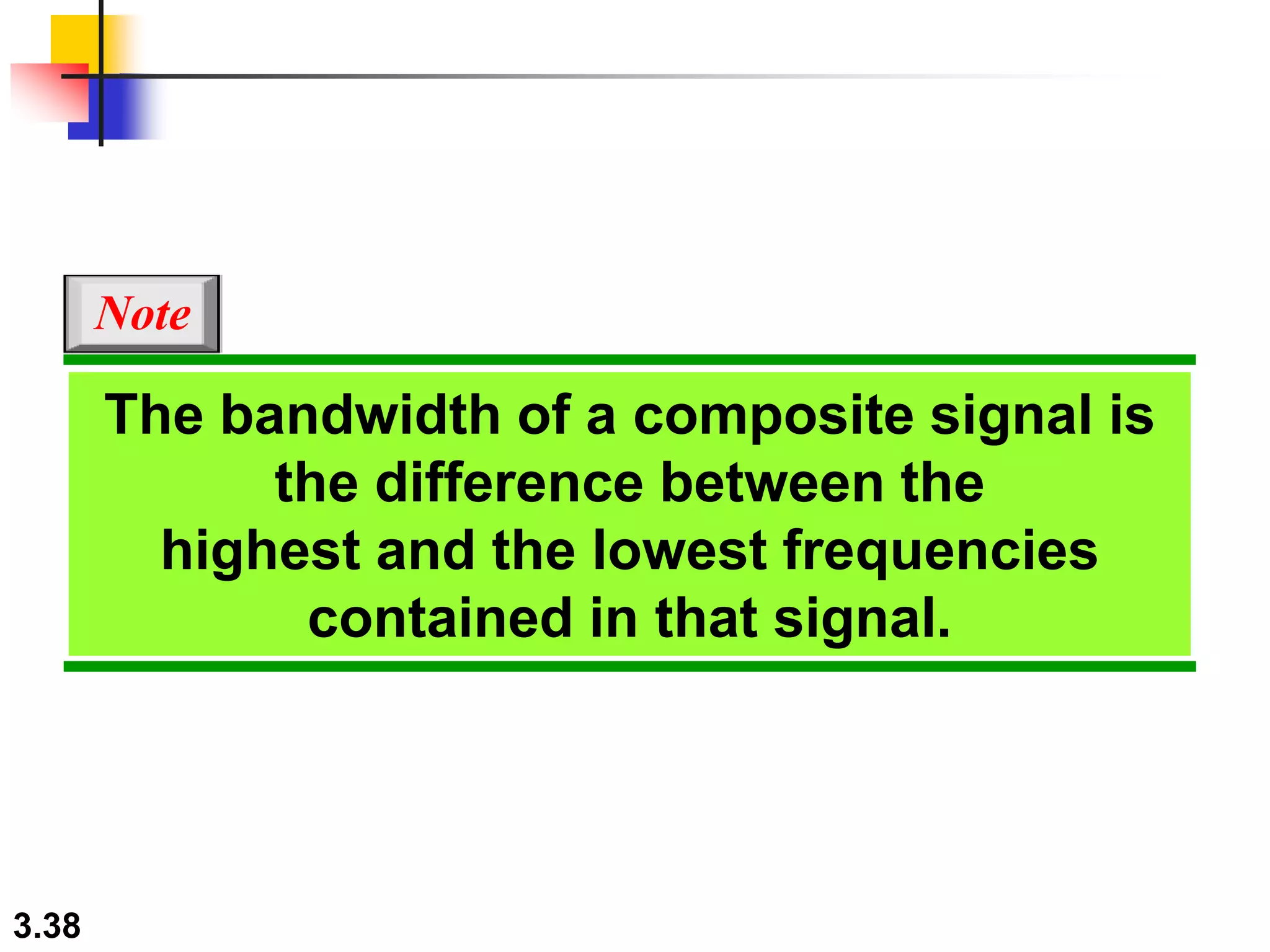
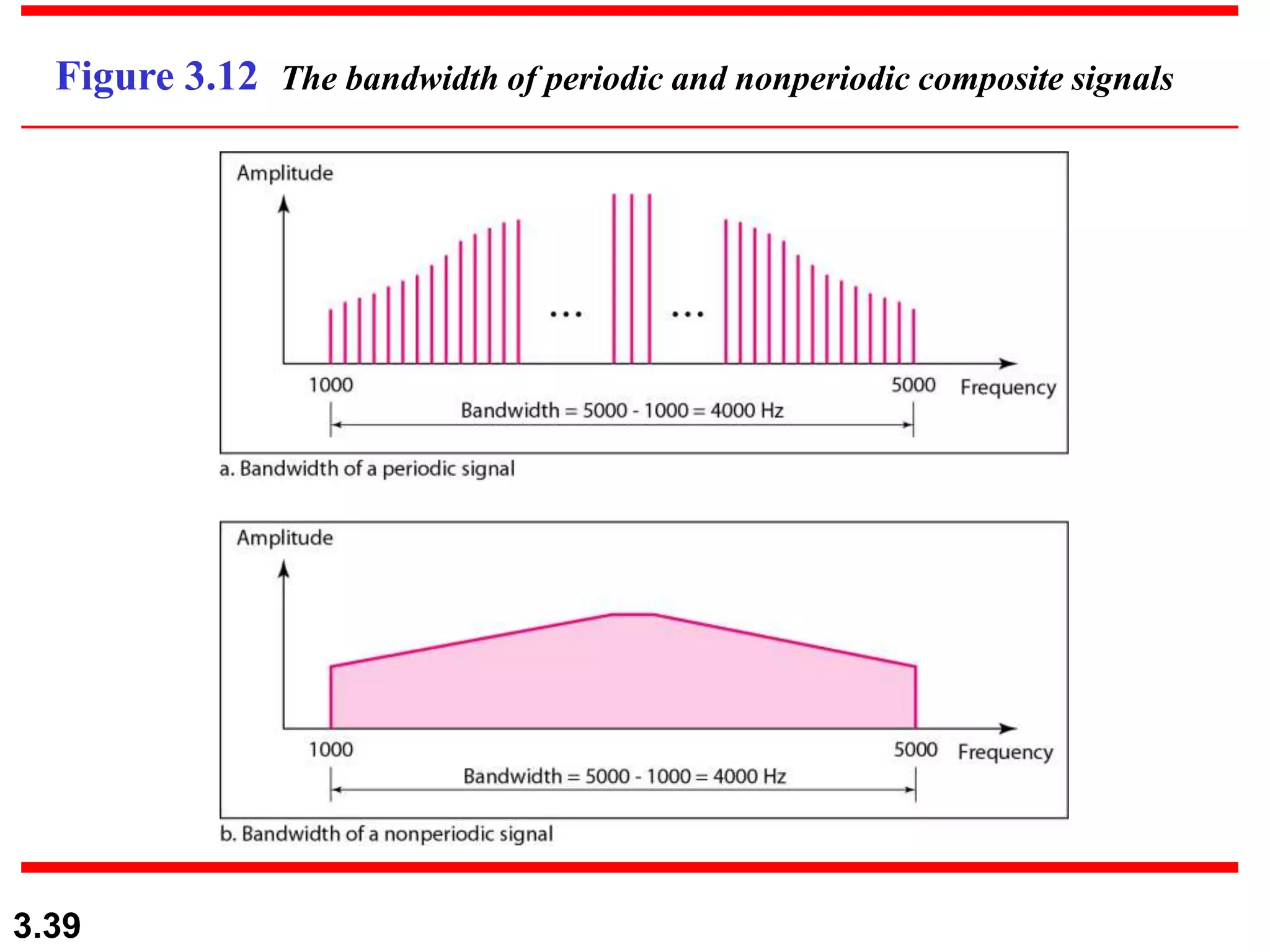
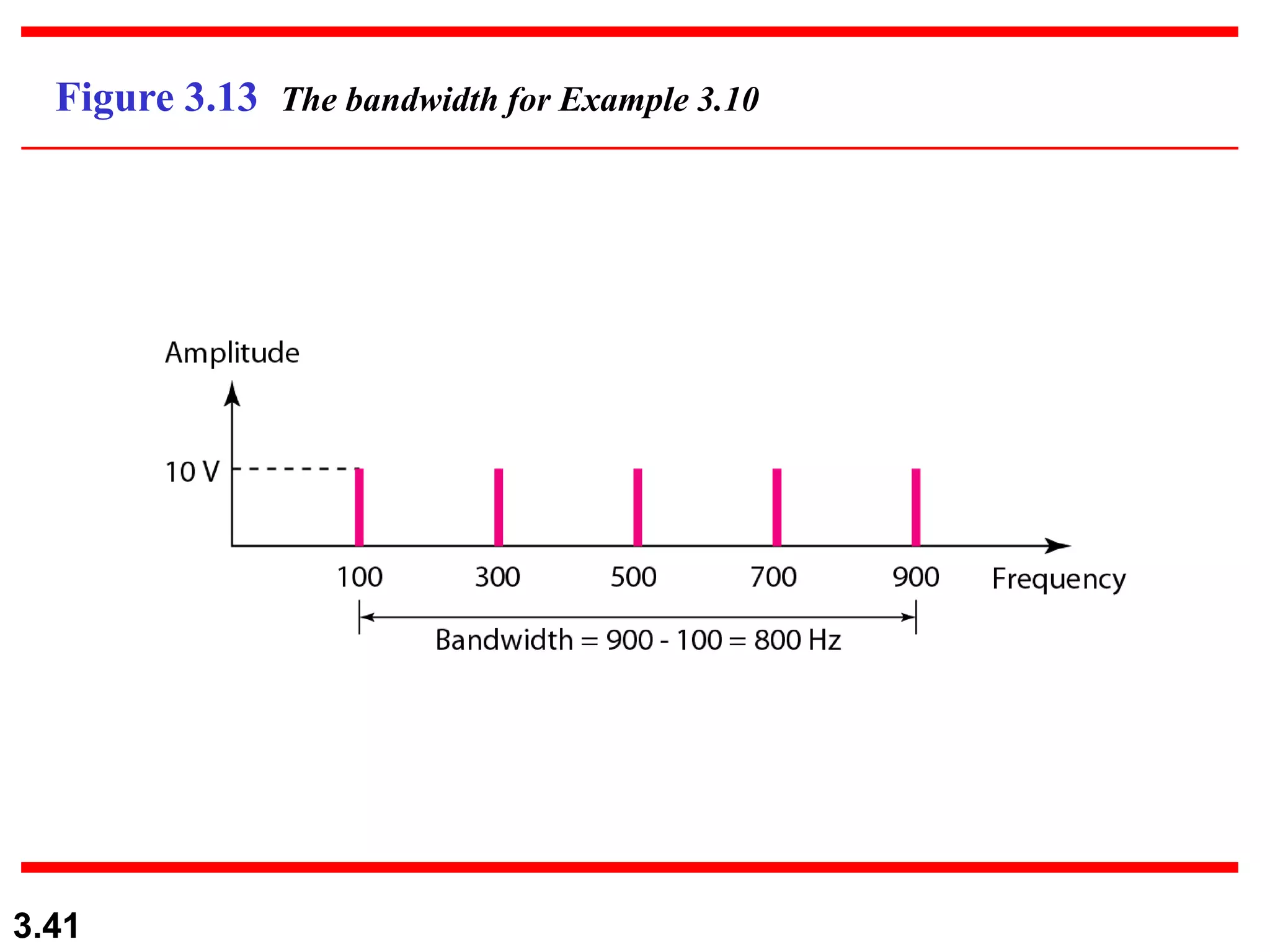
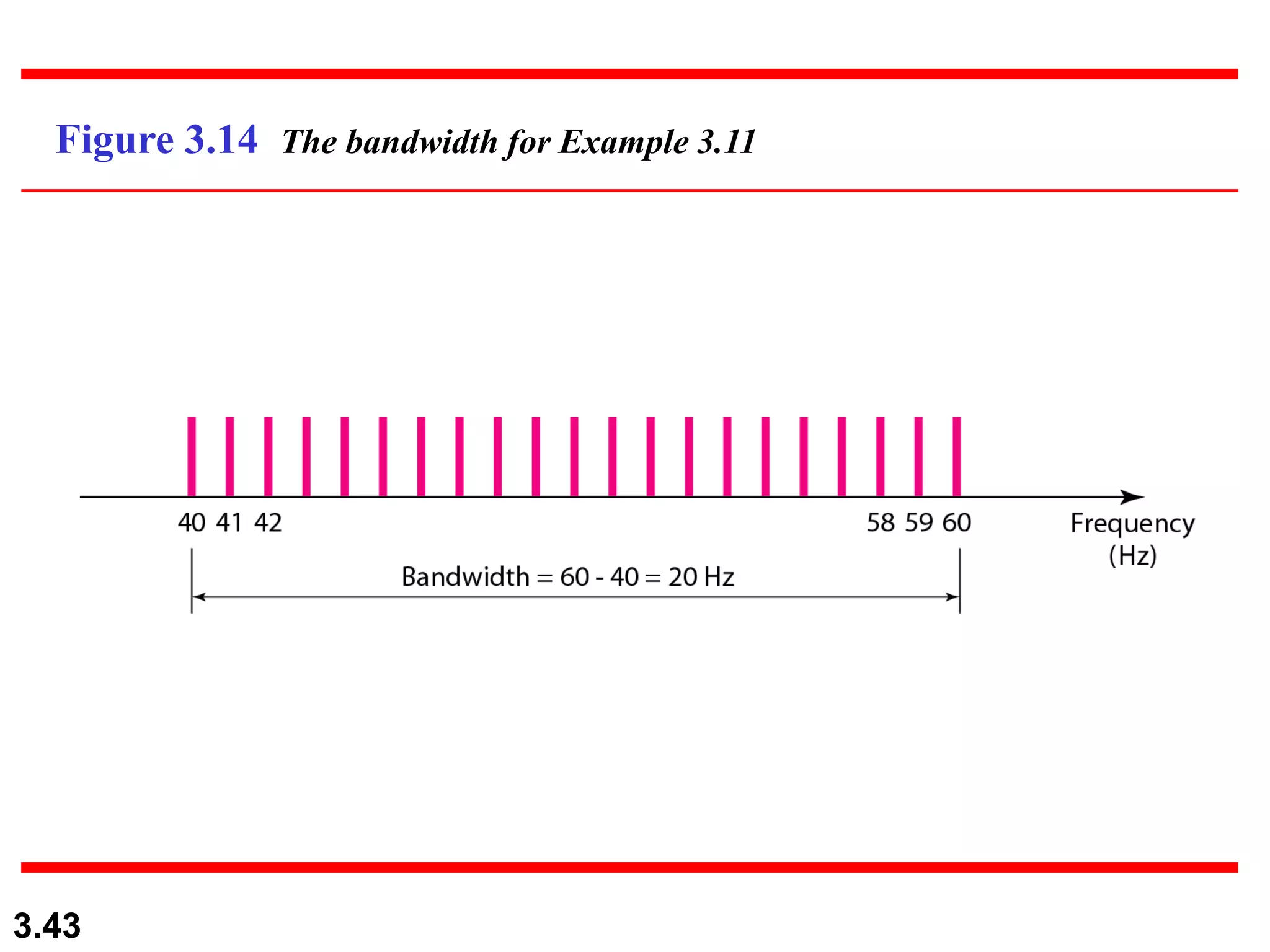
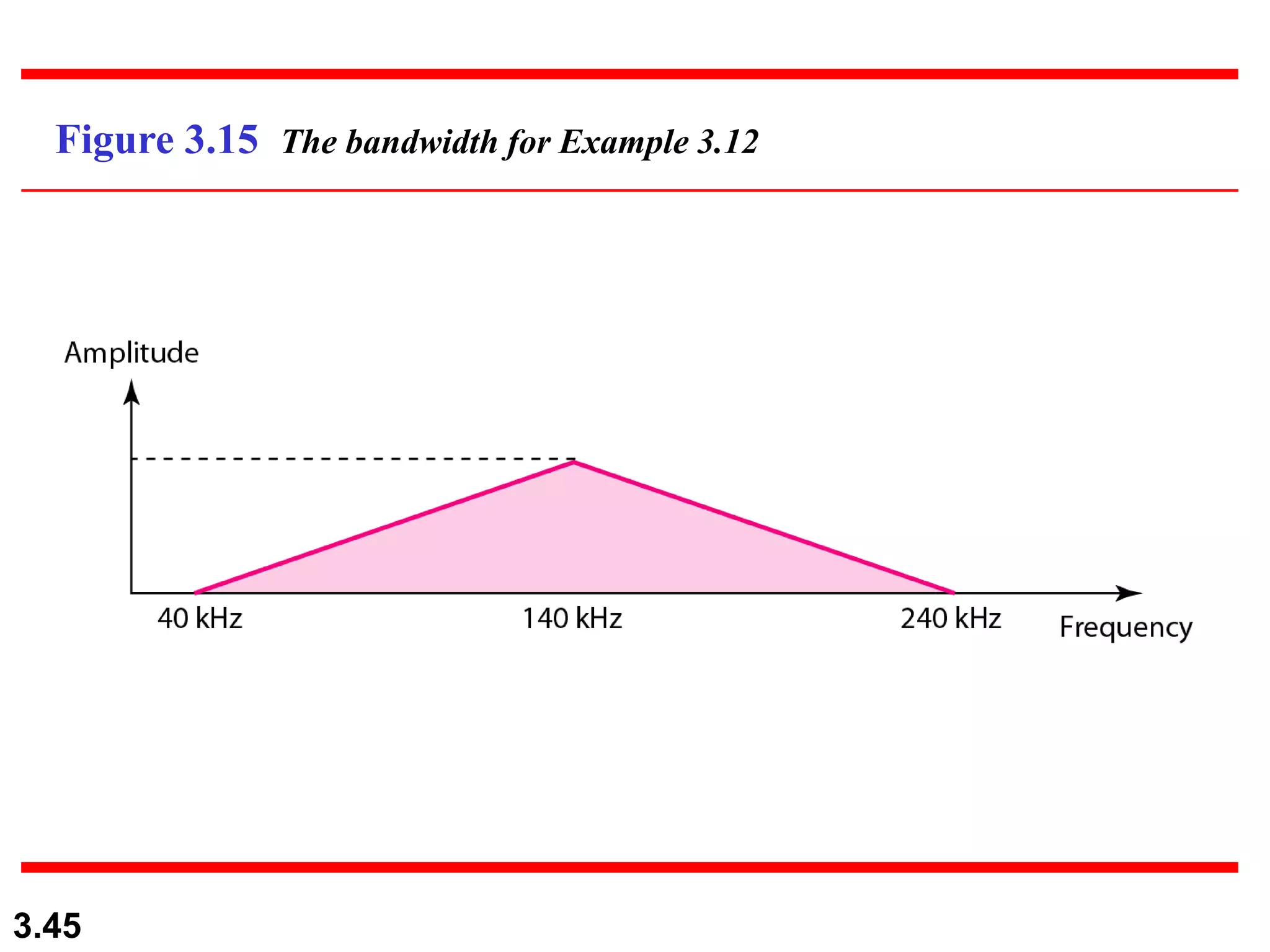
- Periodic analog signals include sine waves and composite signals made of multiple sine waves. Frequency is the rate of change over time, while period is the inverse of frequency.
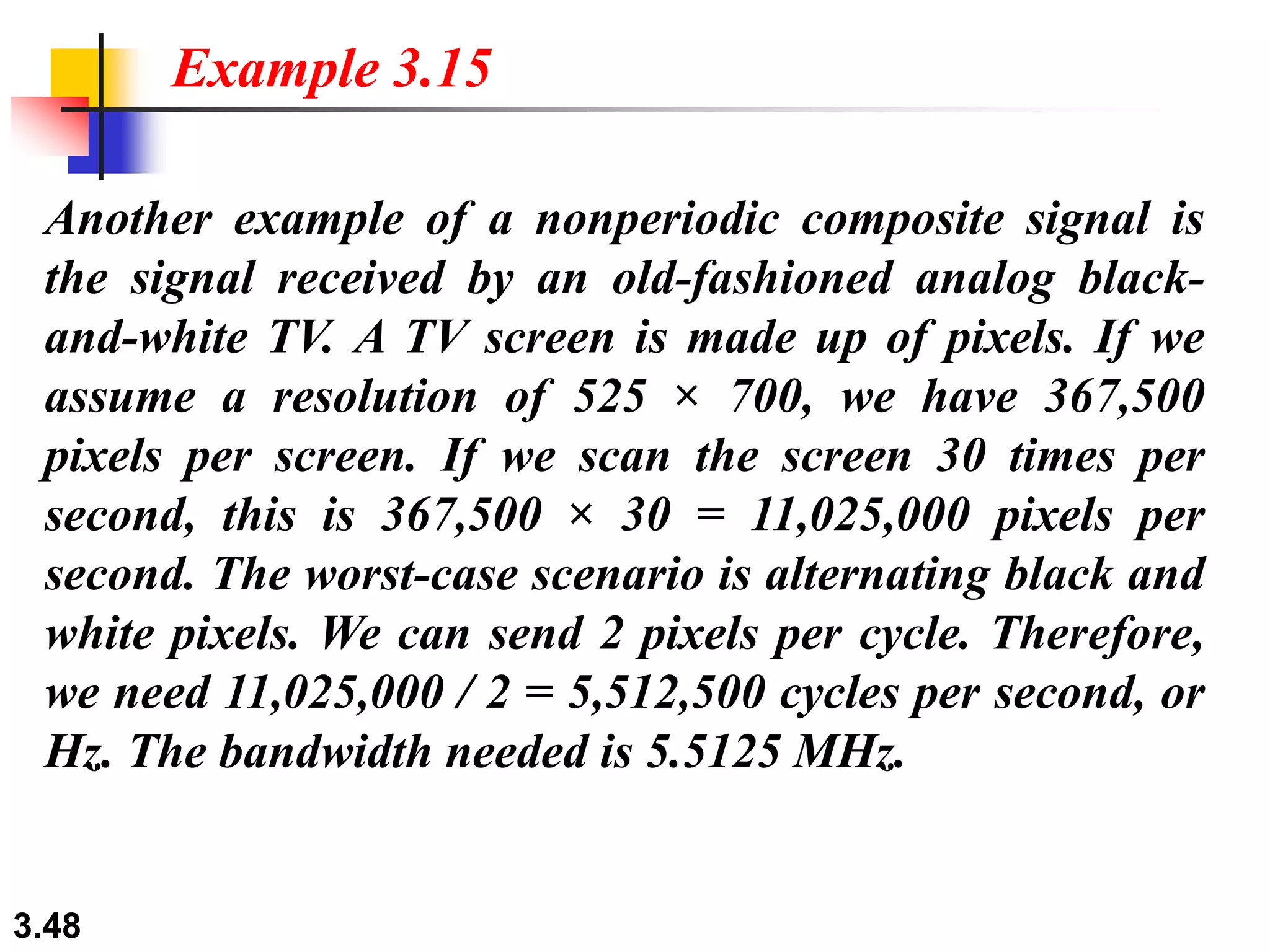
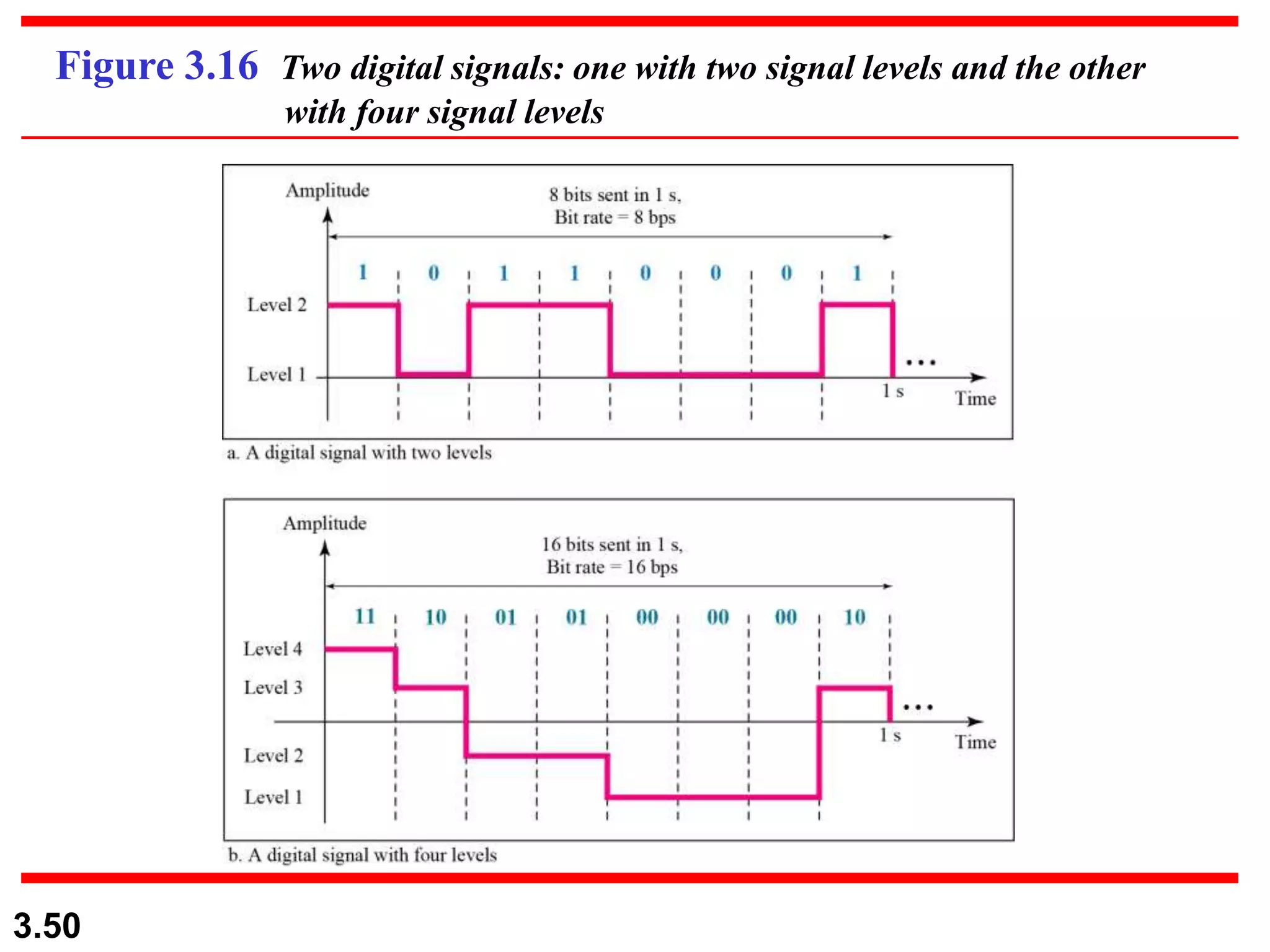
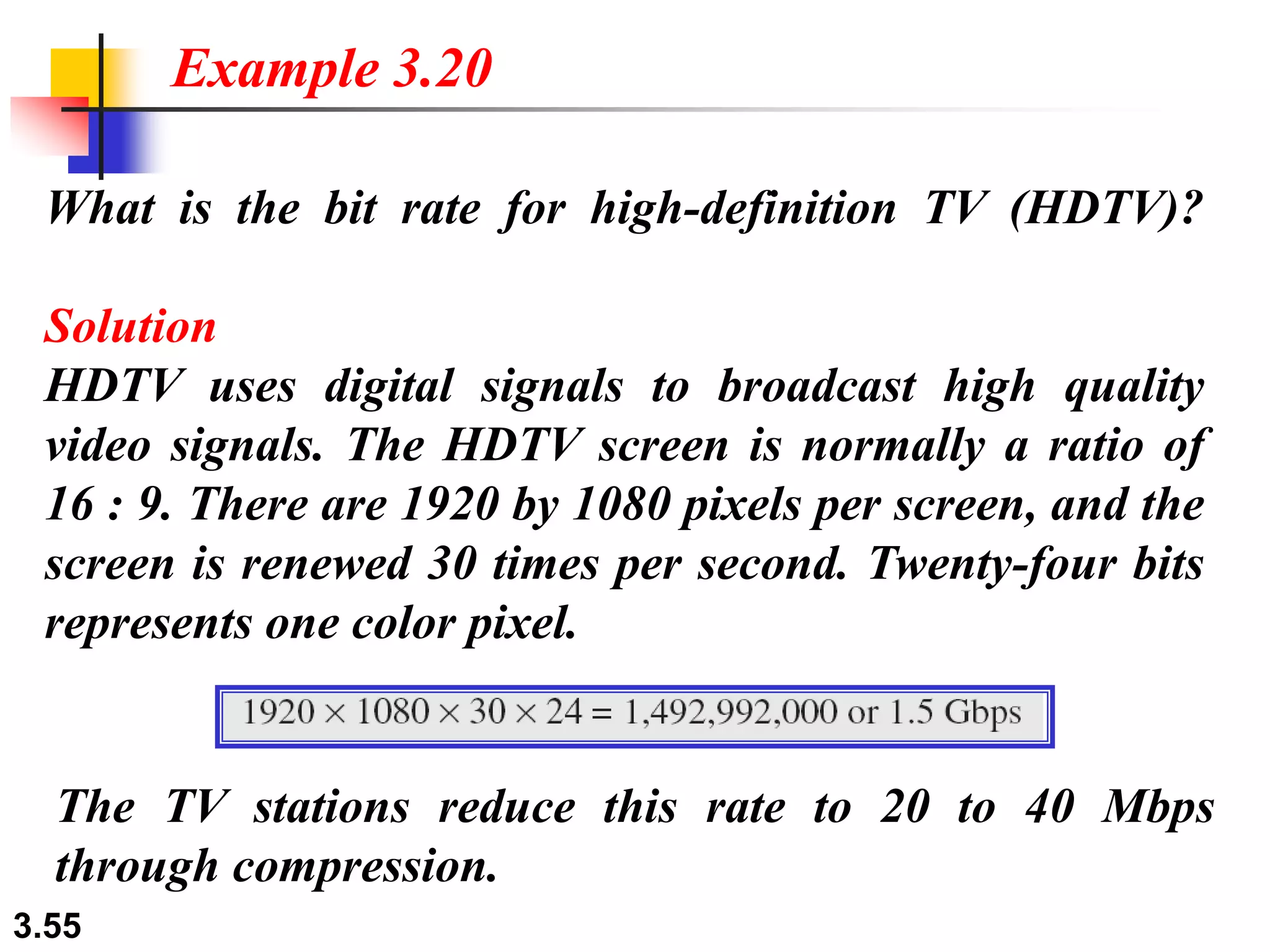
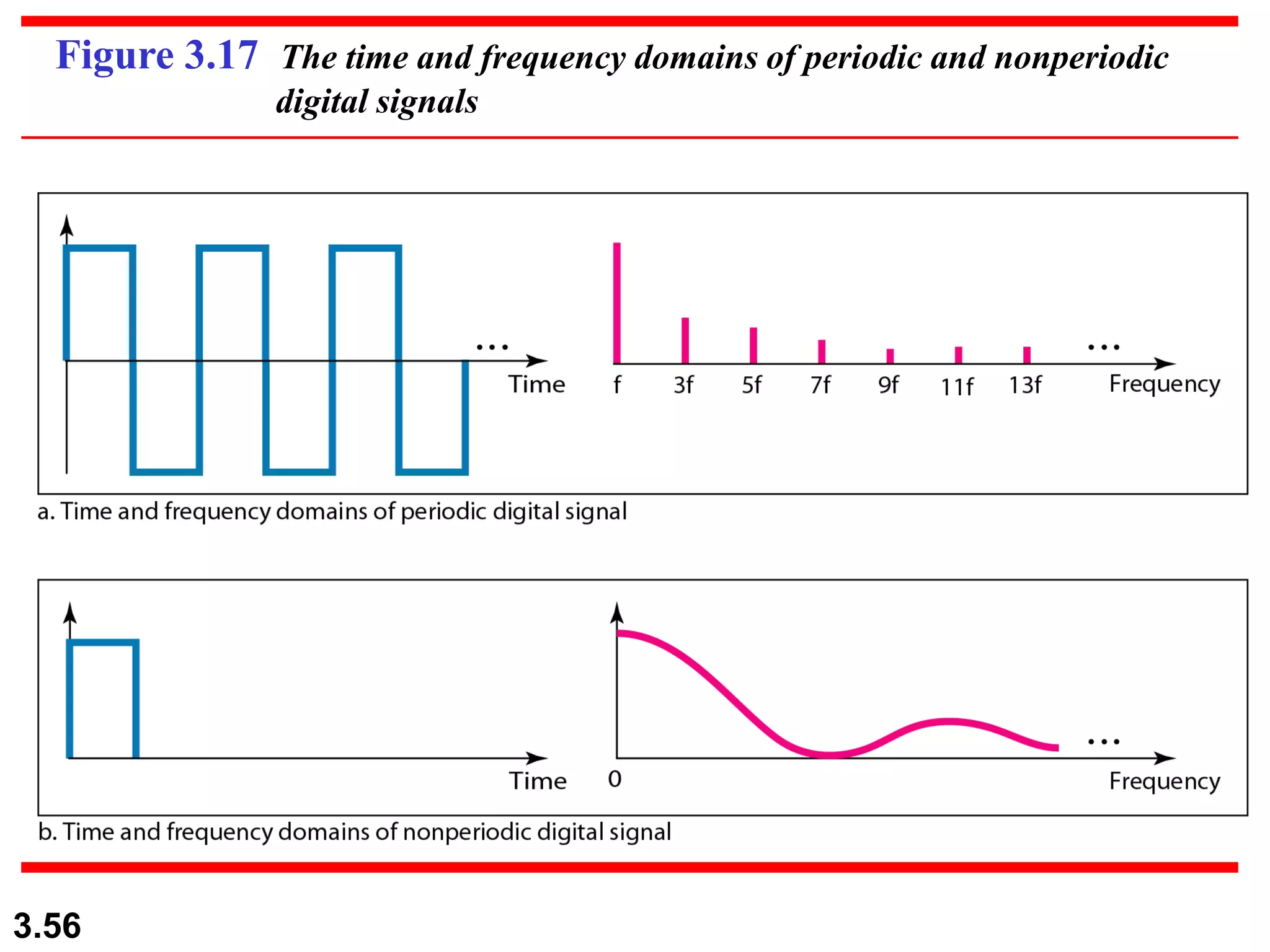
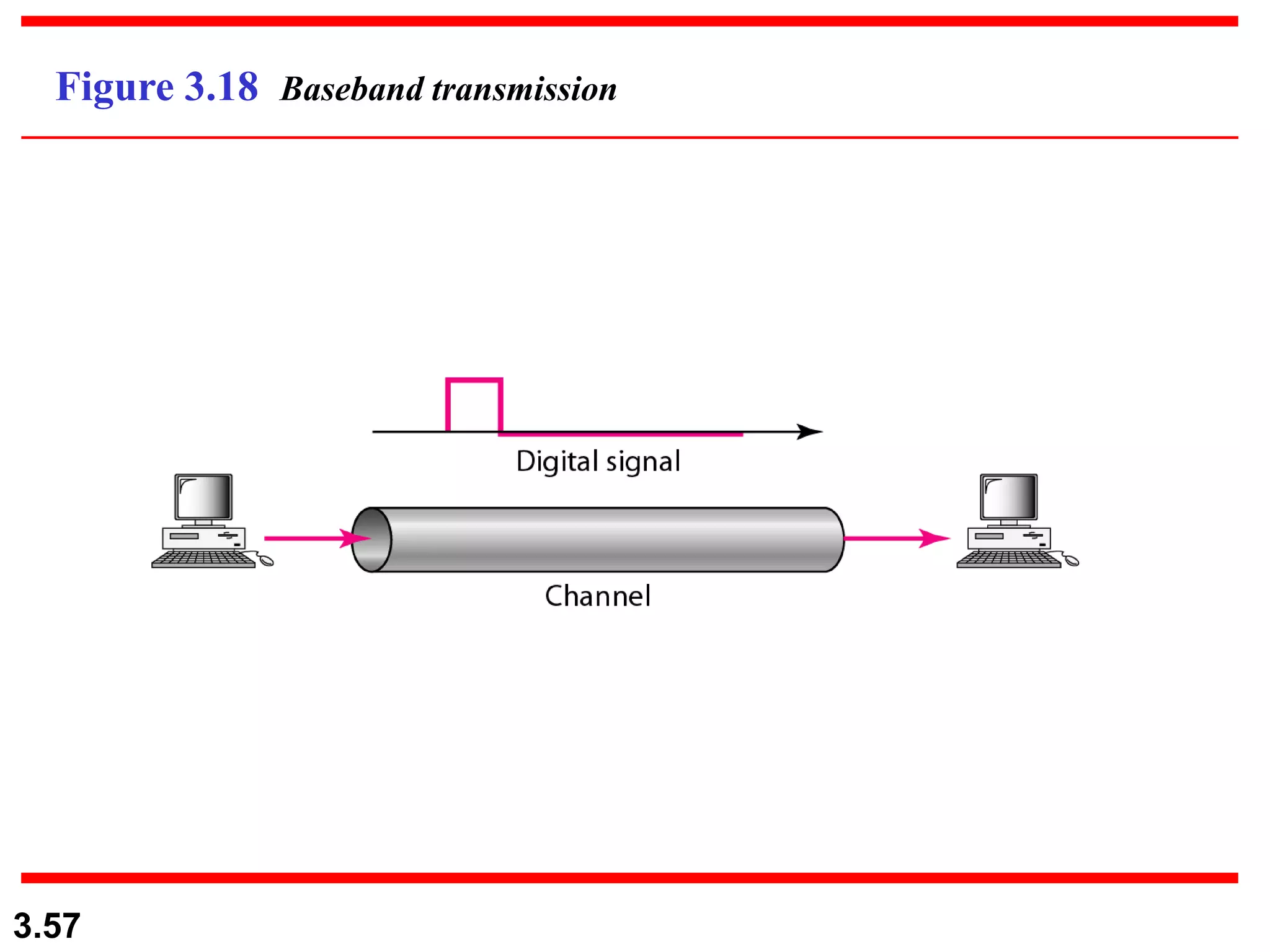
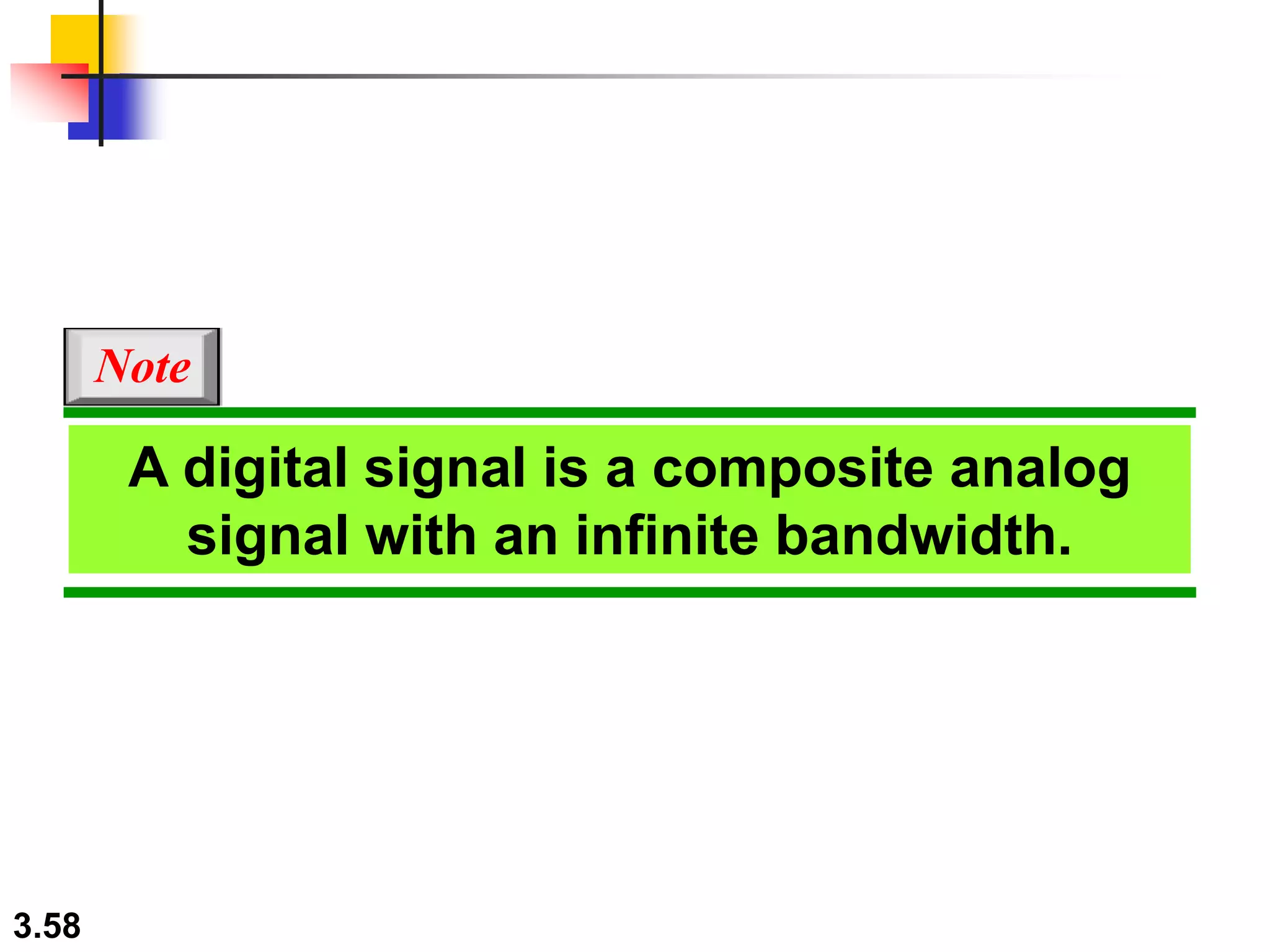
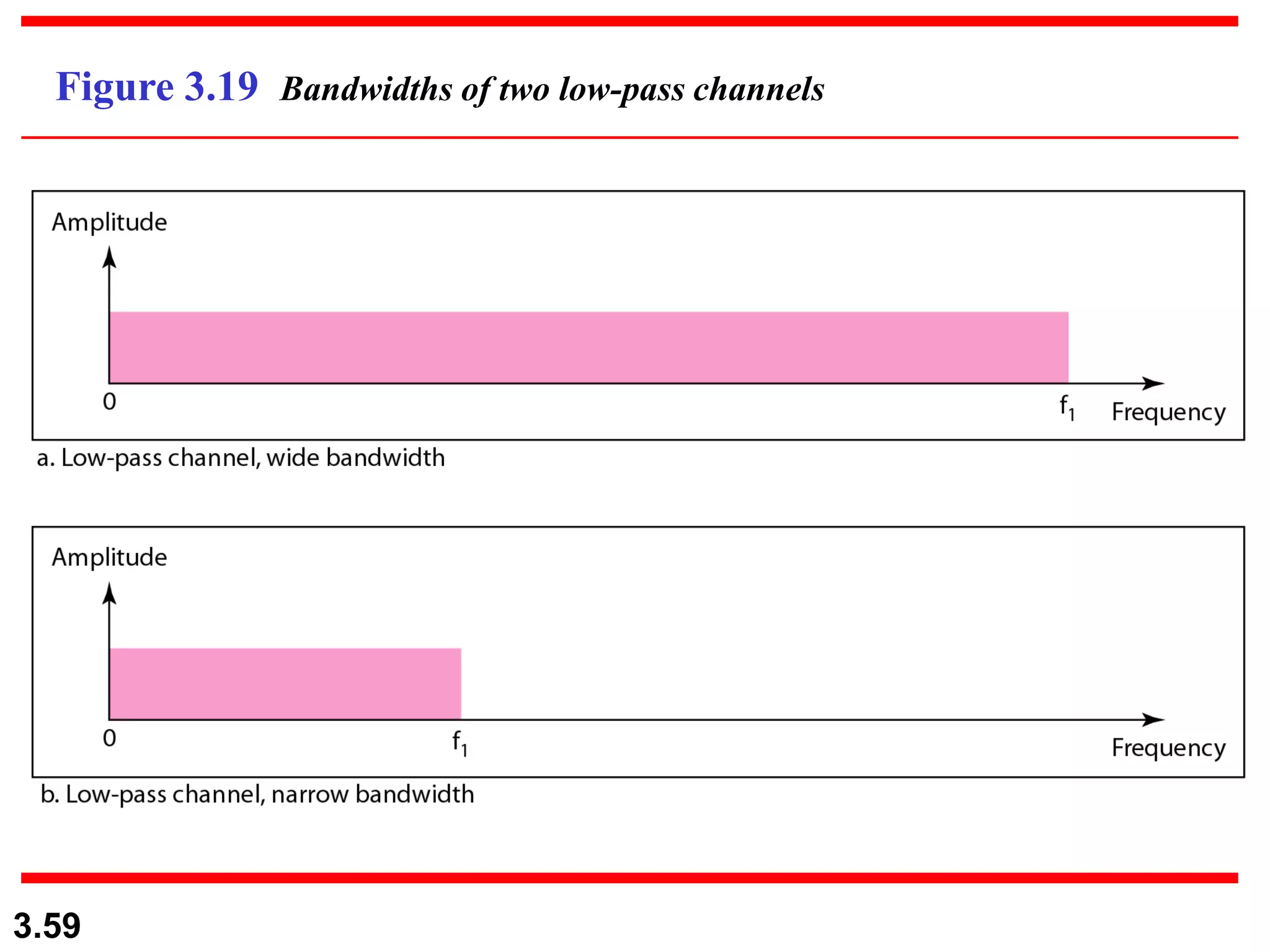
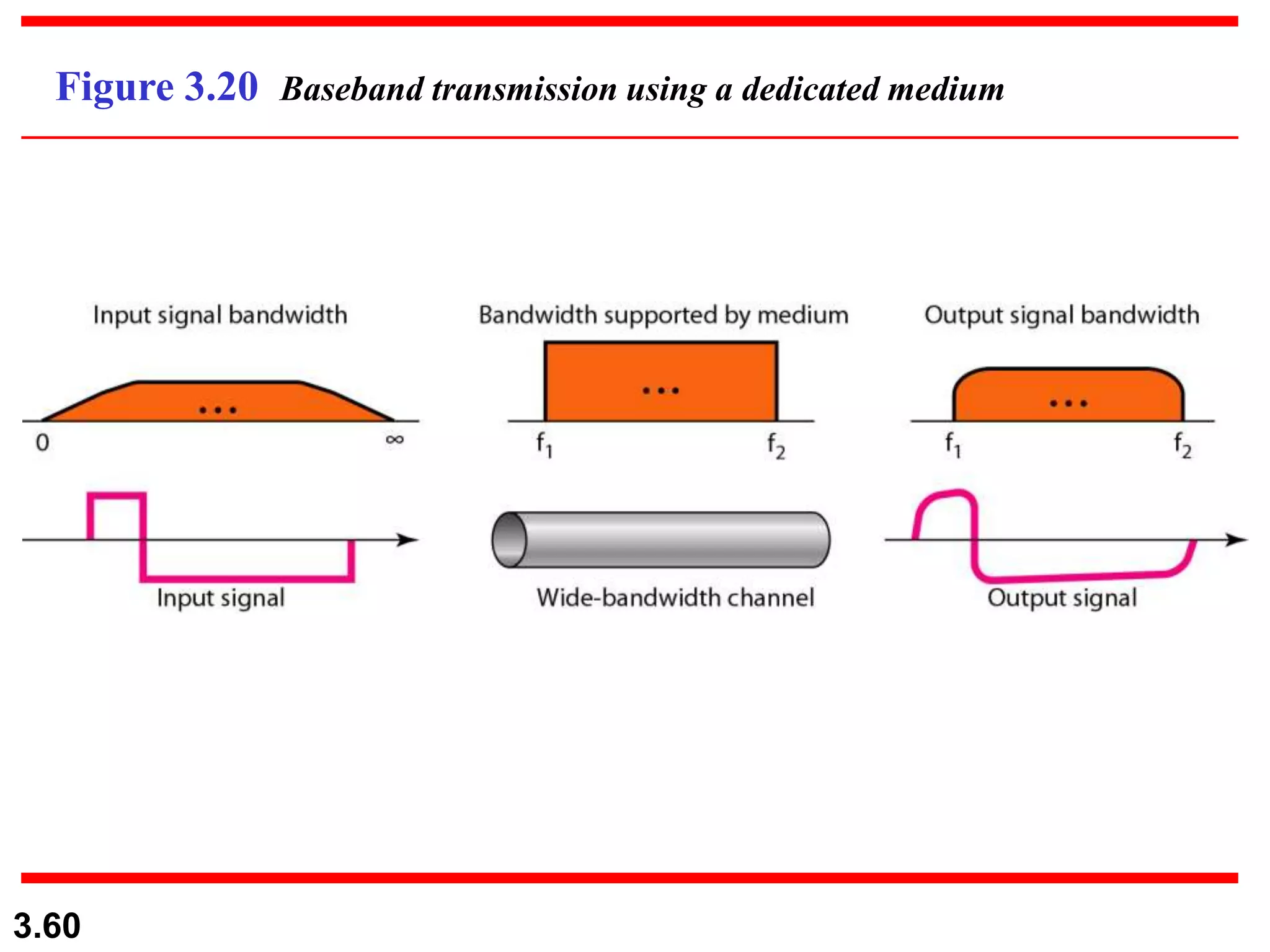
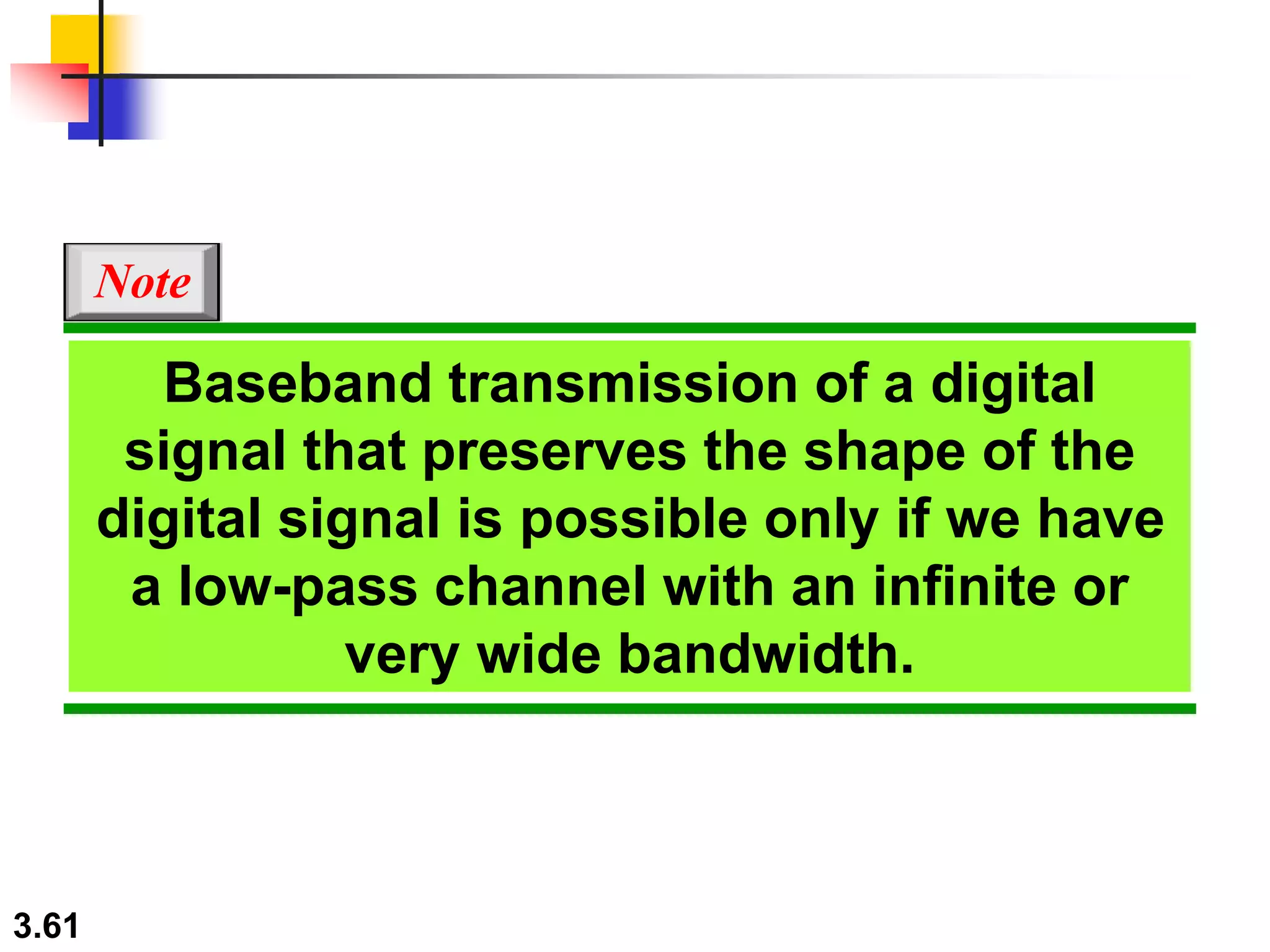
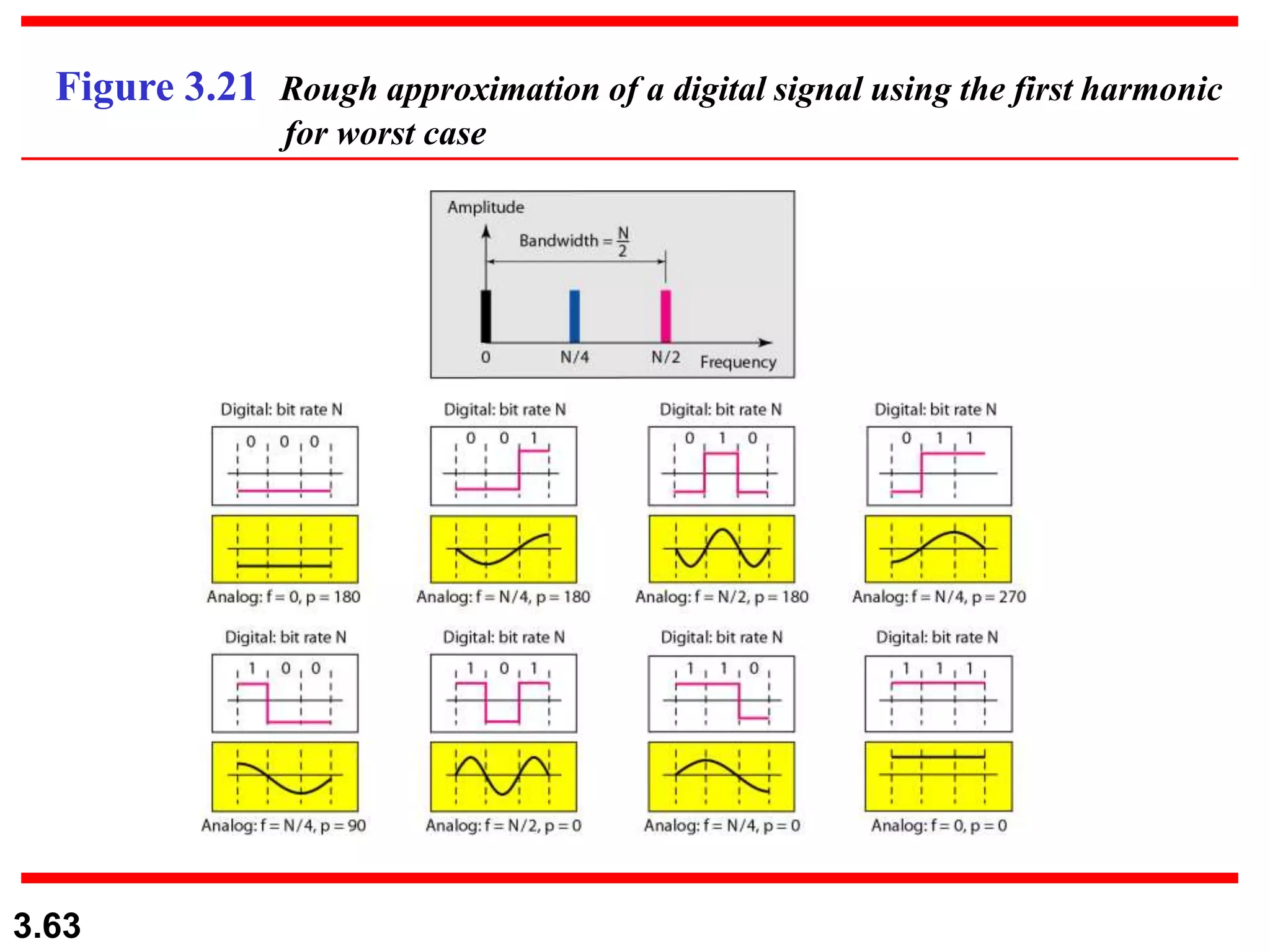
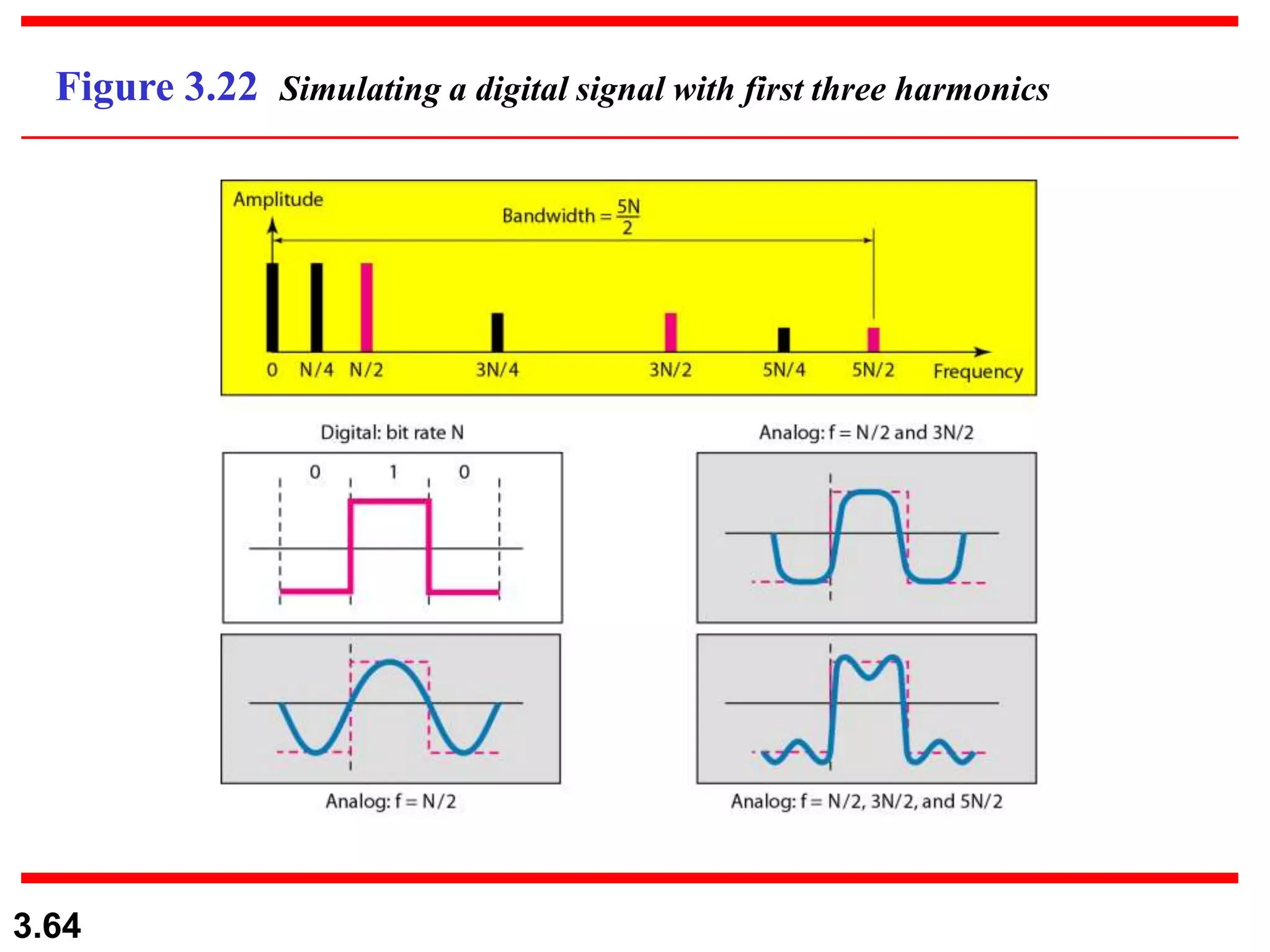
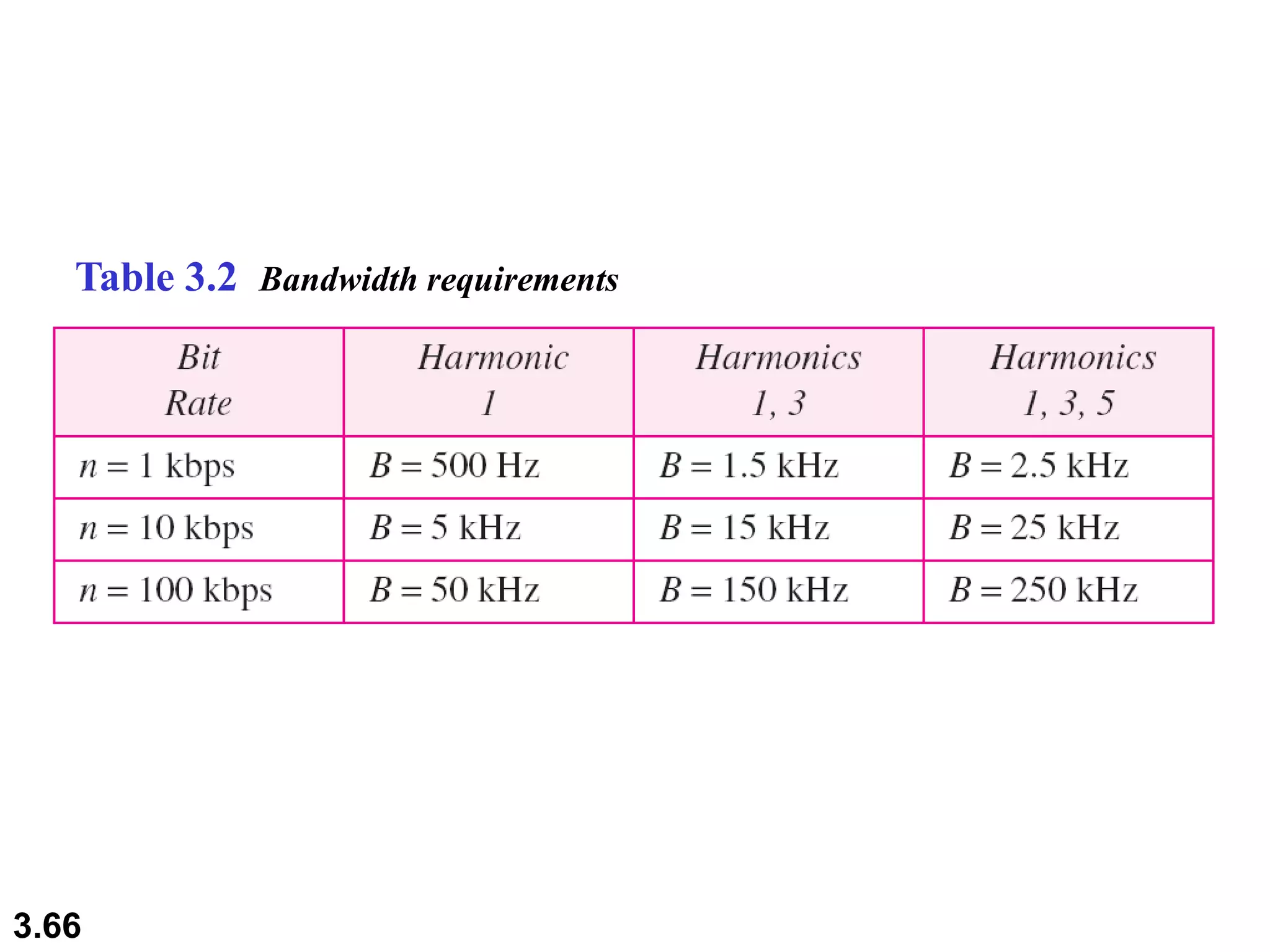
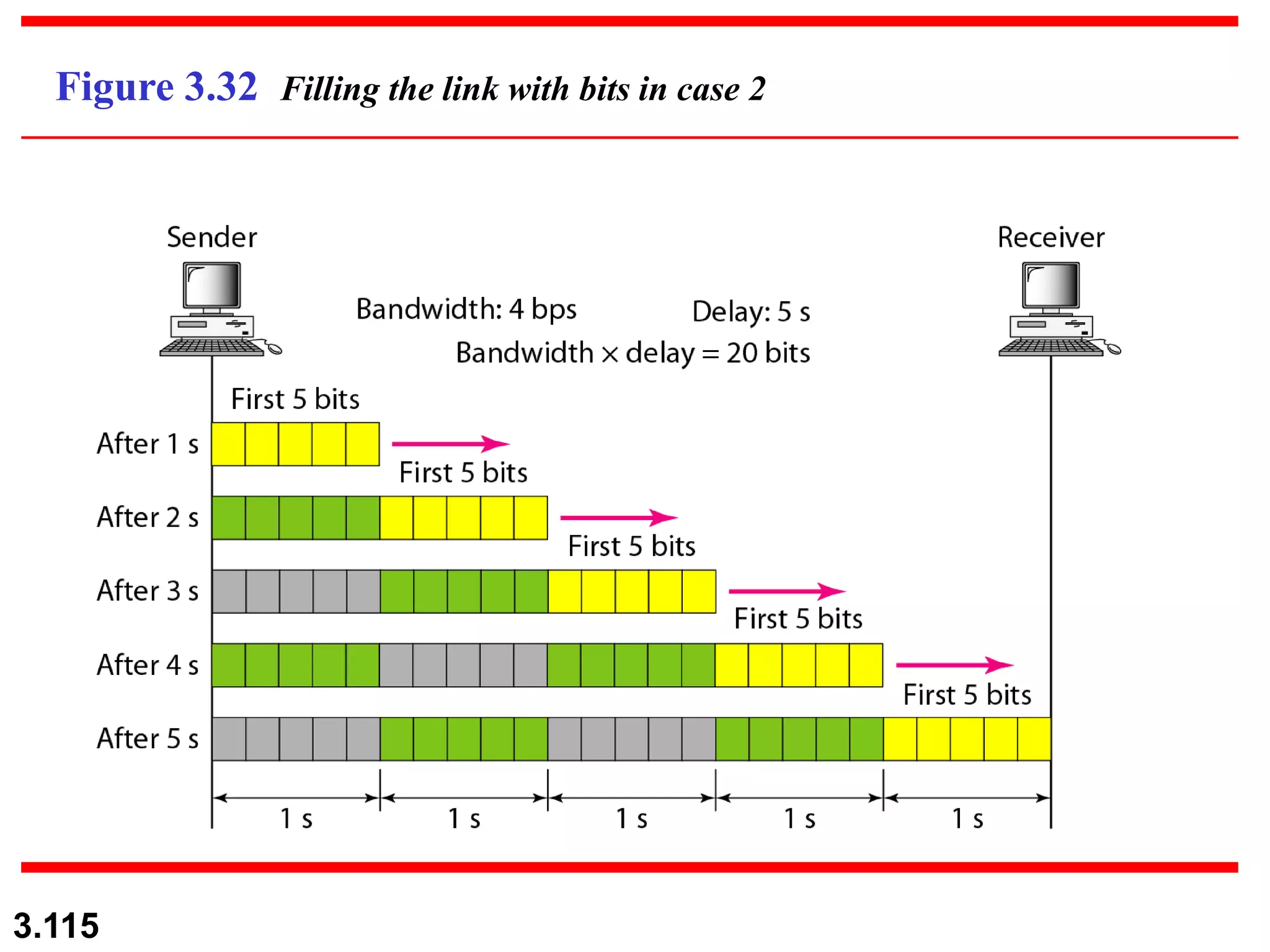
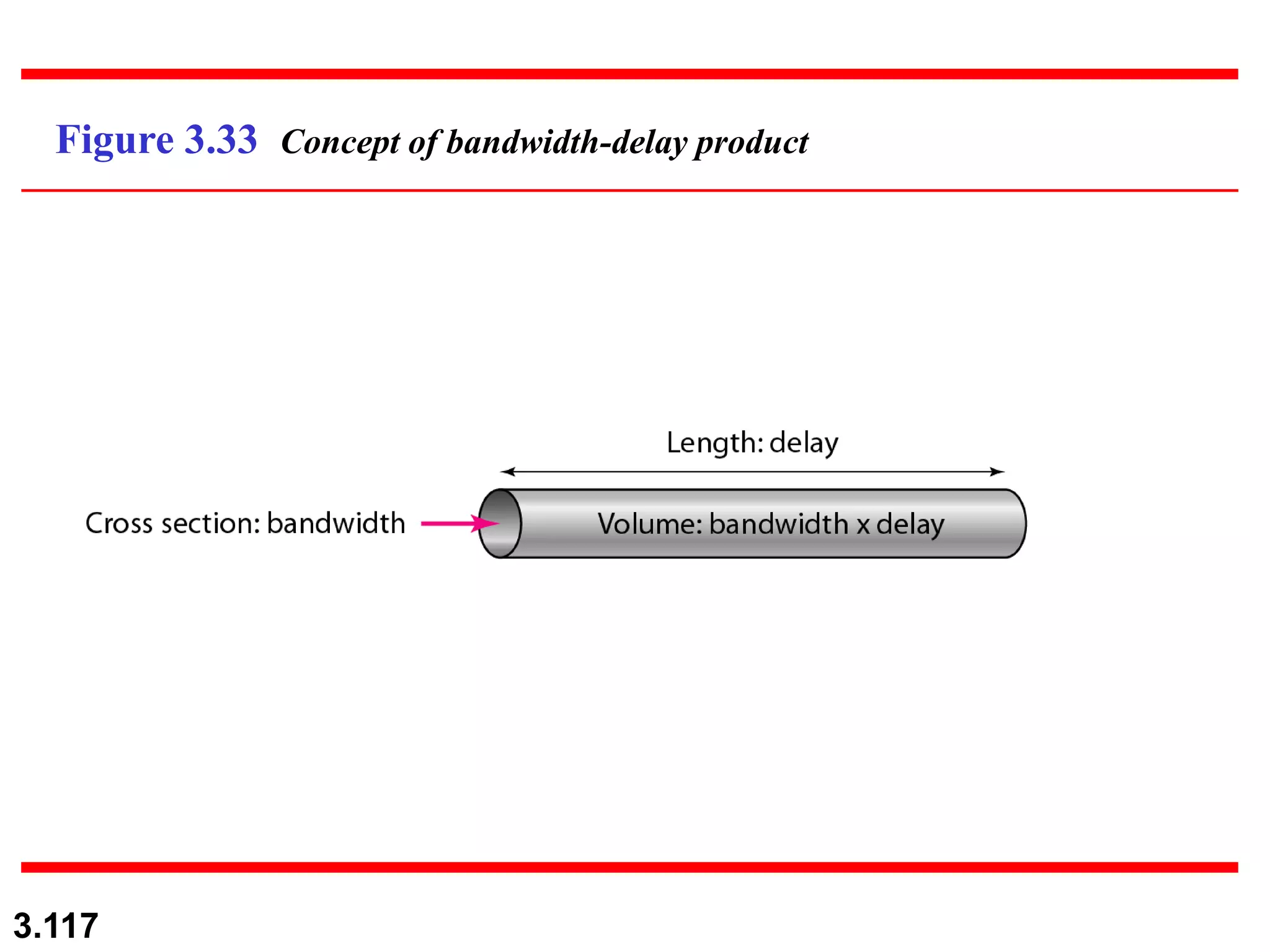
- Digital signals represent information as discrete voltage levels, allowing multiple bits to be encoded in each signal level. The required bit rate depends on factors like sampling rate and number of bits per sample.