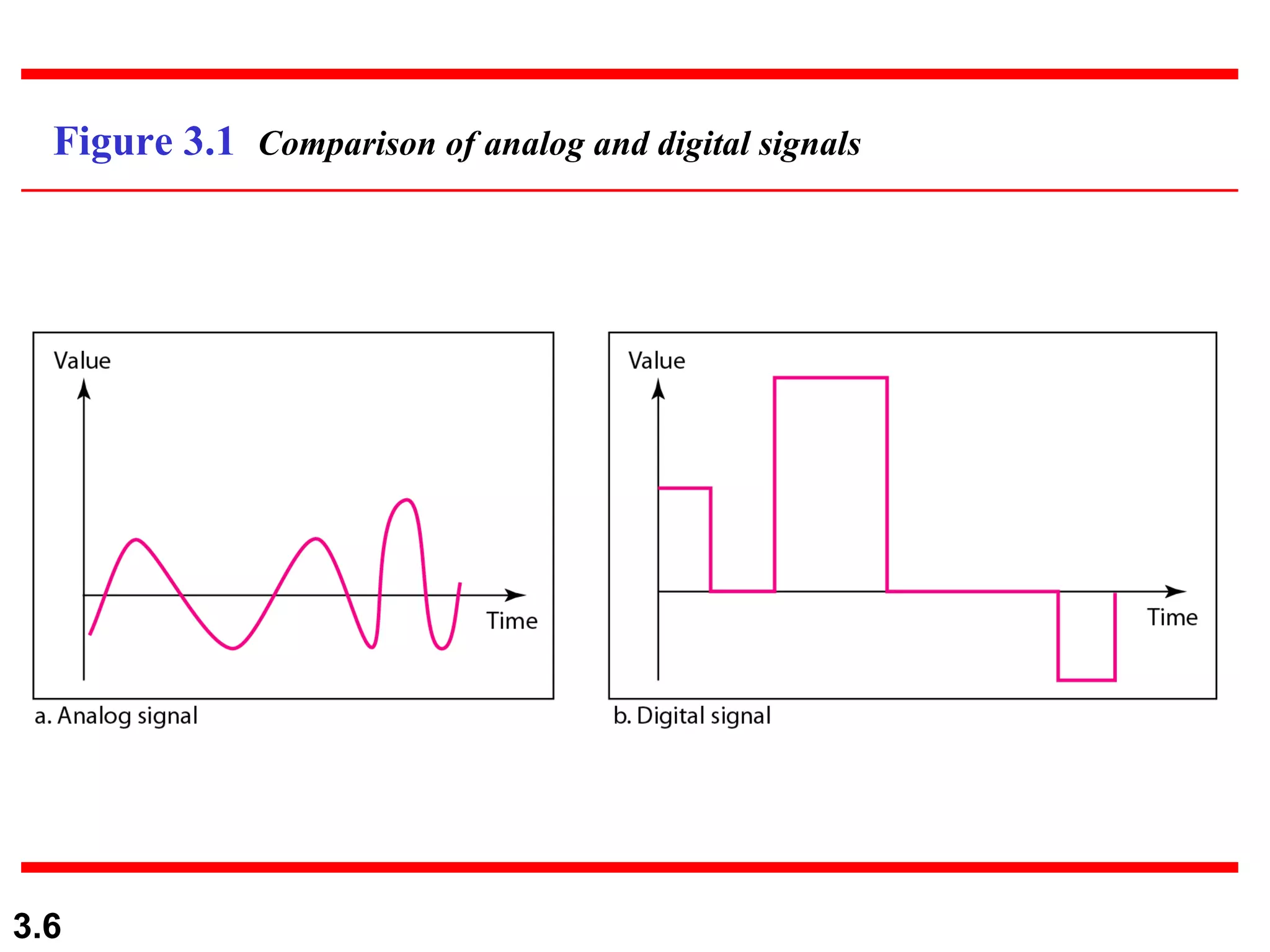
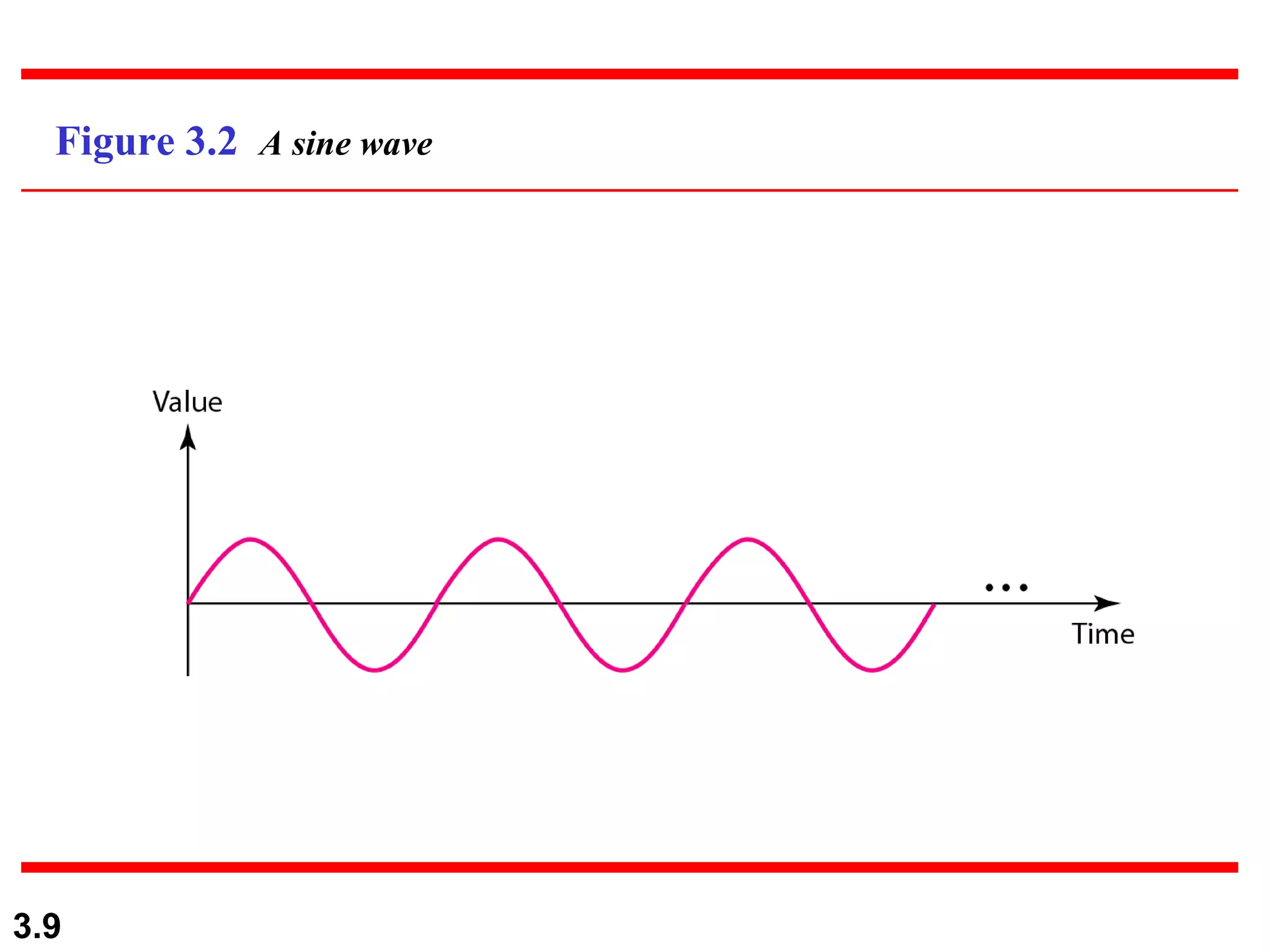
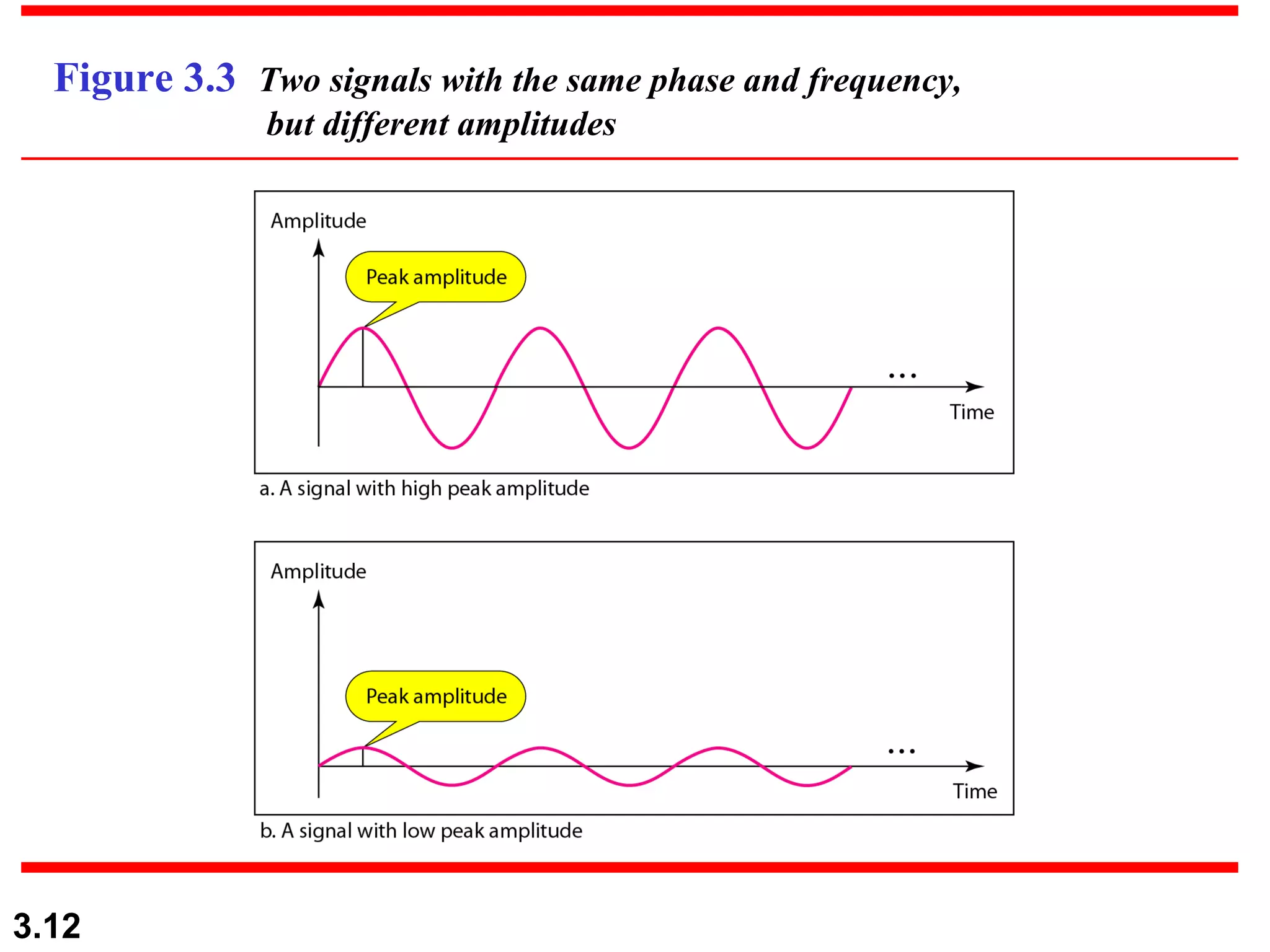
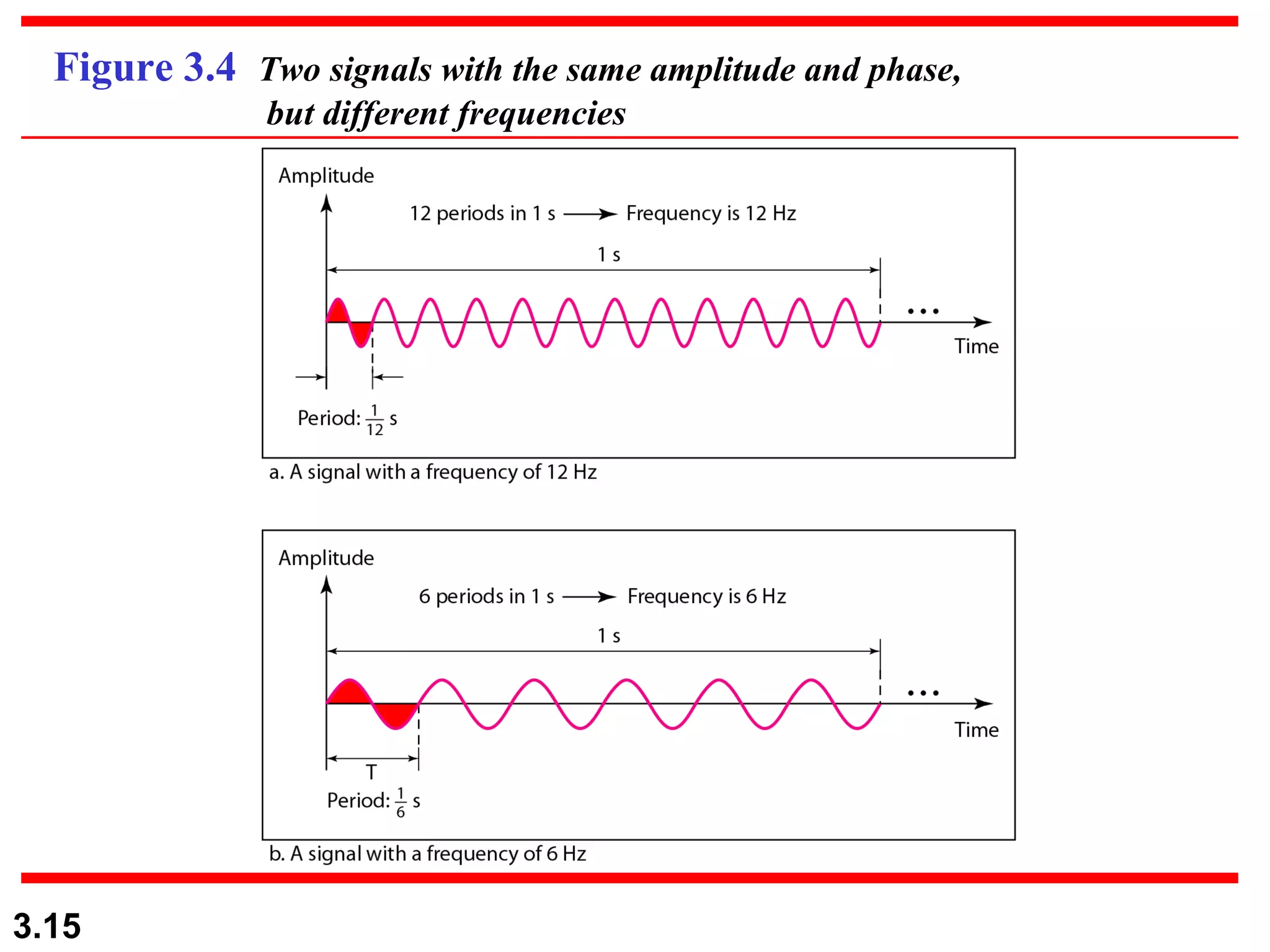
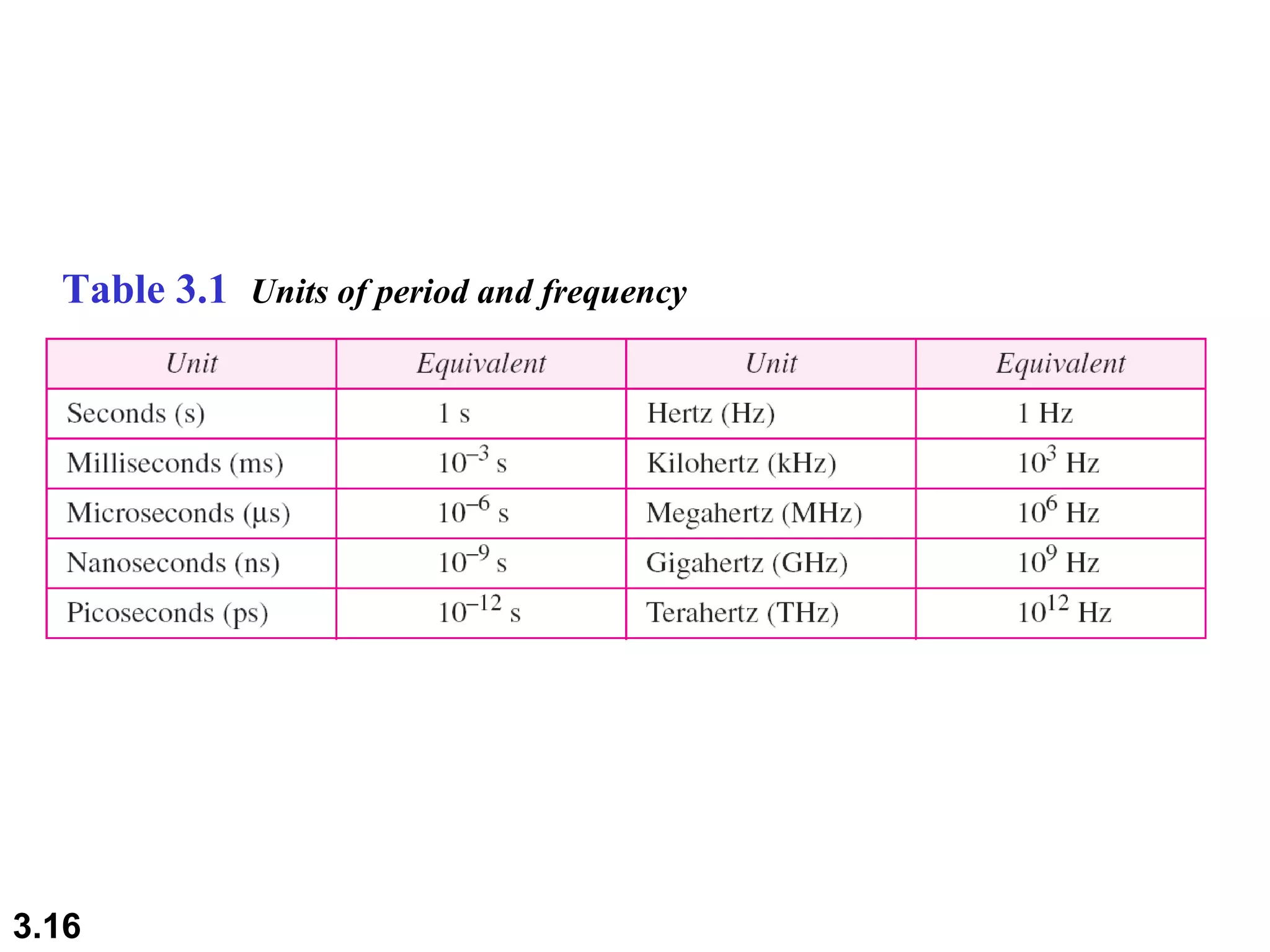
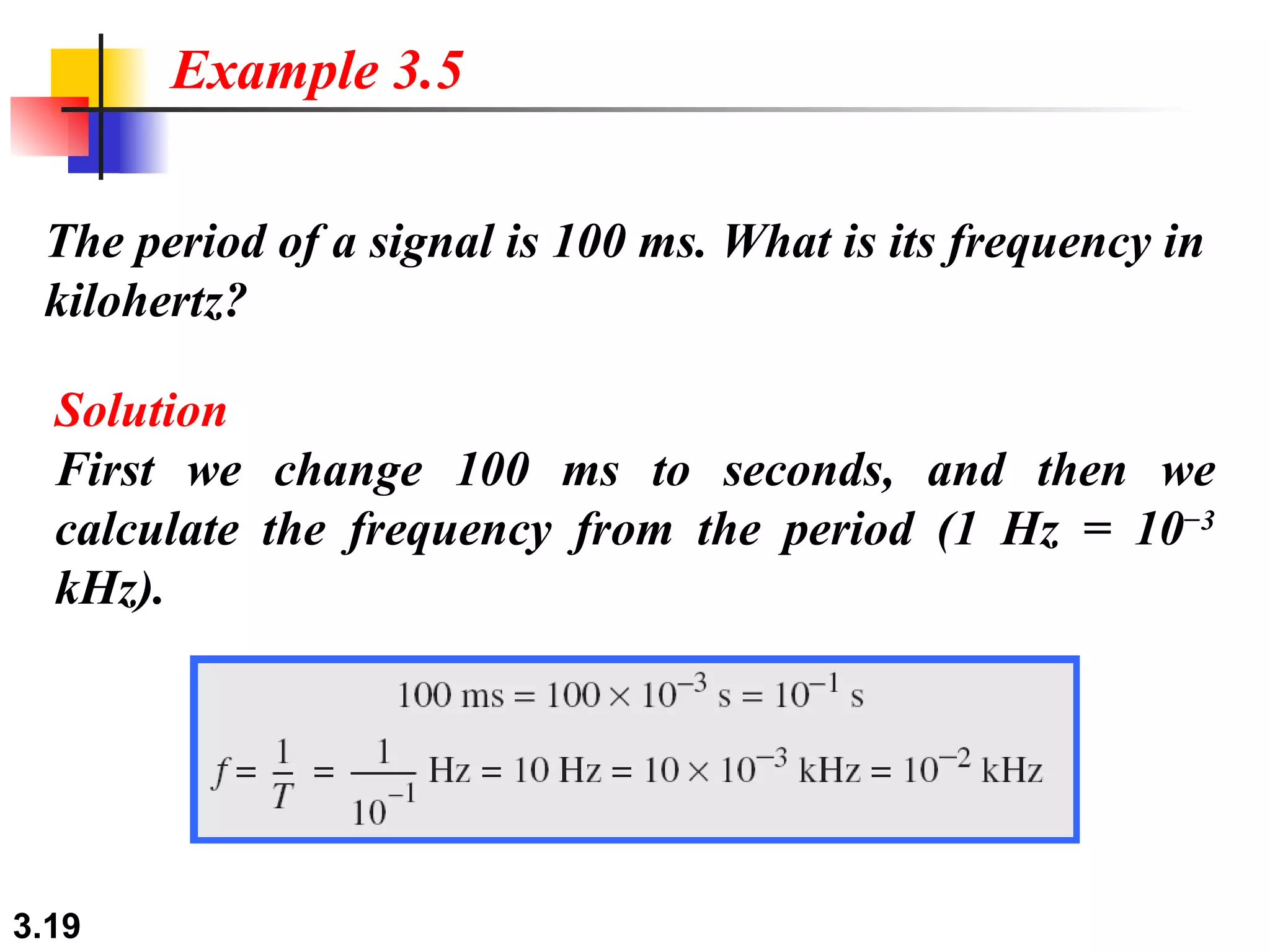
- Data can be analog or digital, with analog being continuous and digital having discrete states. Analog signals are also continuous while digital signals have a limited set of values.
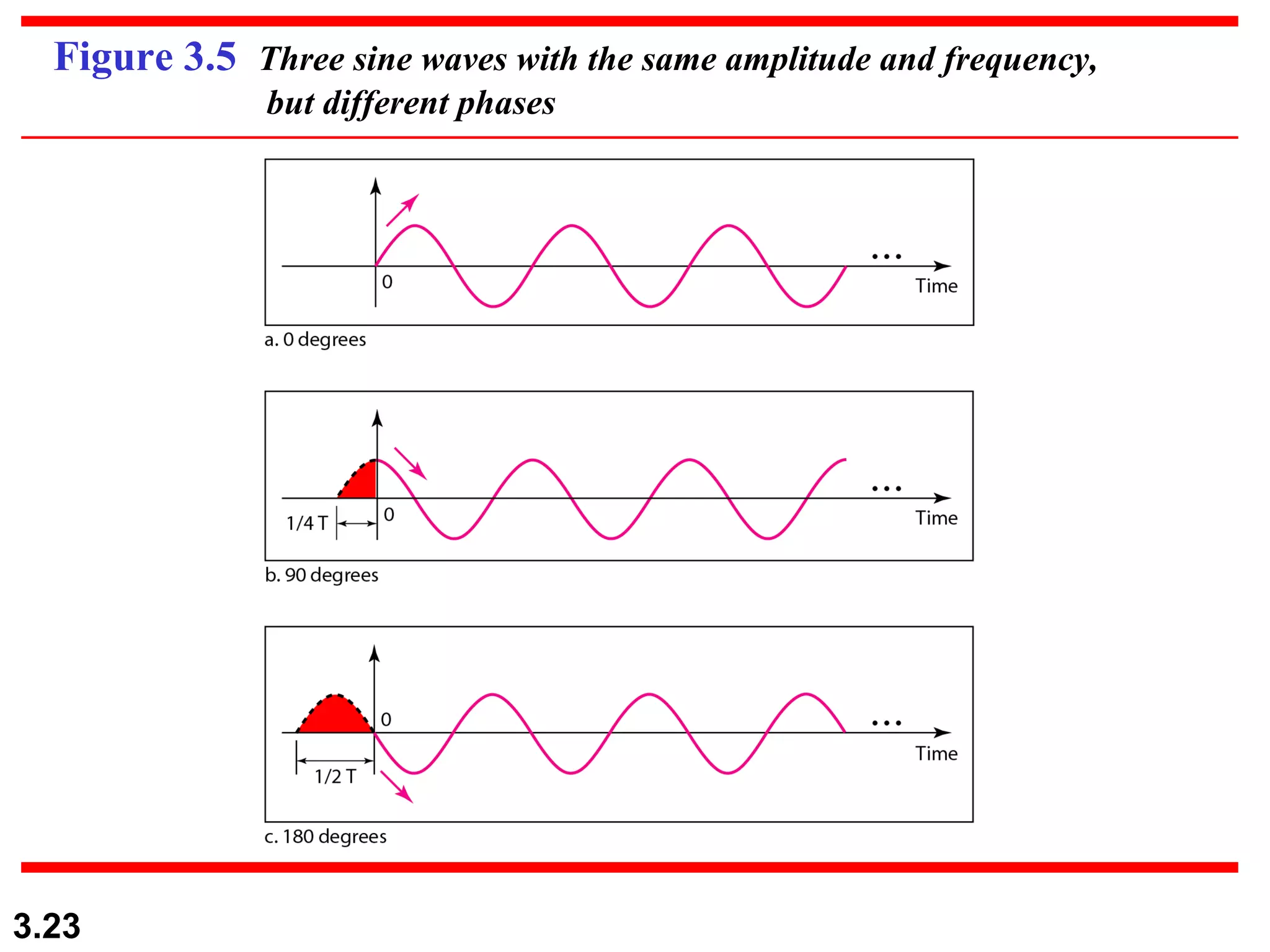
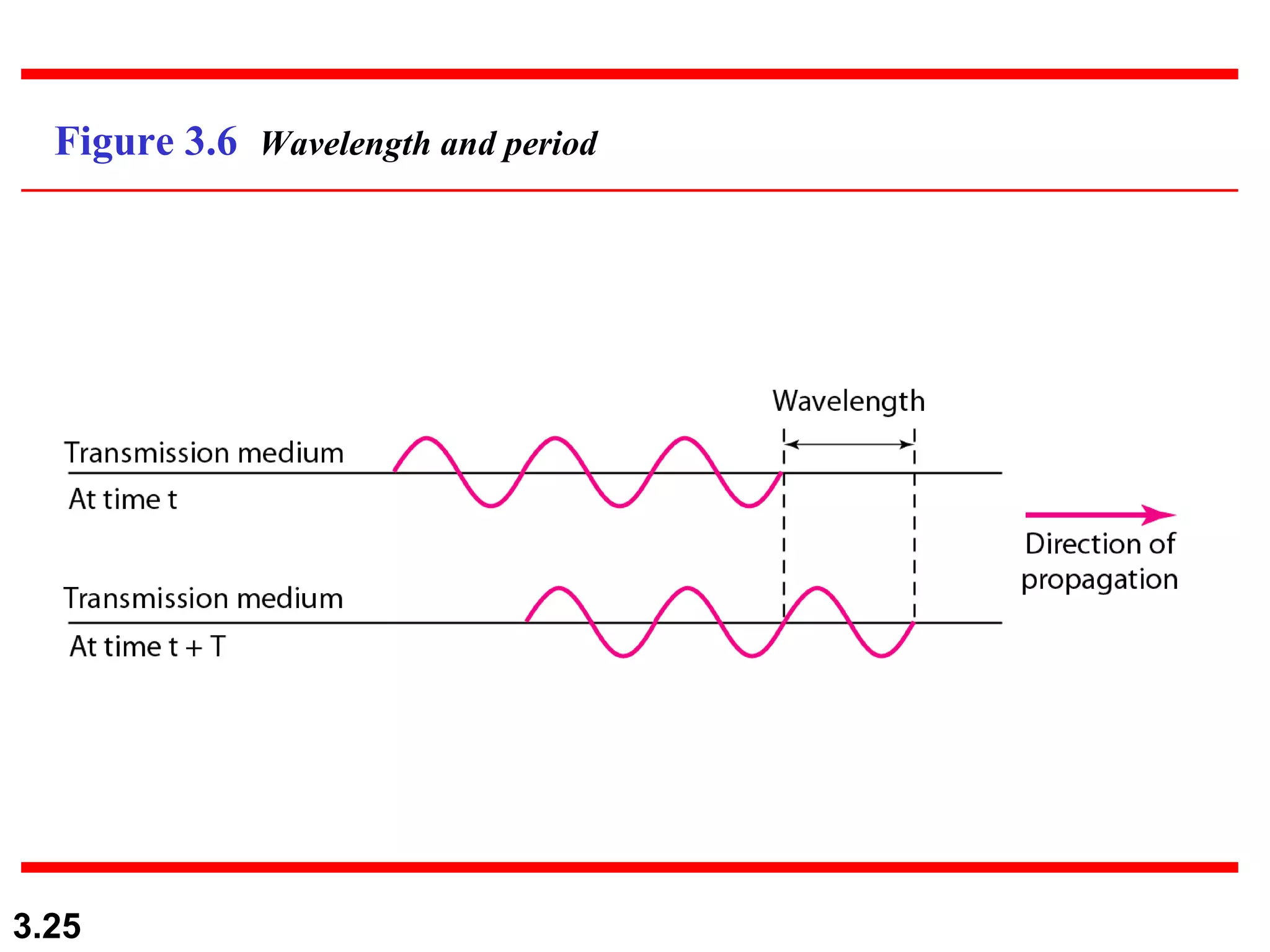
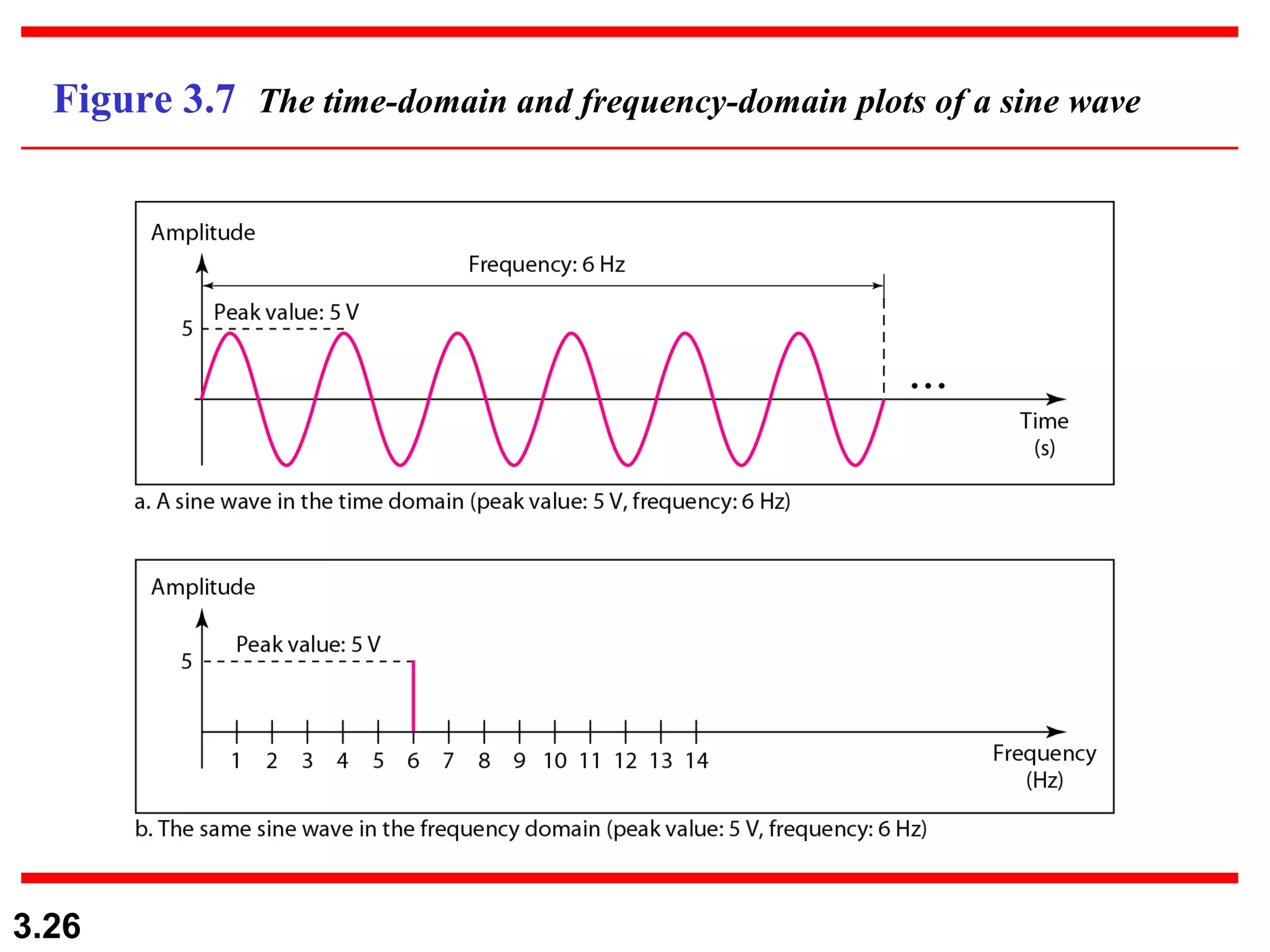
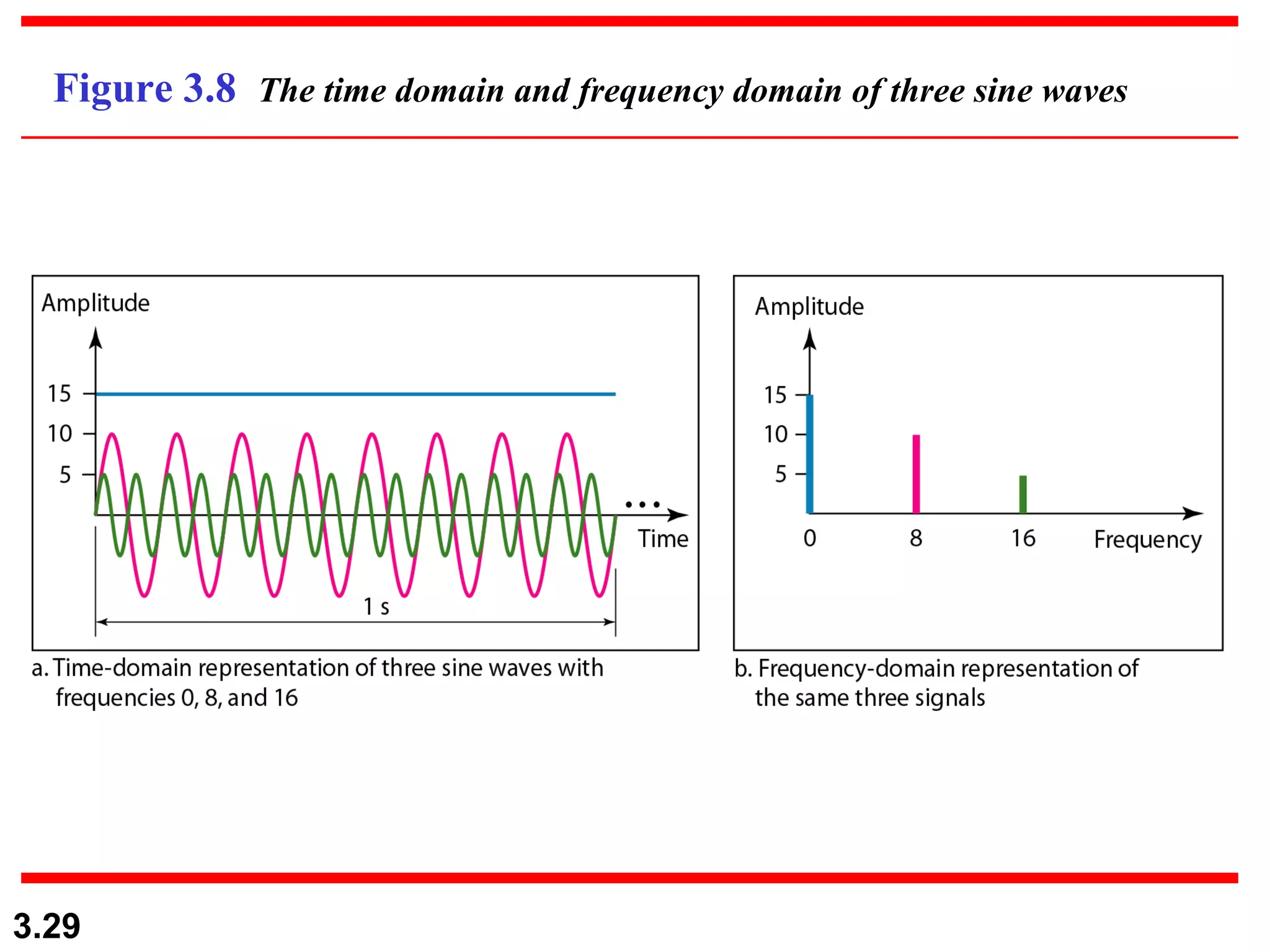
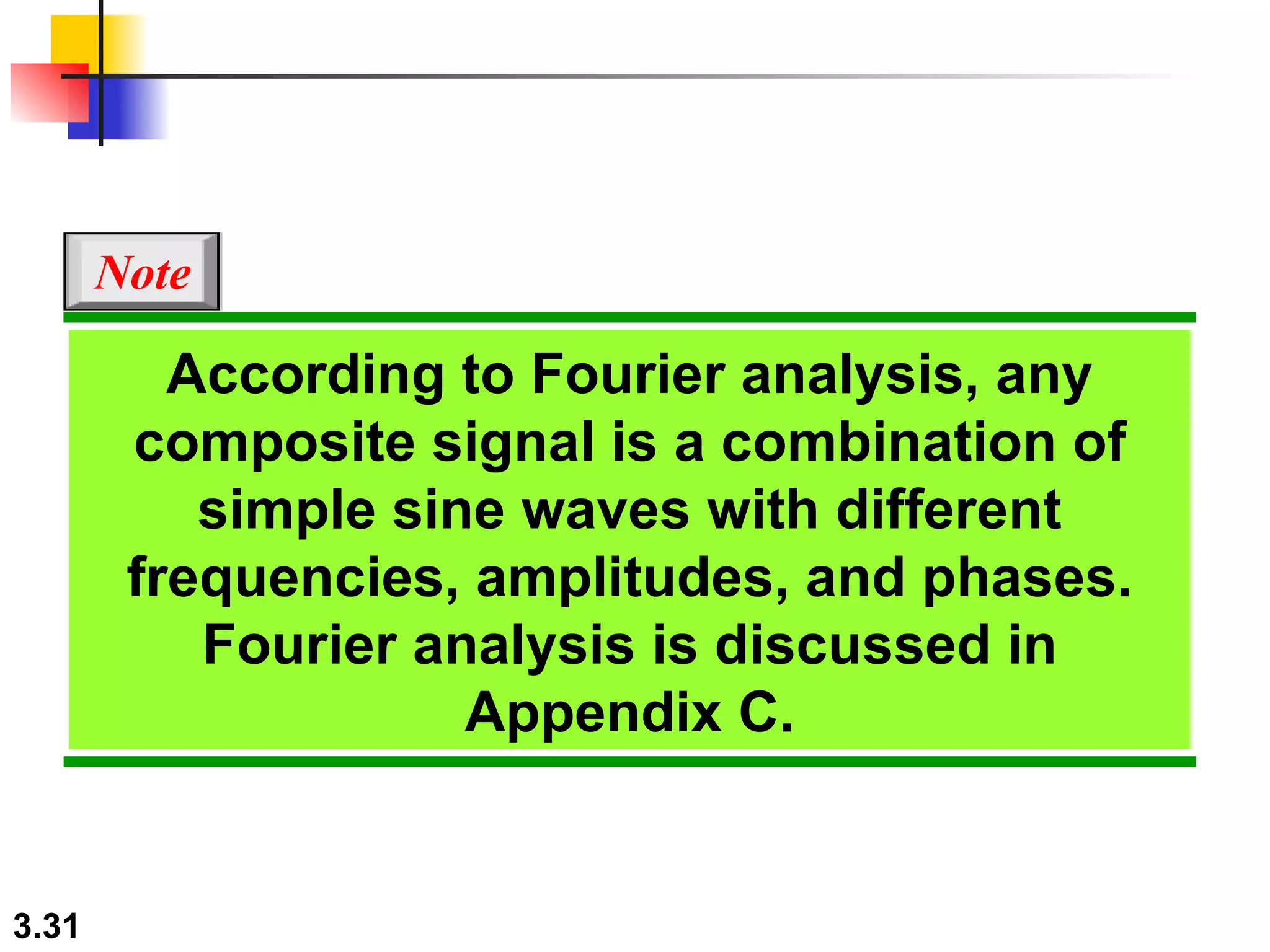
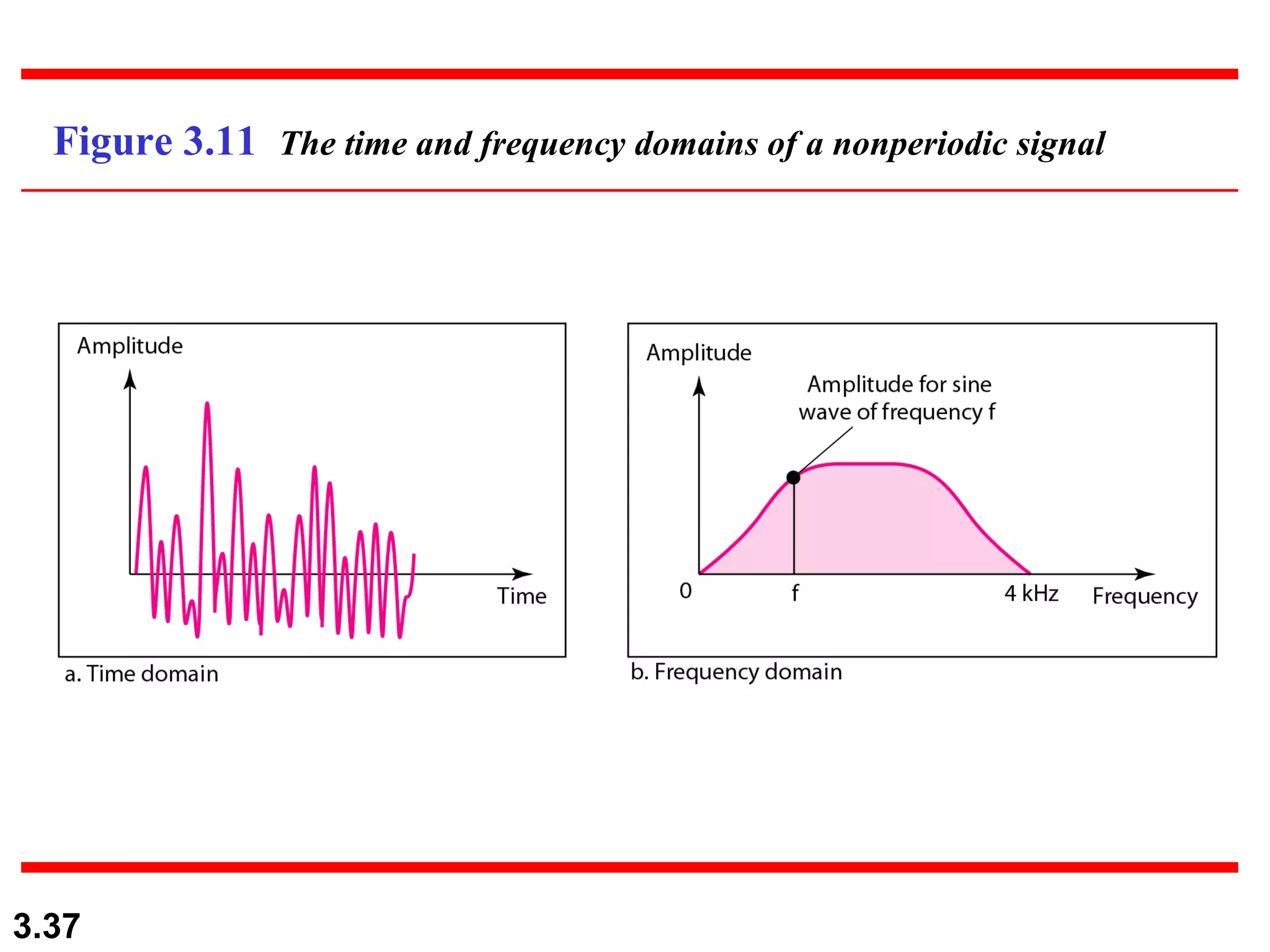
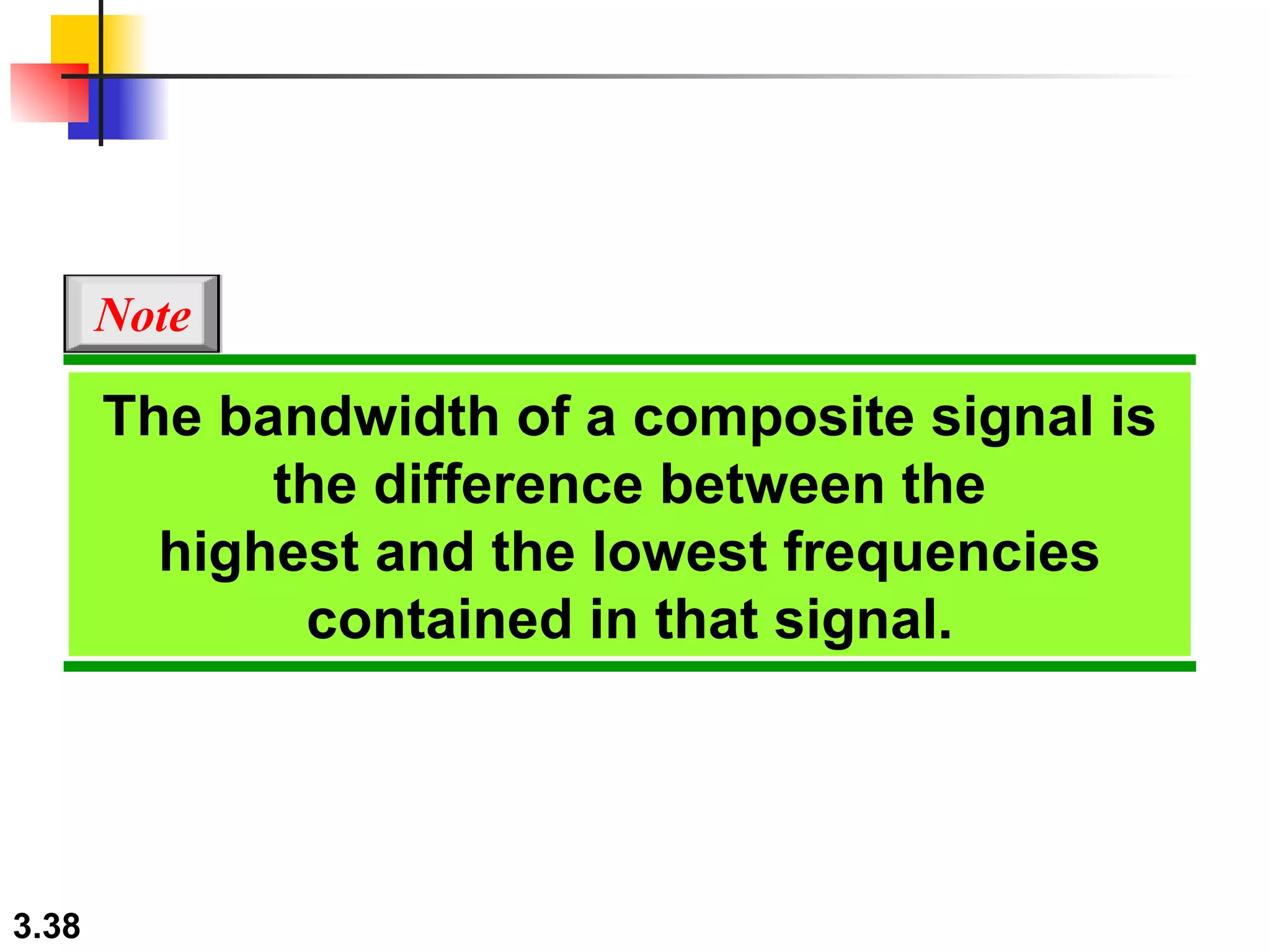
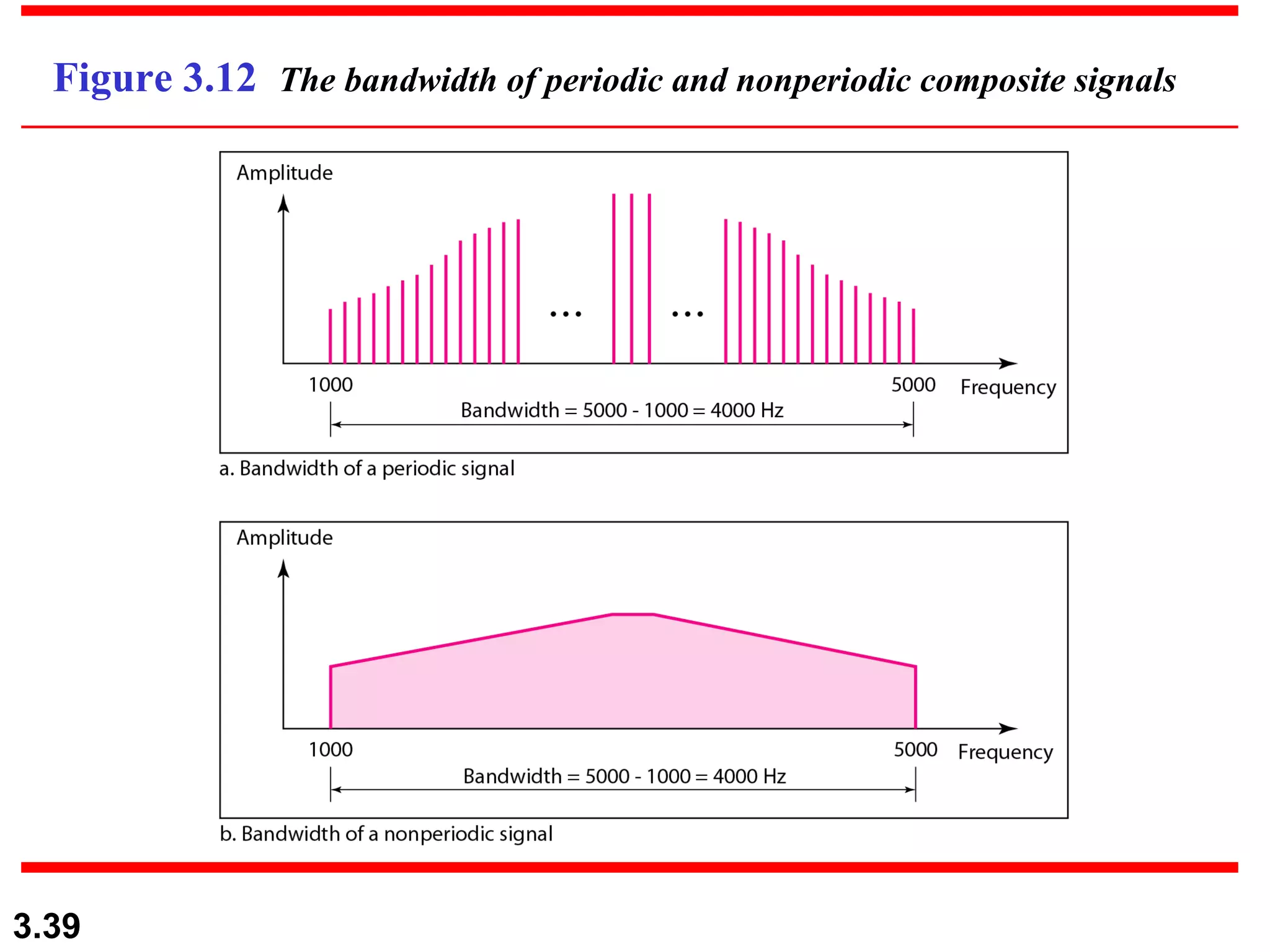
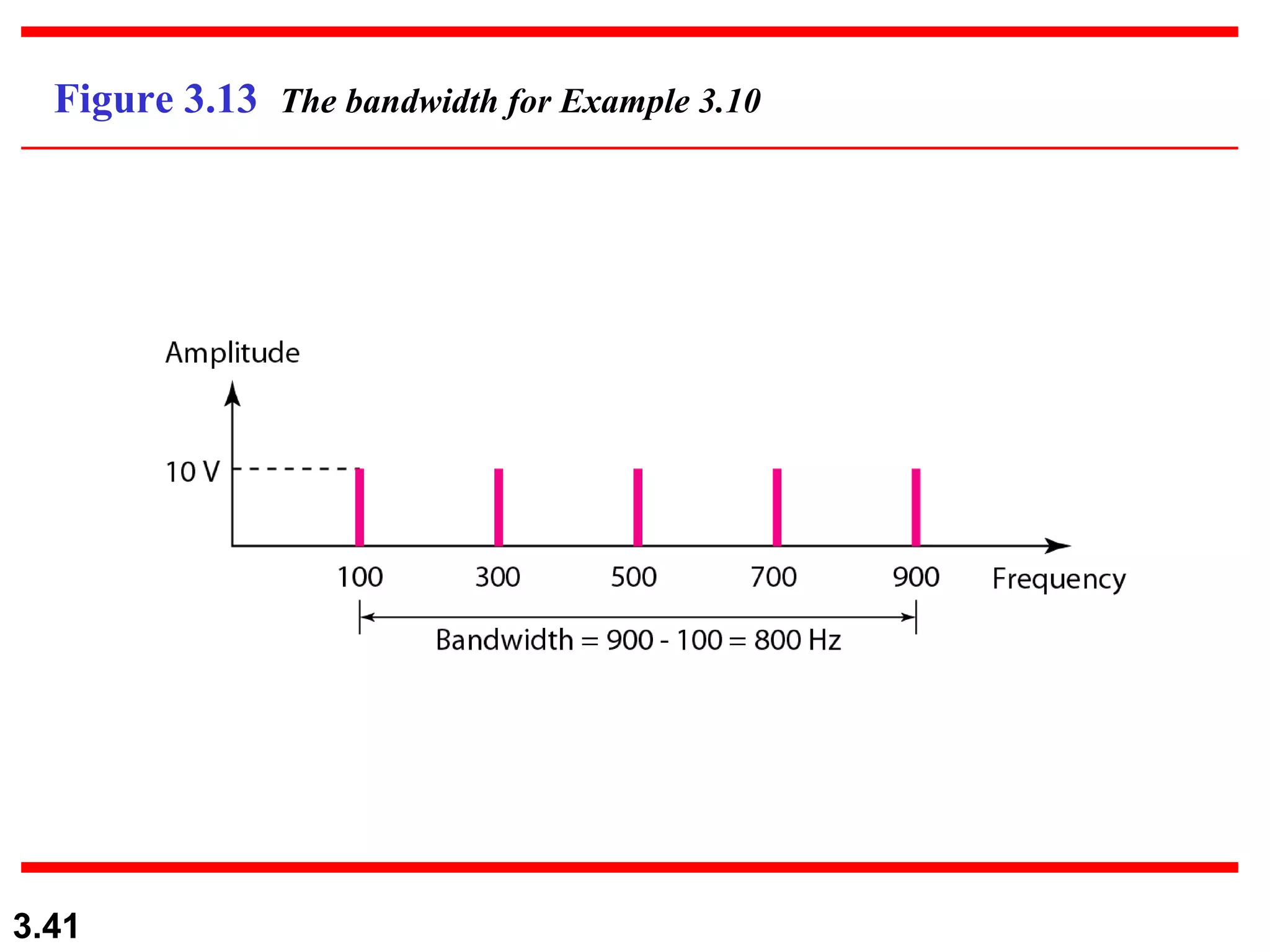
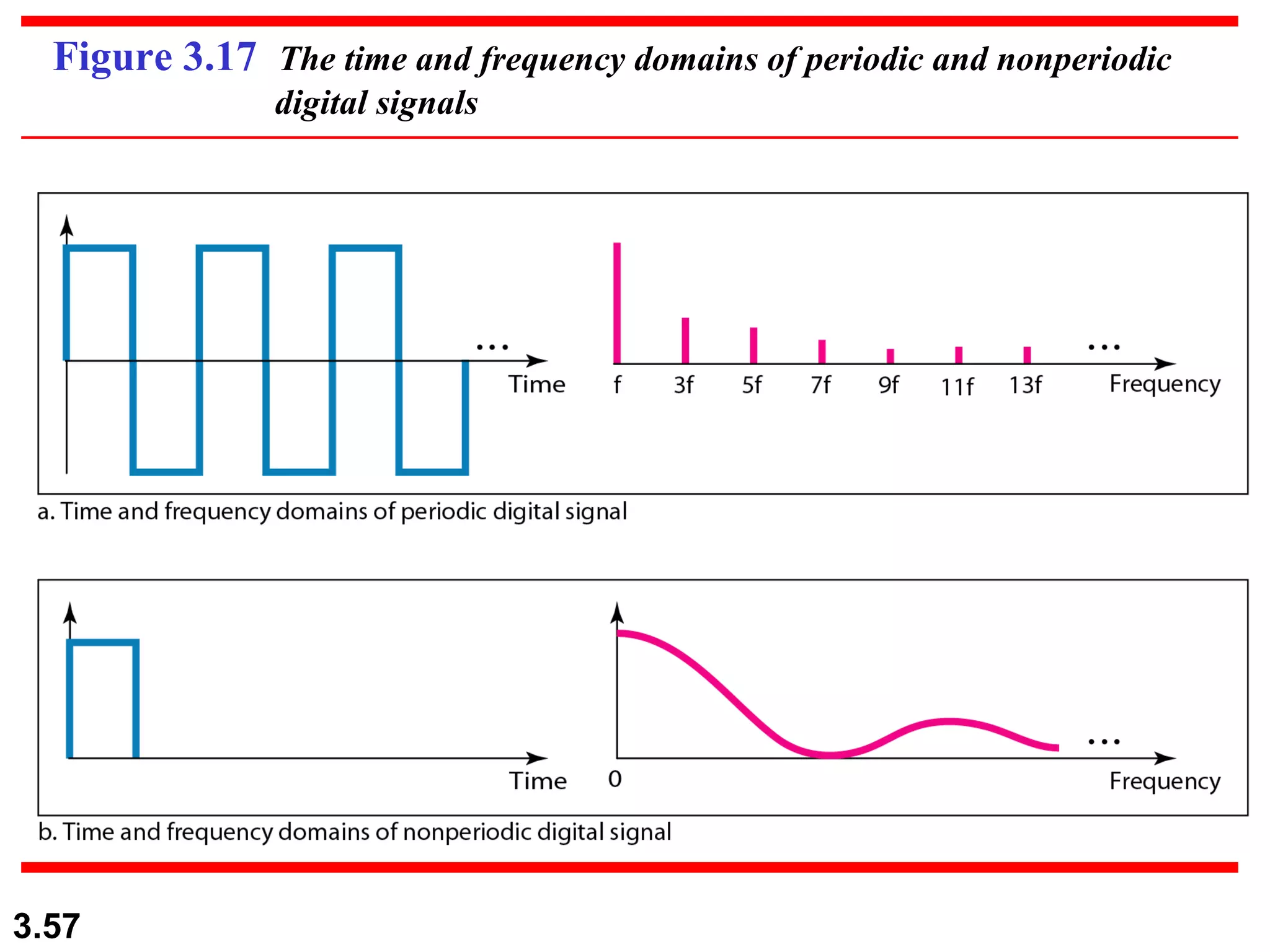
- Periodic analog signals like sine waves can be simple or composite, consisting of multiple sine waves. Nonperiodic signals are commonly used for digital data transmission.
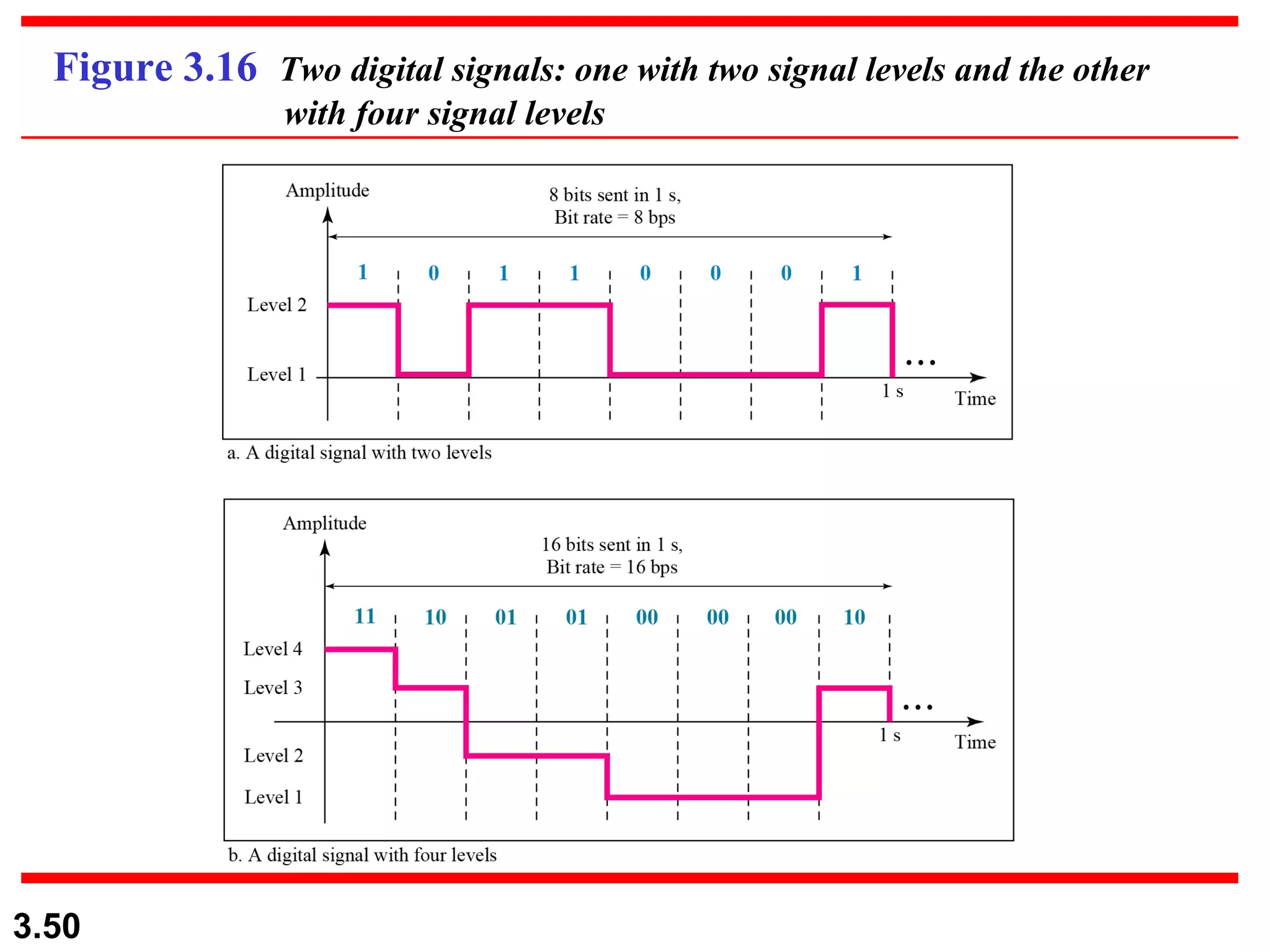
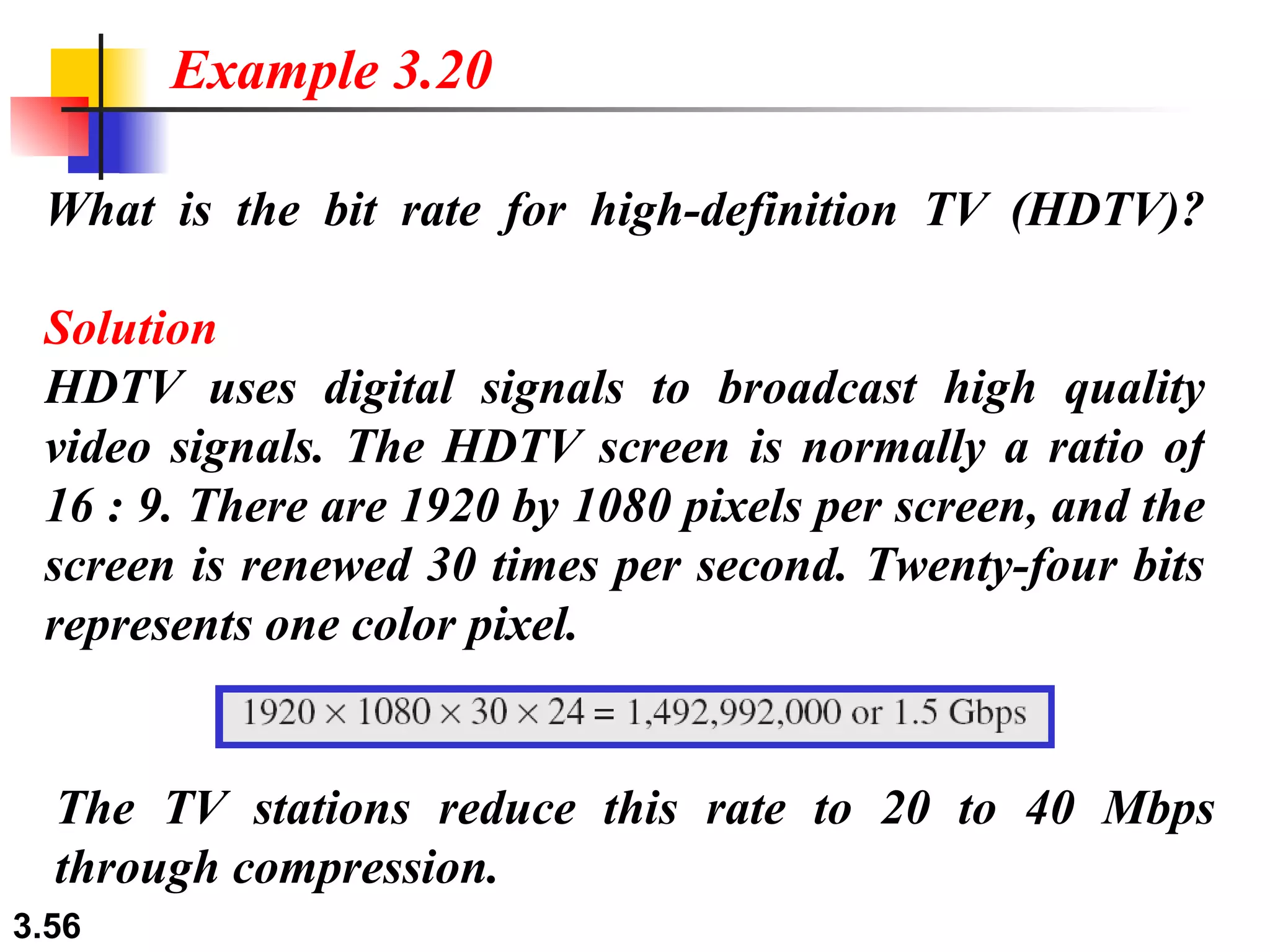
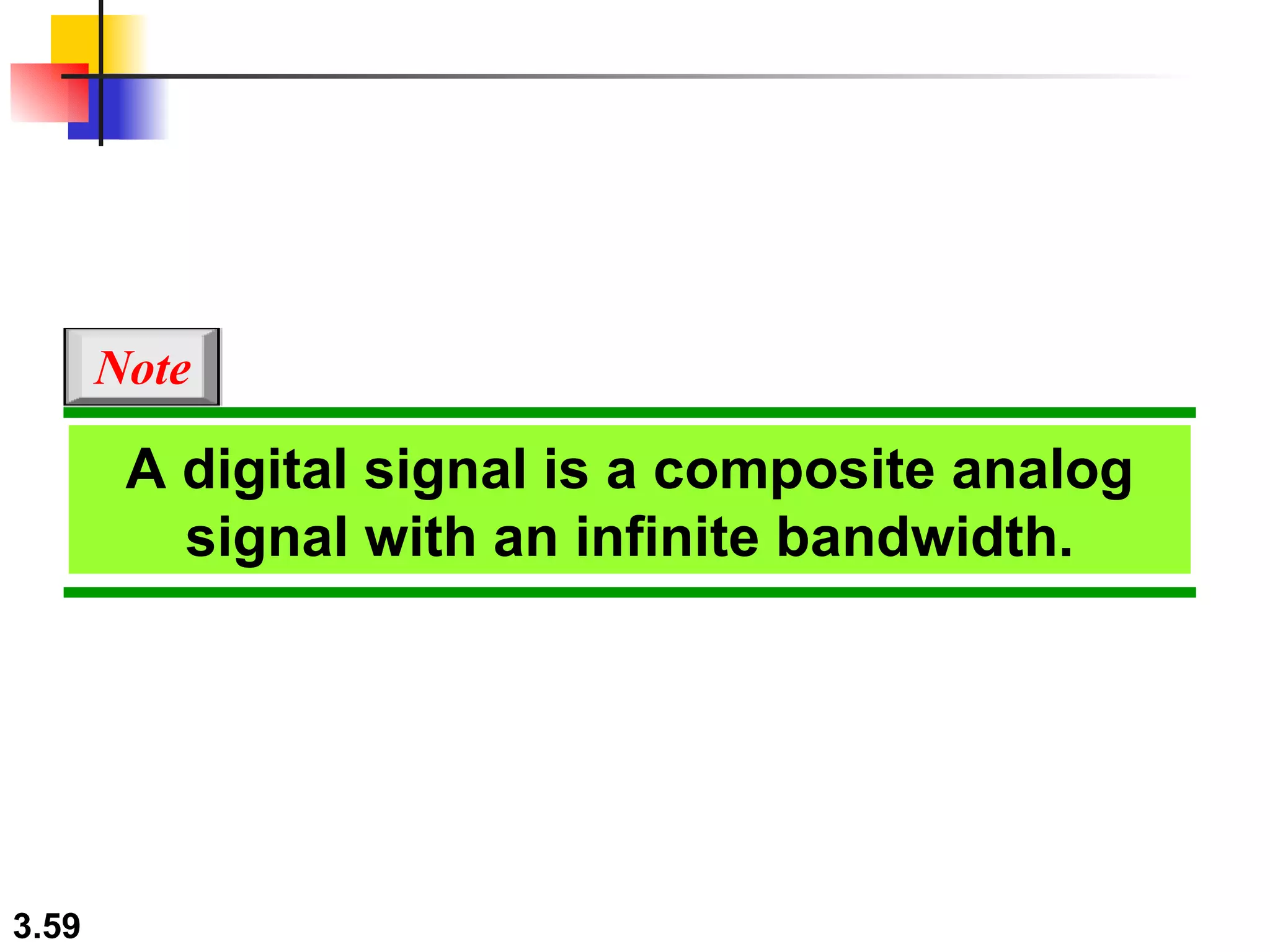
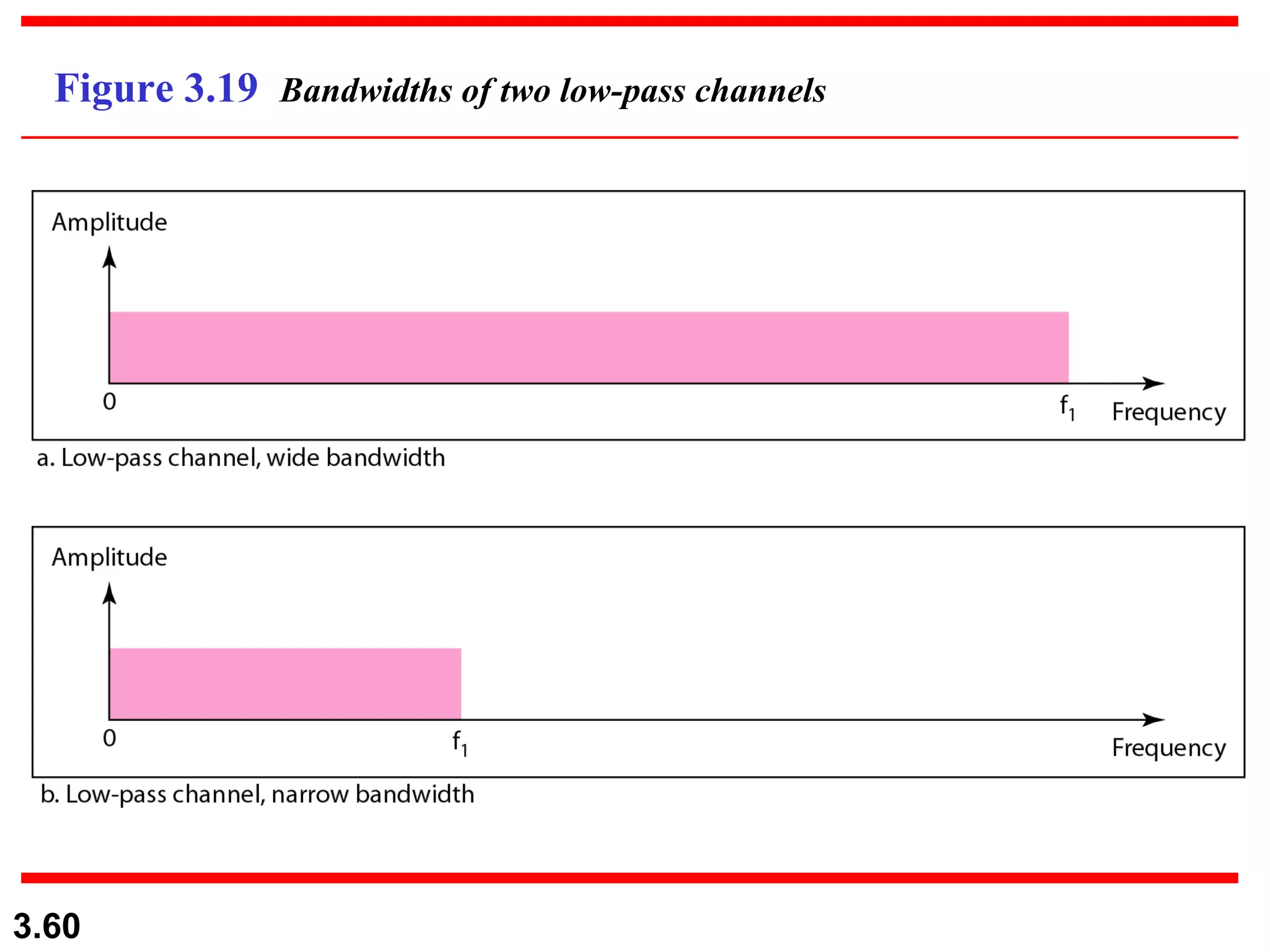
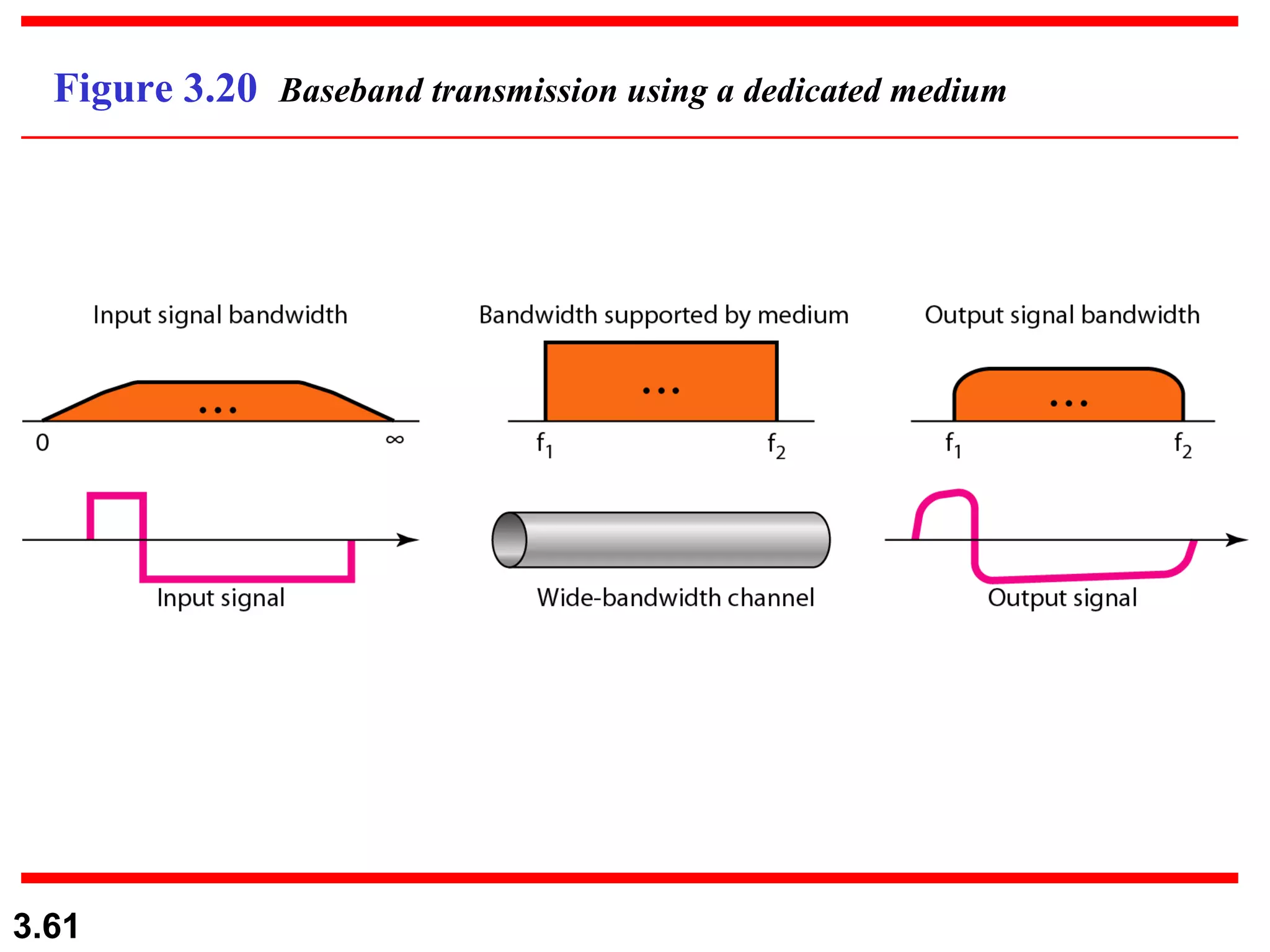
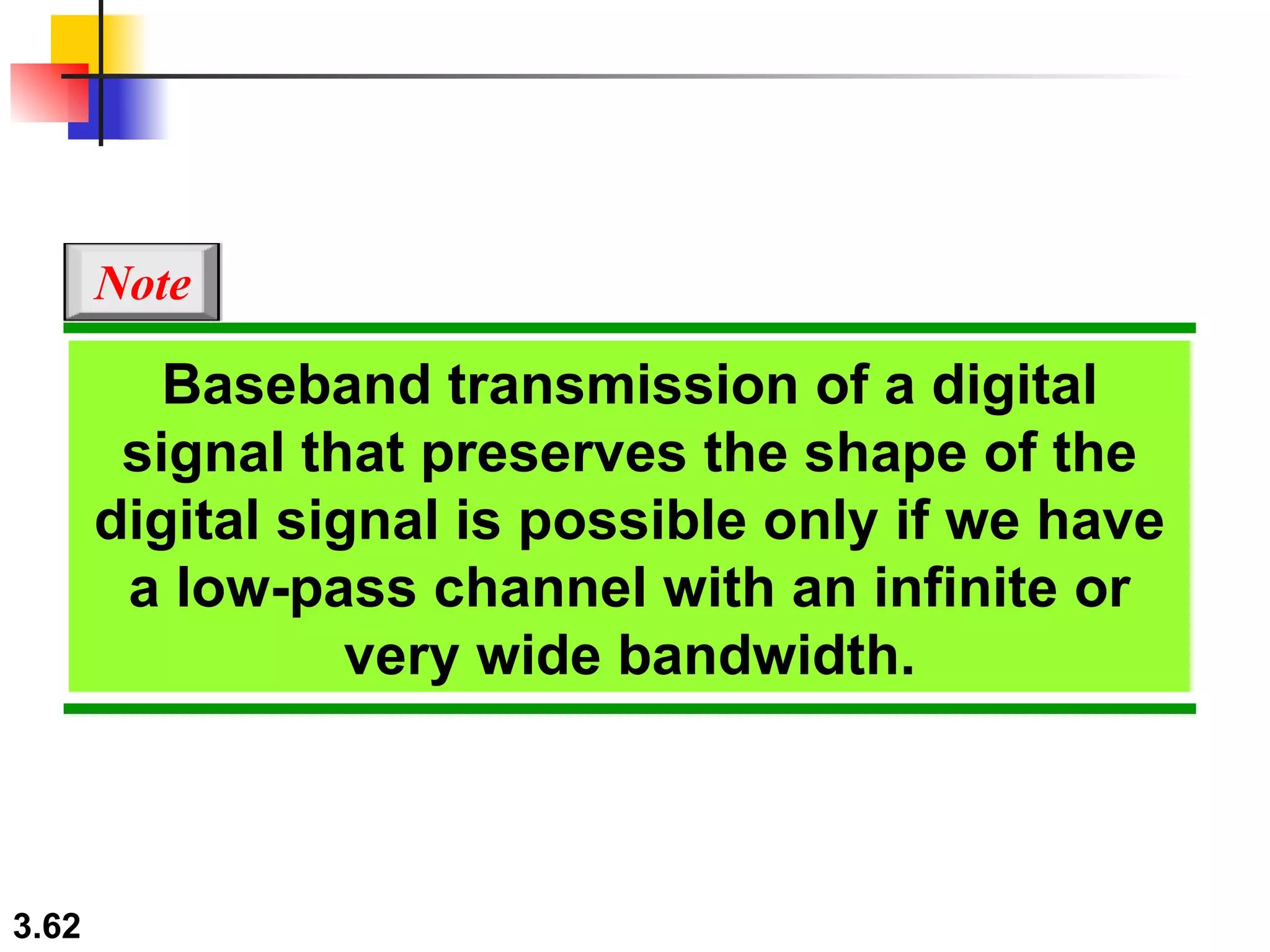
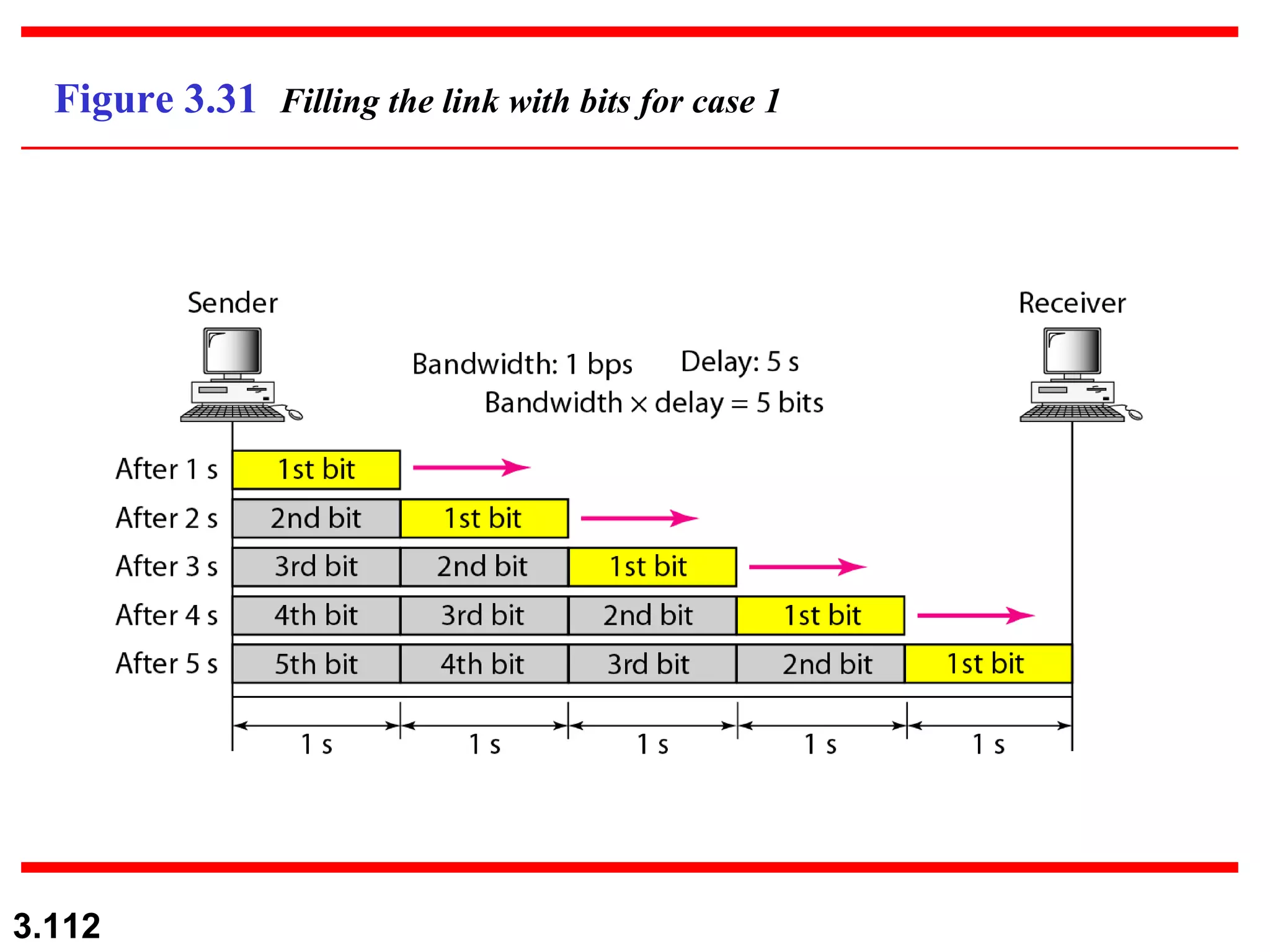
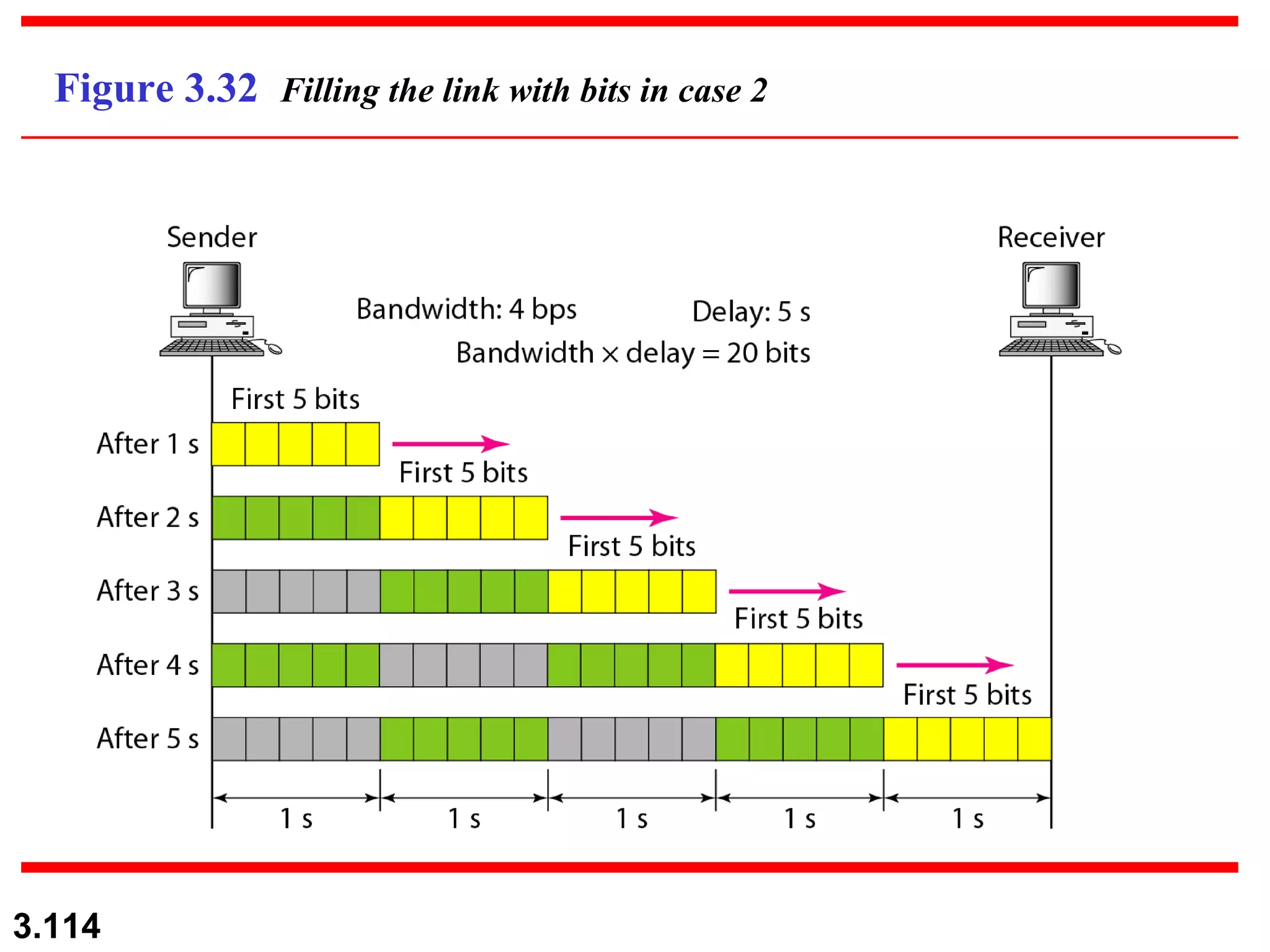
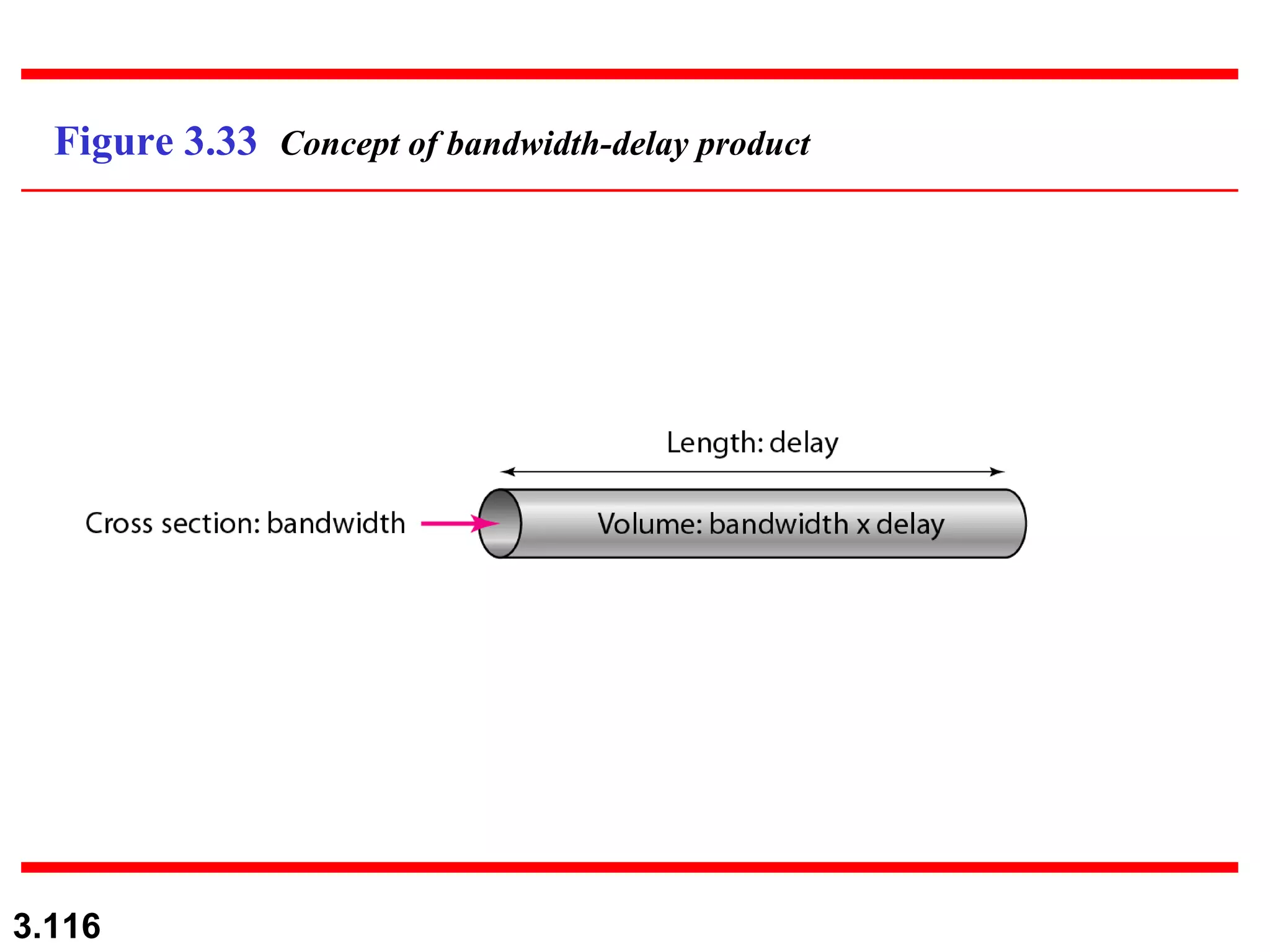
- Digital signals represent information using discrete signal levels that can be encoded as voltages, with more levels allowing more bits to be sent per signal. The required bit rate depends on the data transmission rate and number of bits used per sample or character.