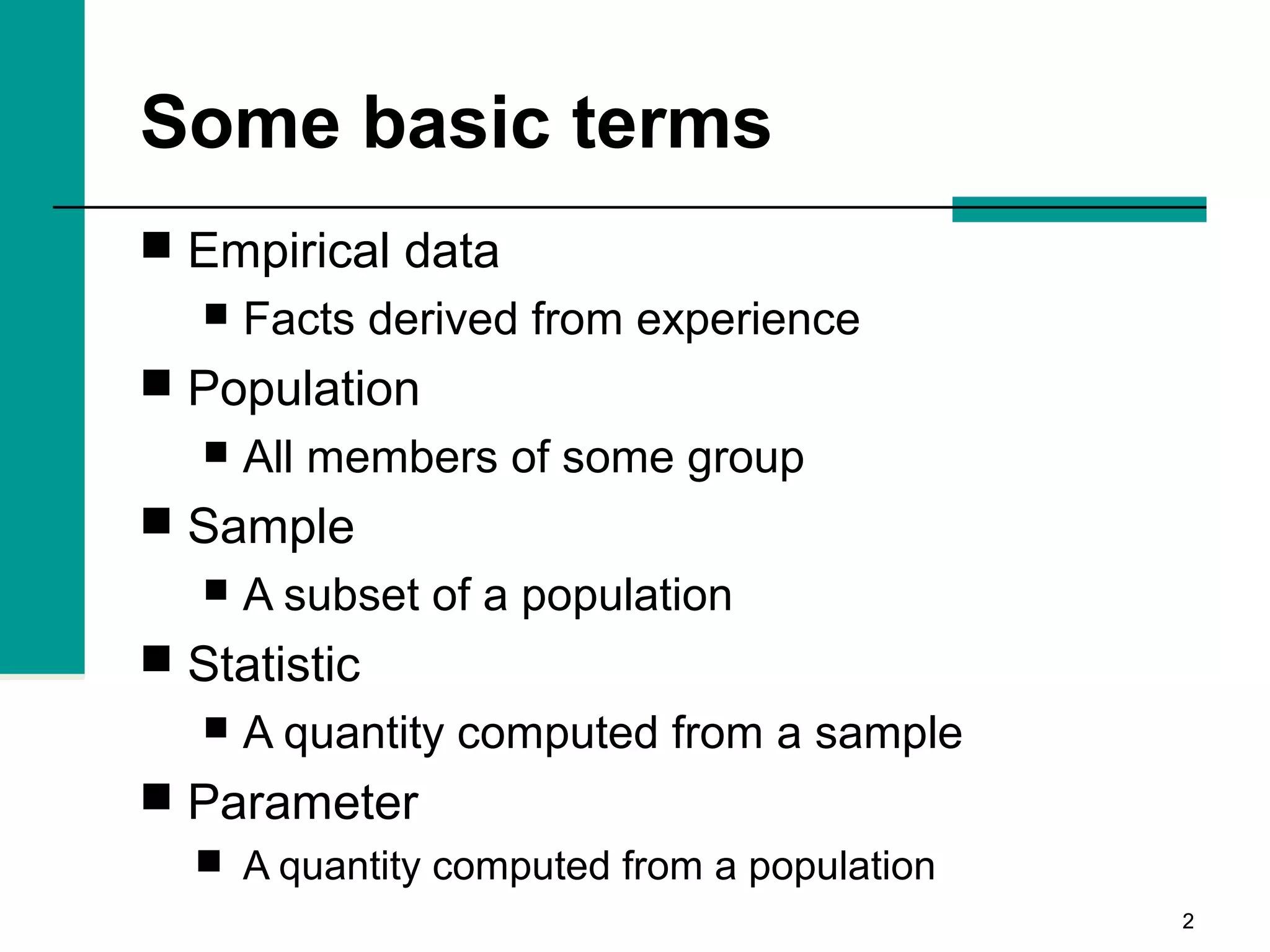
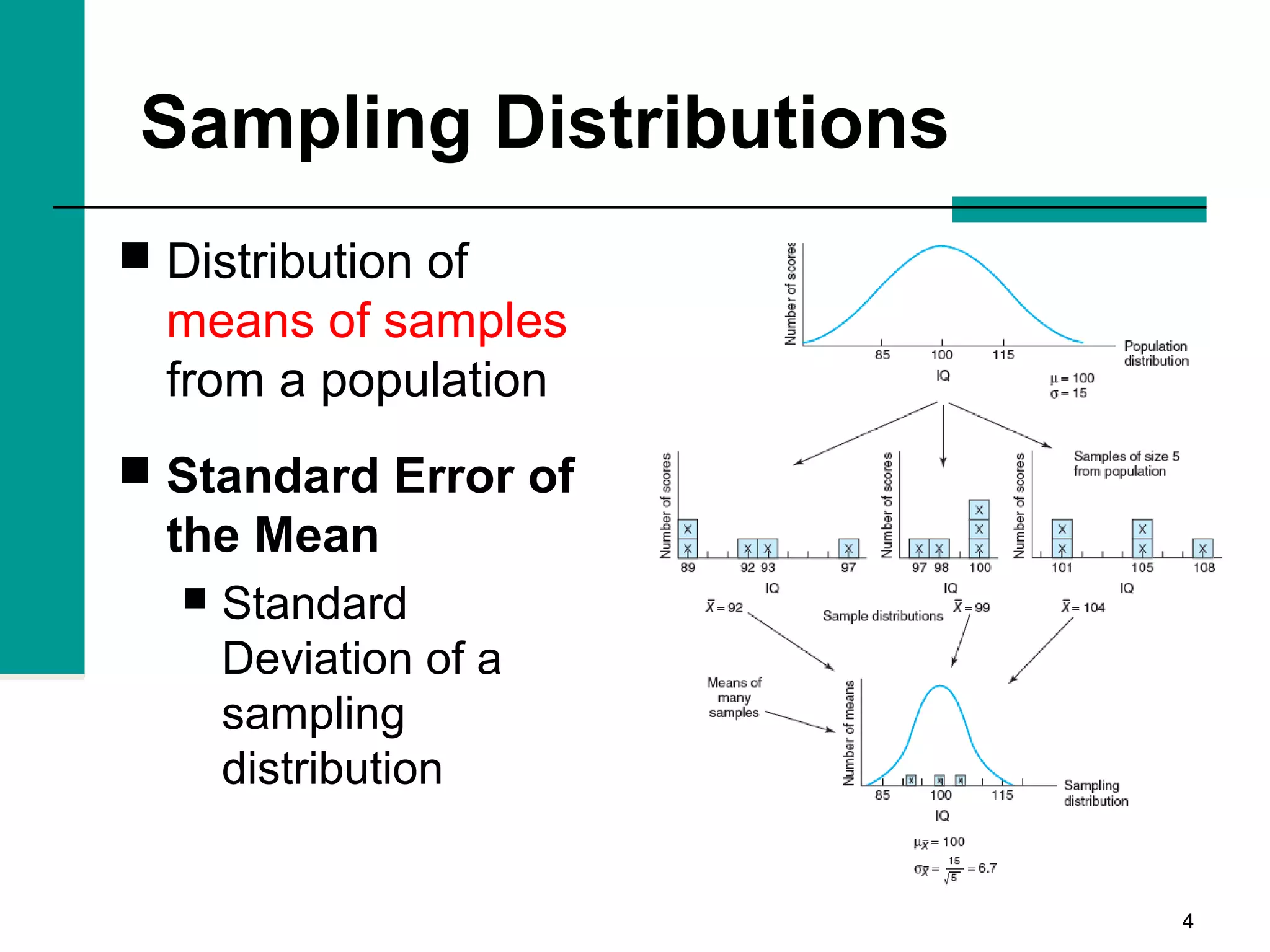
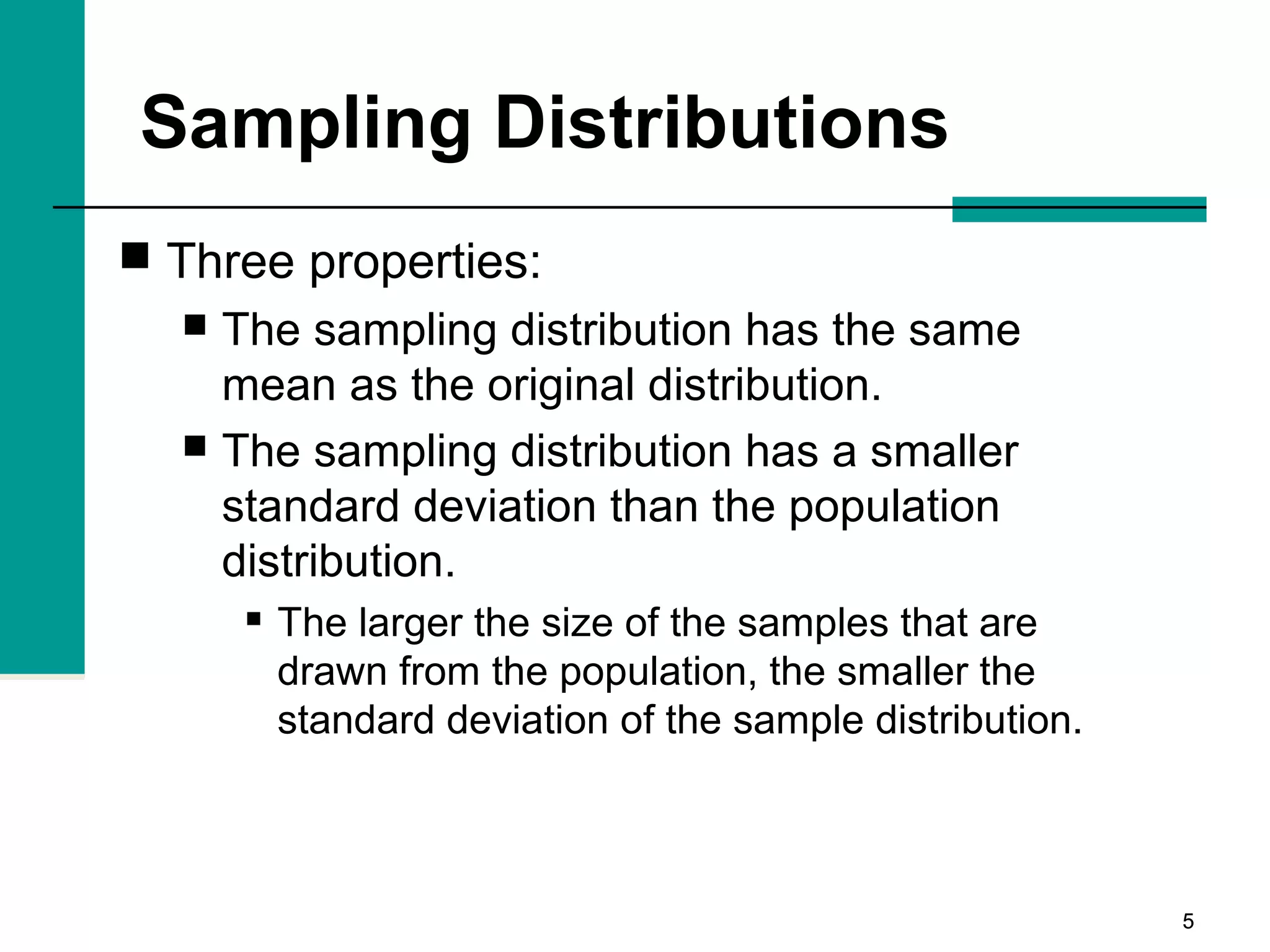
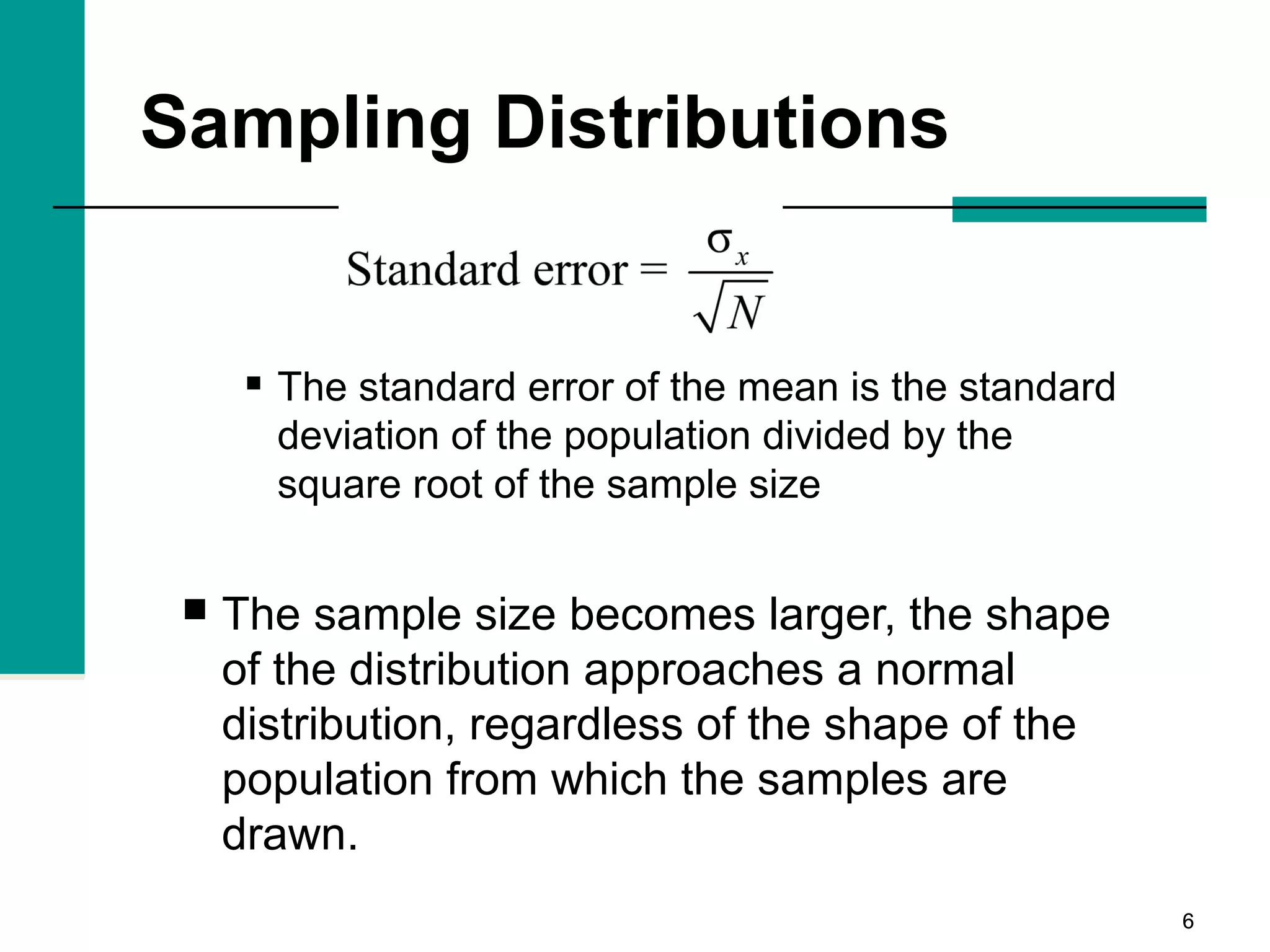
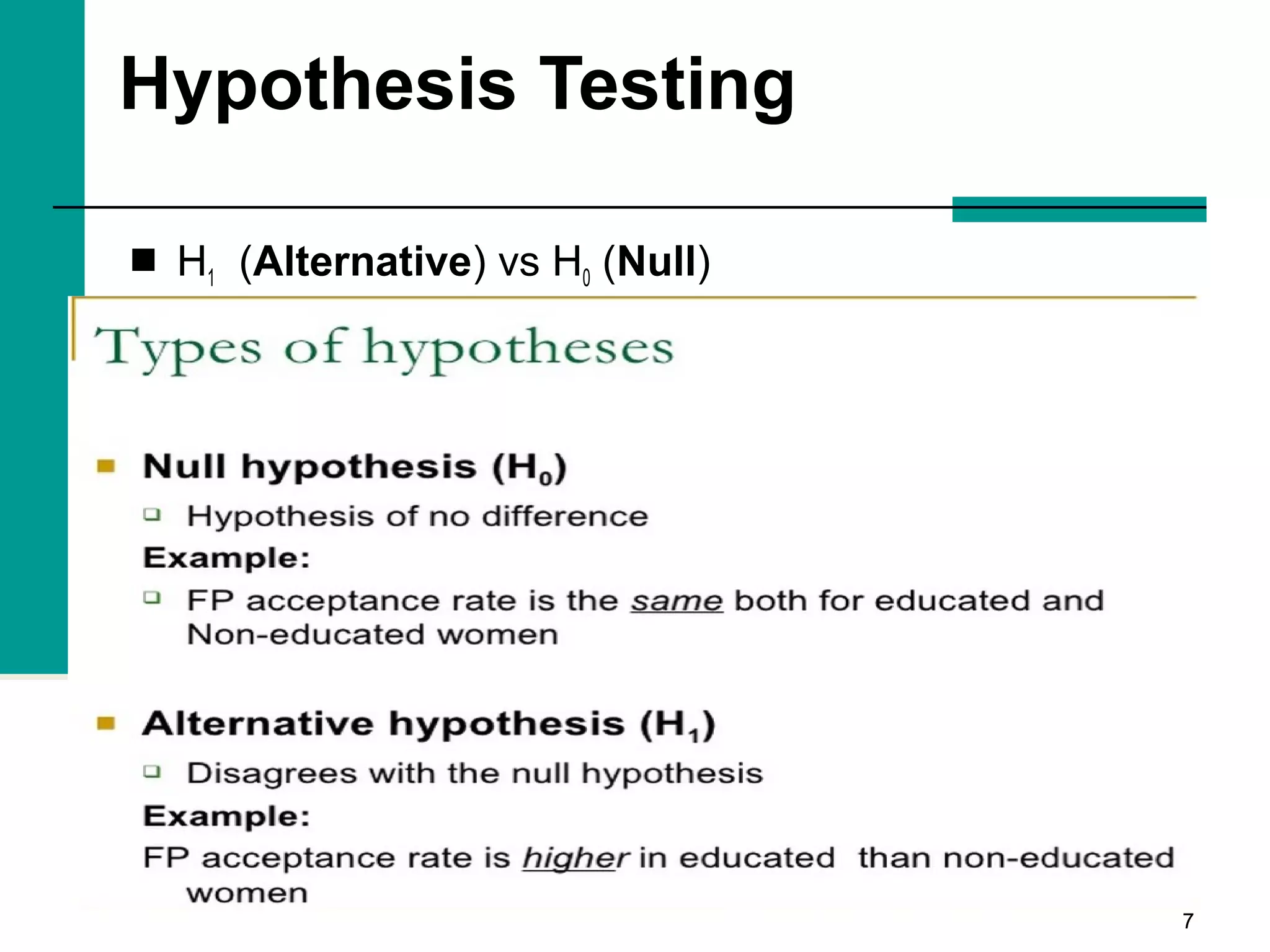
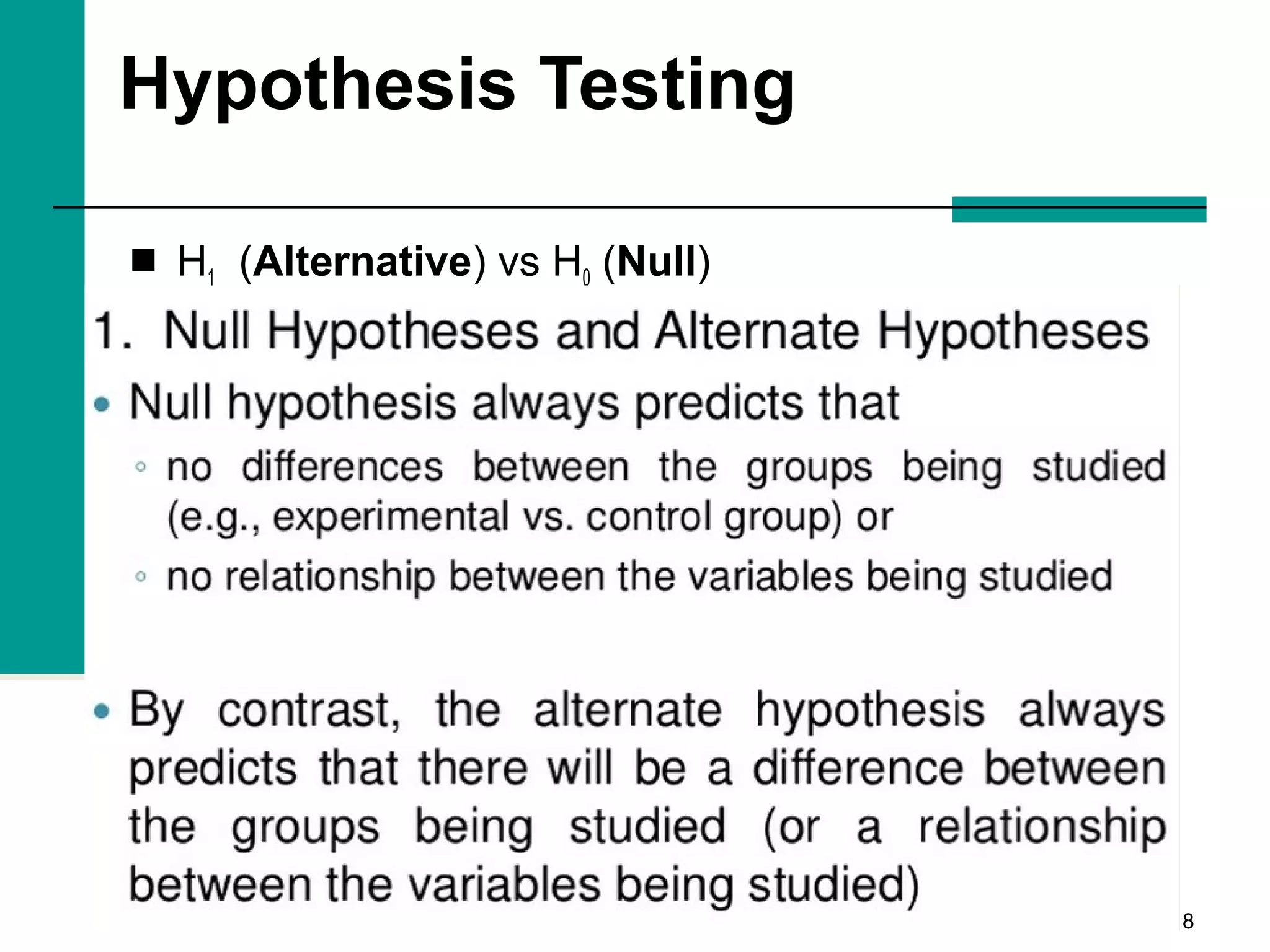
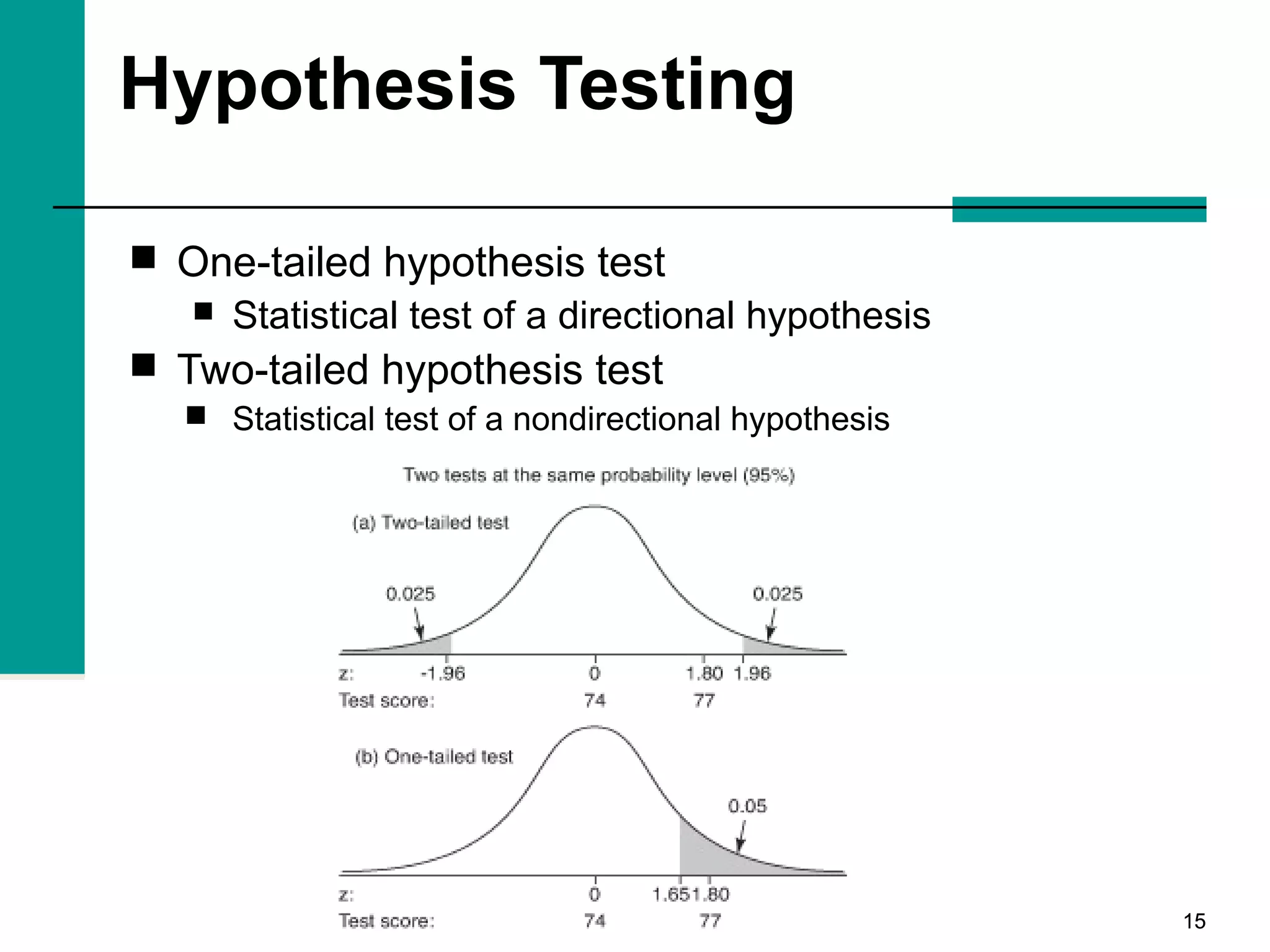
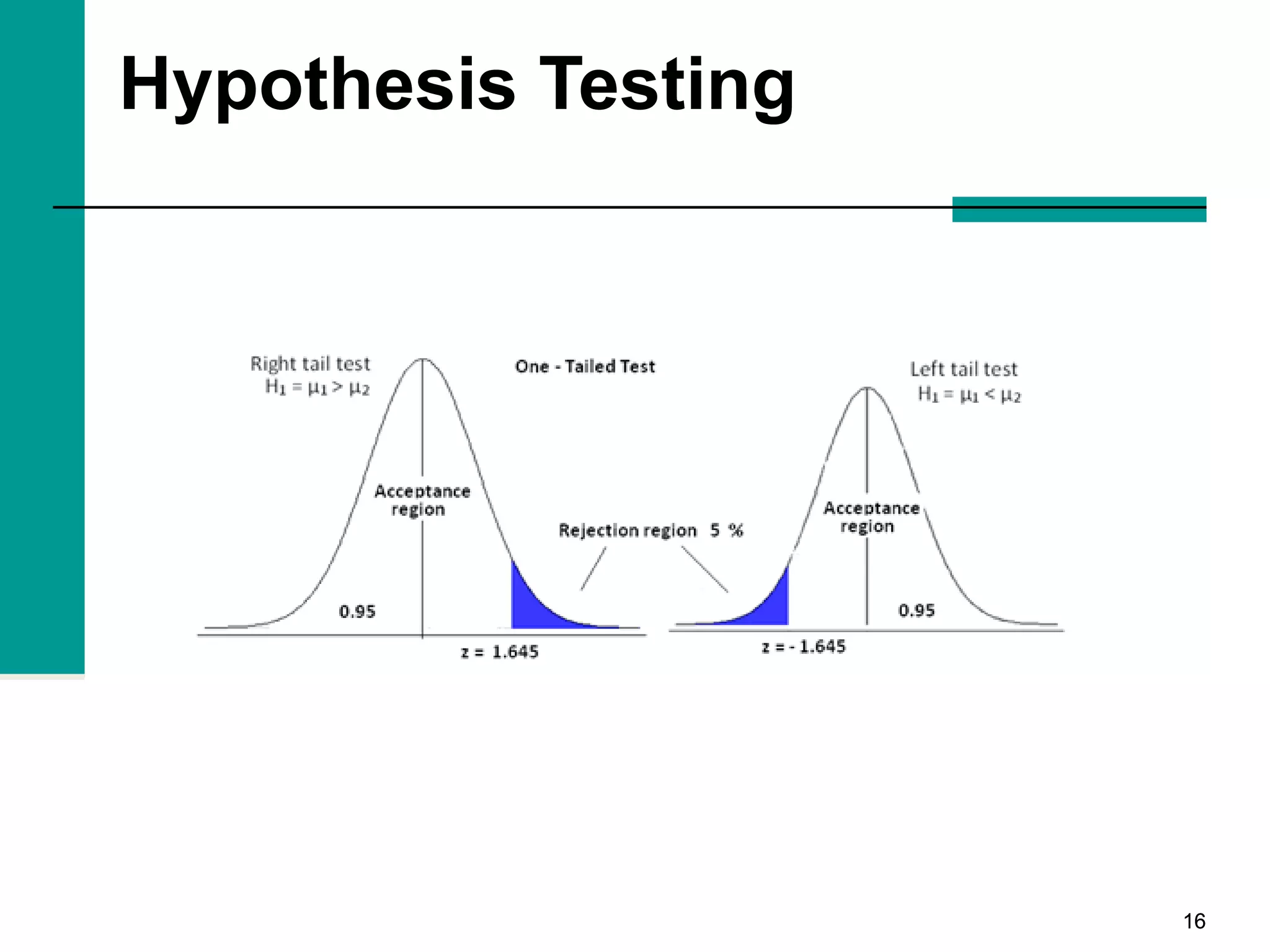
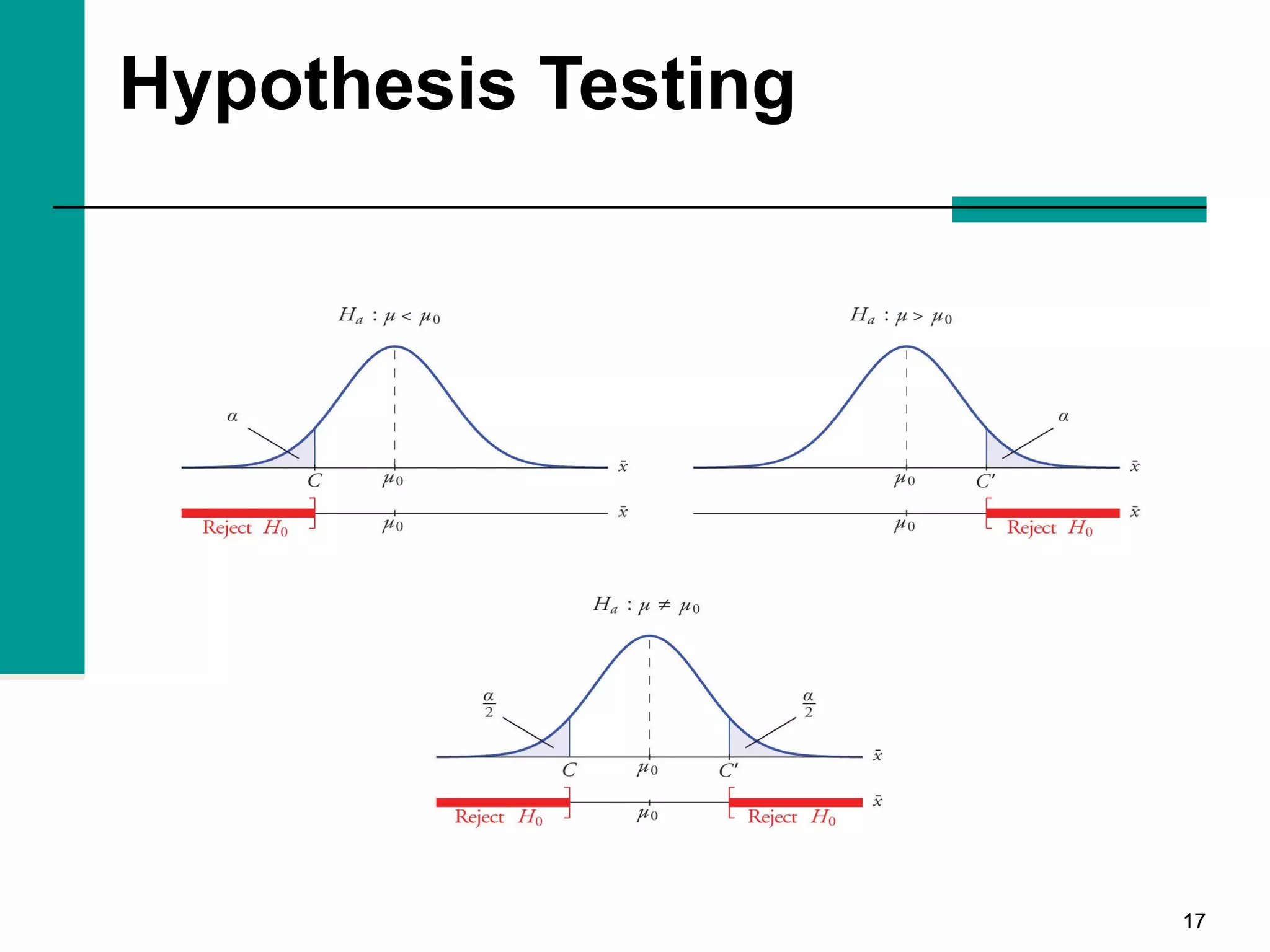
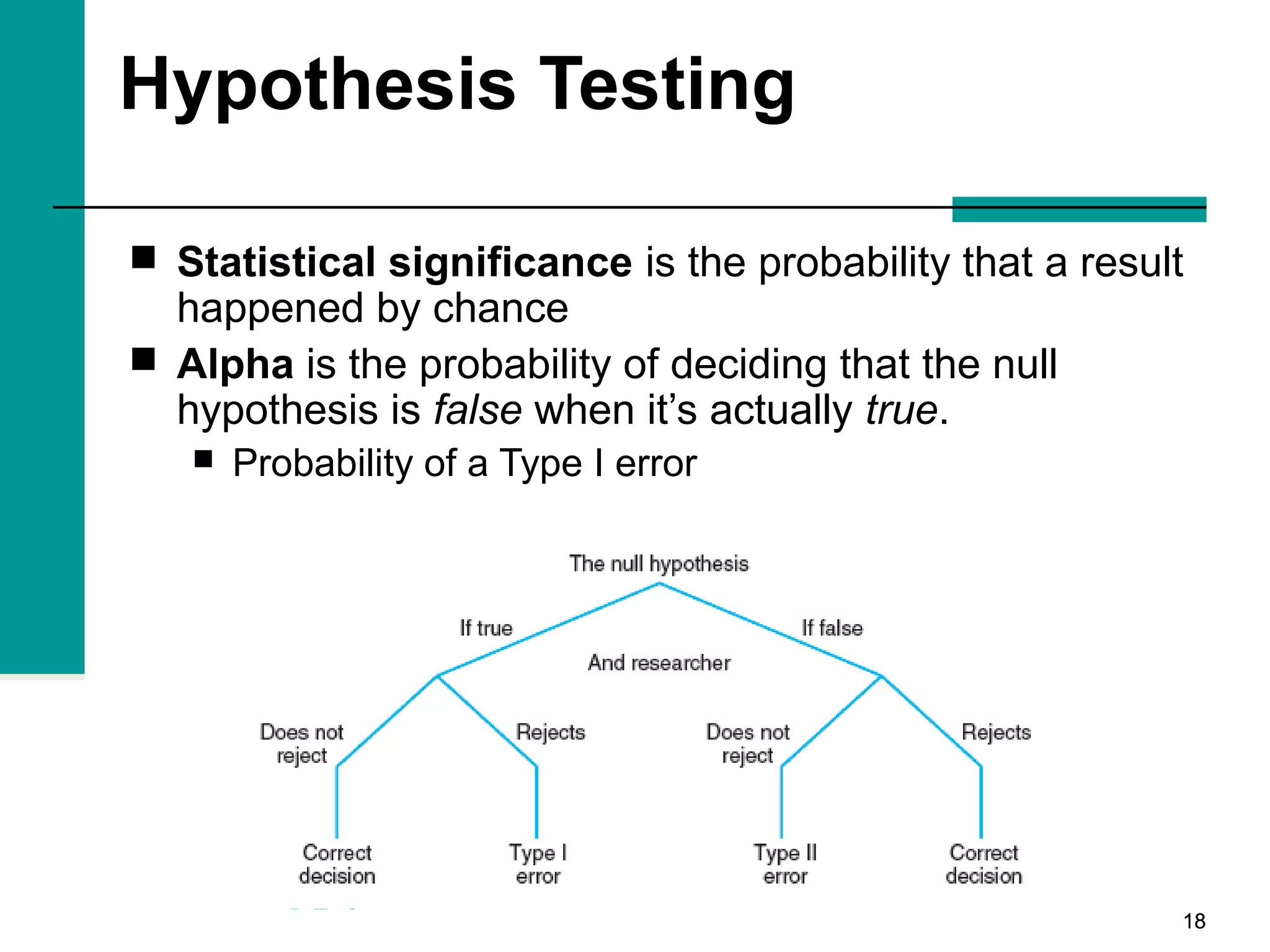
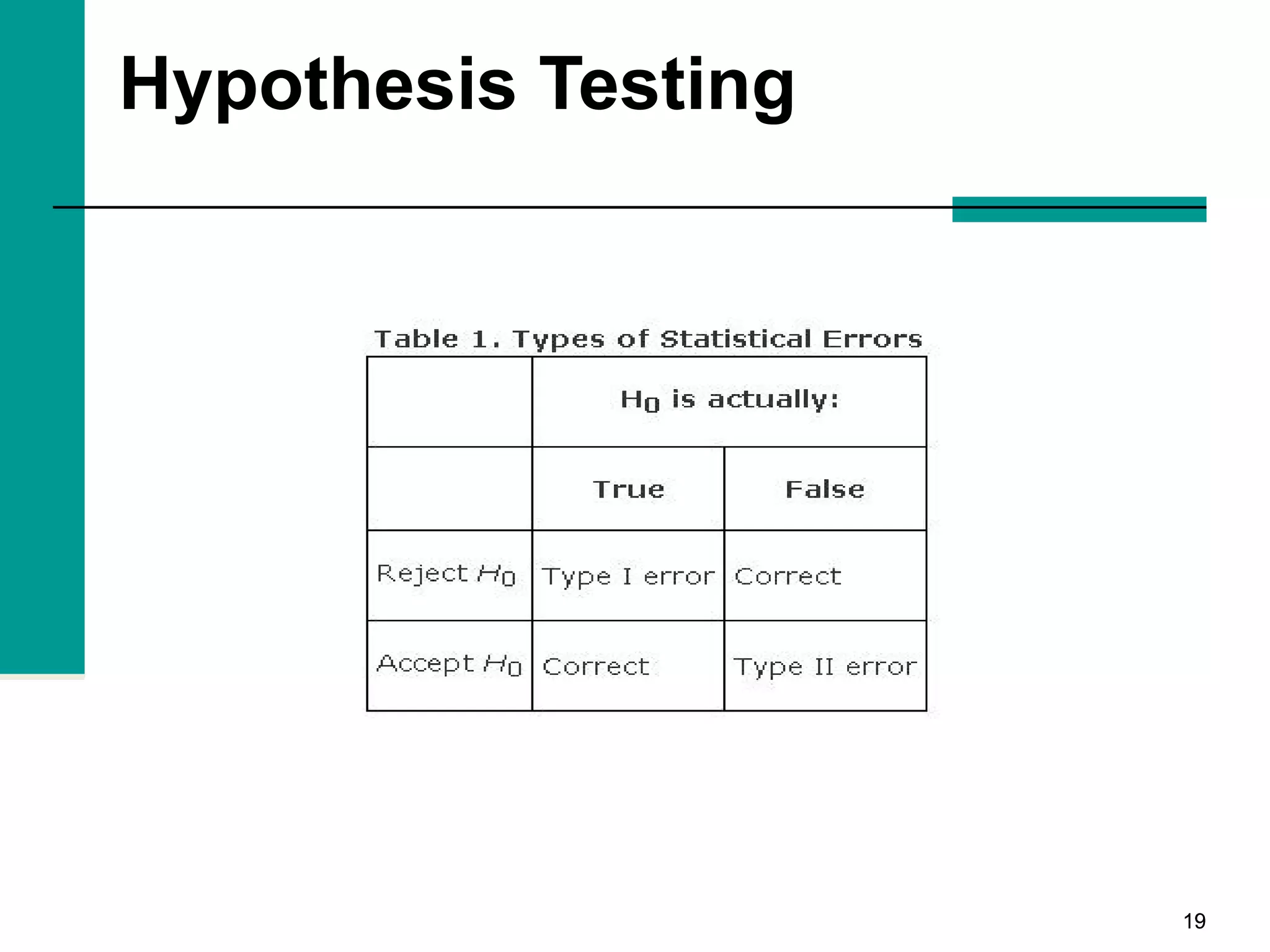
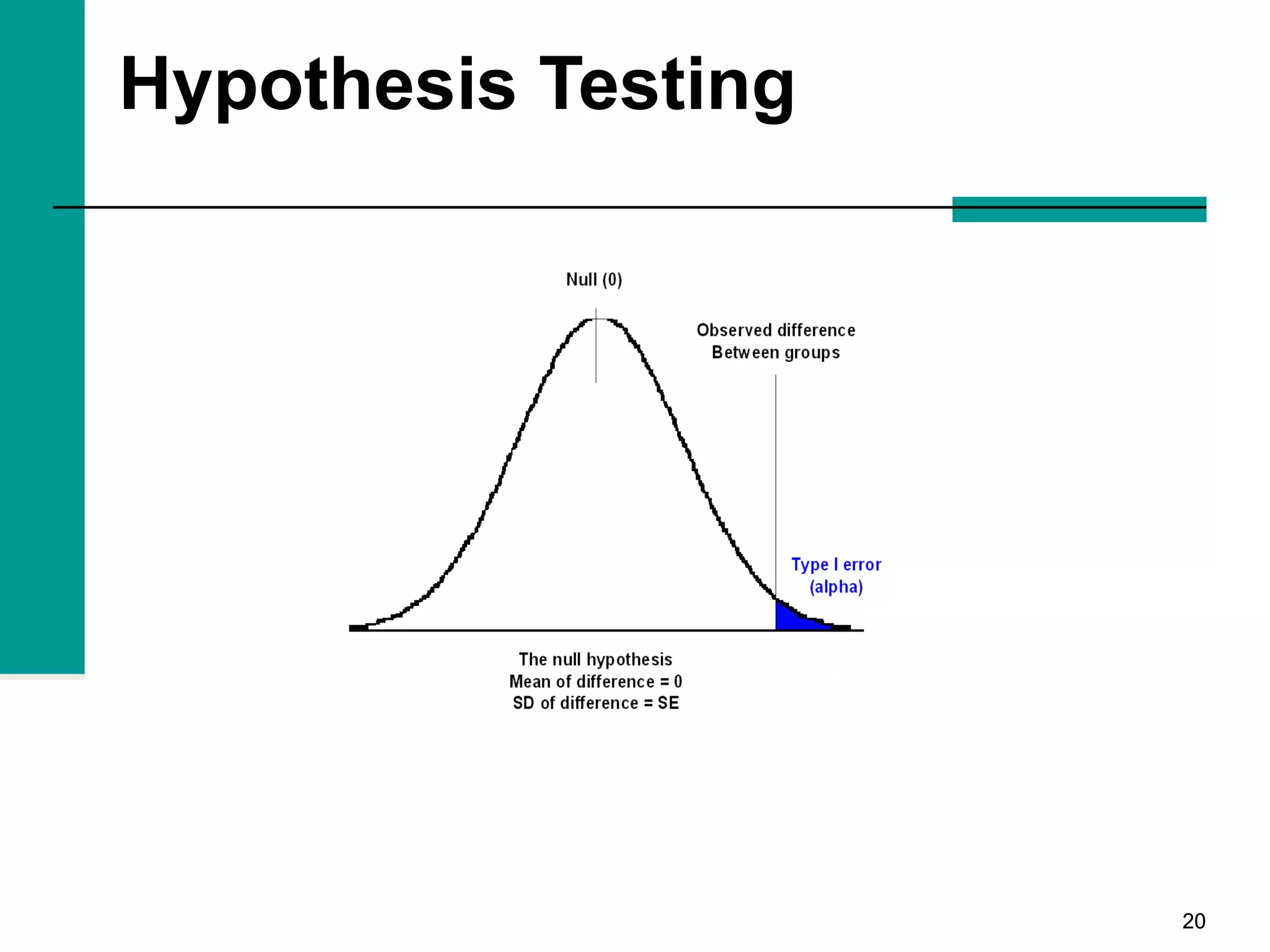
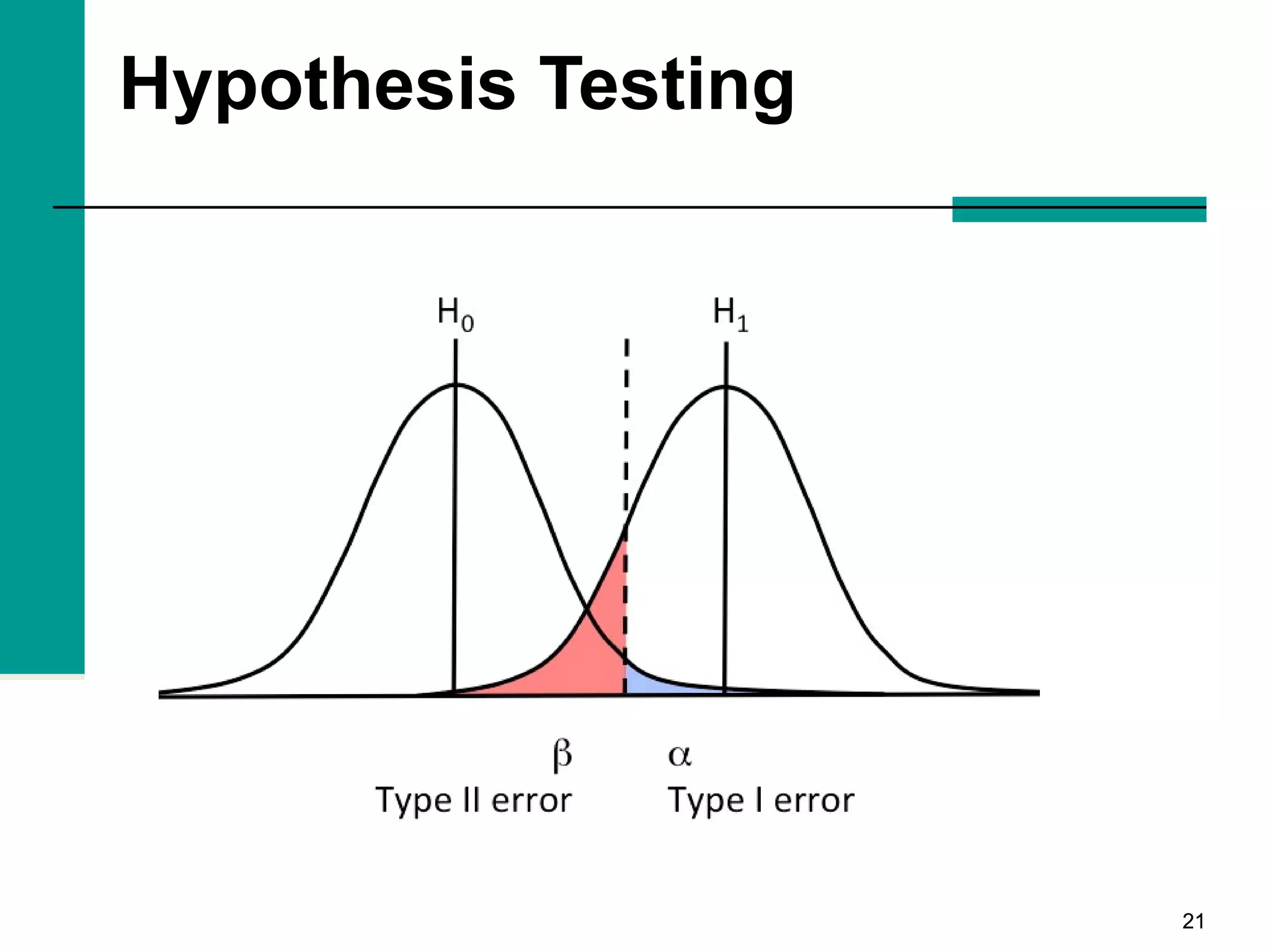
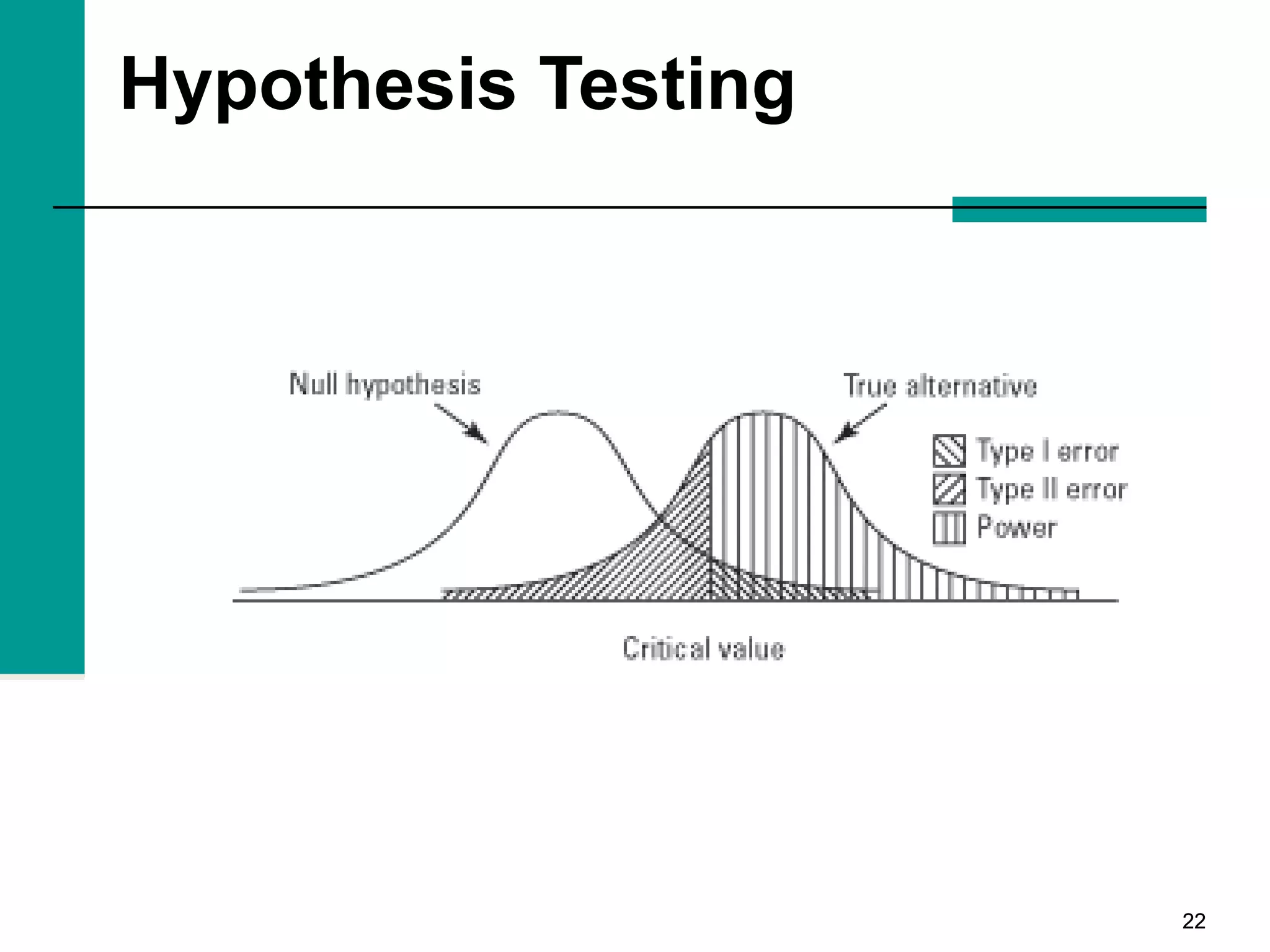
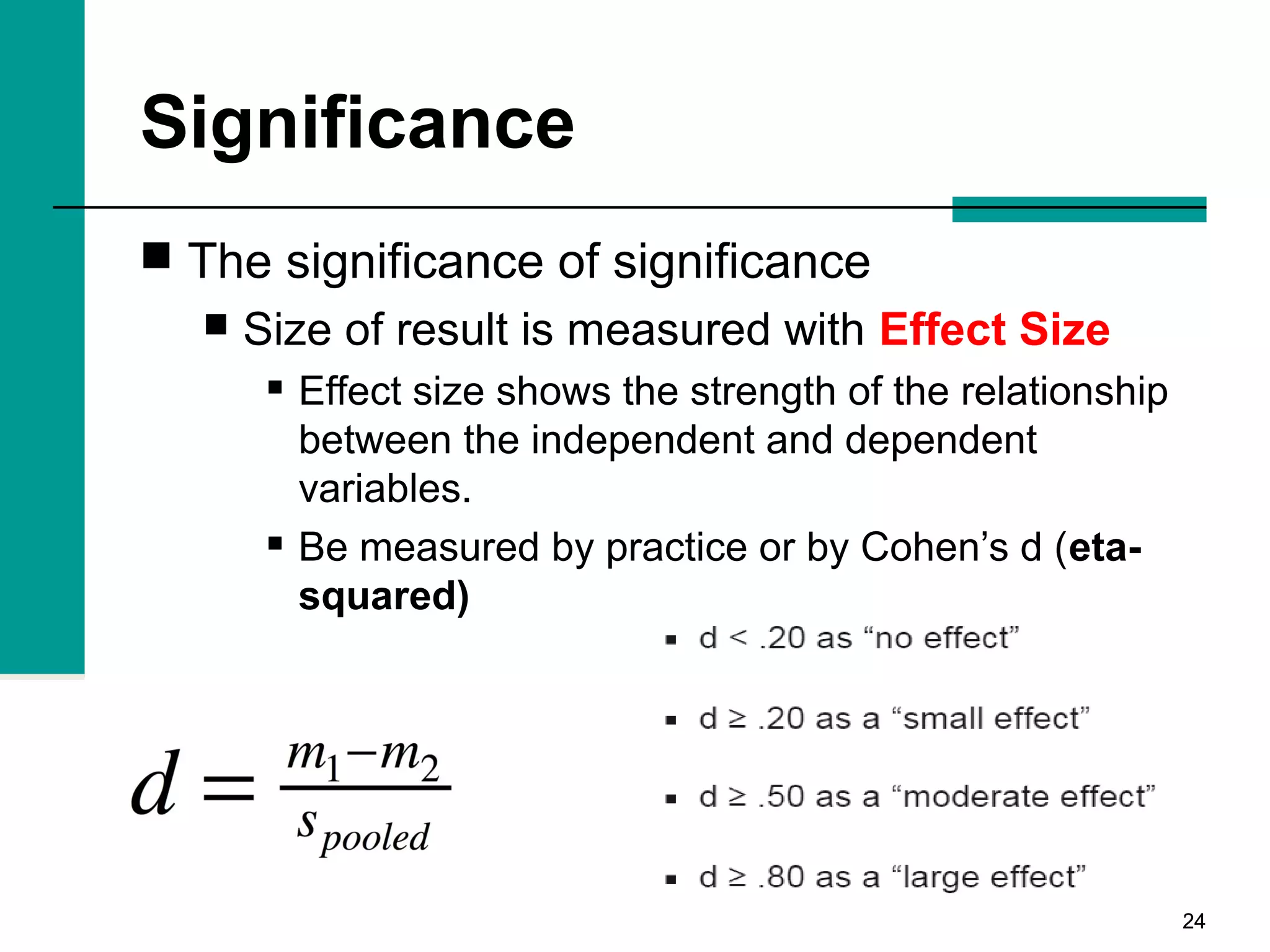
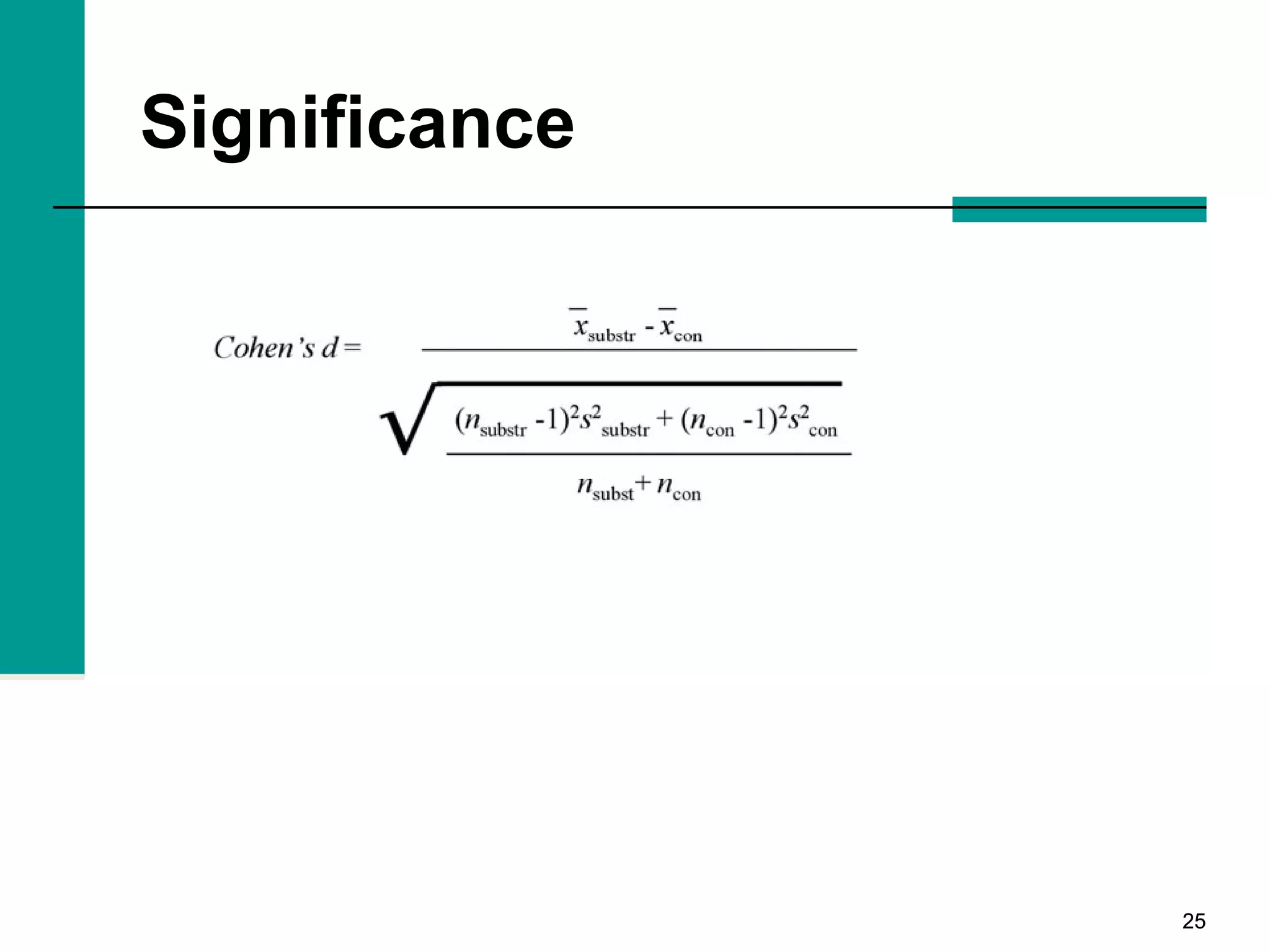
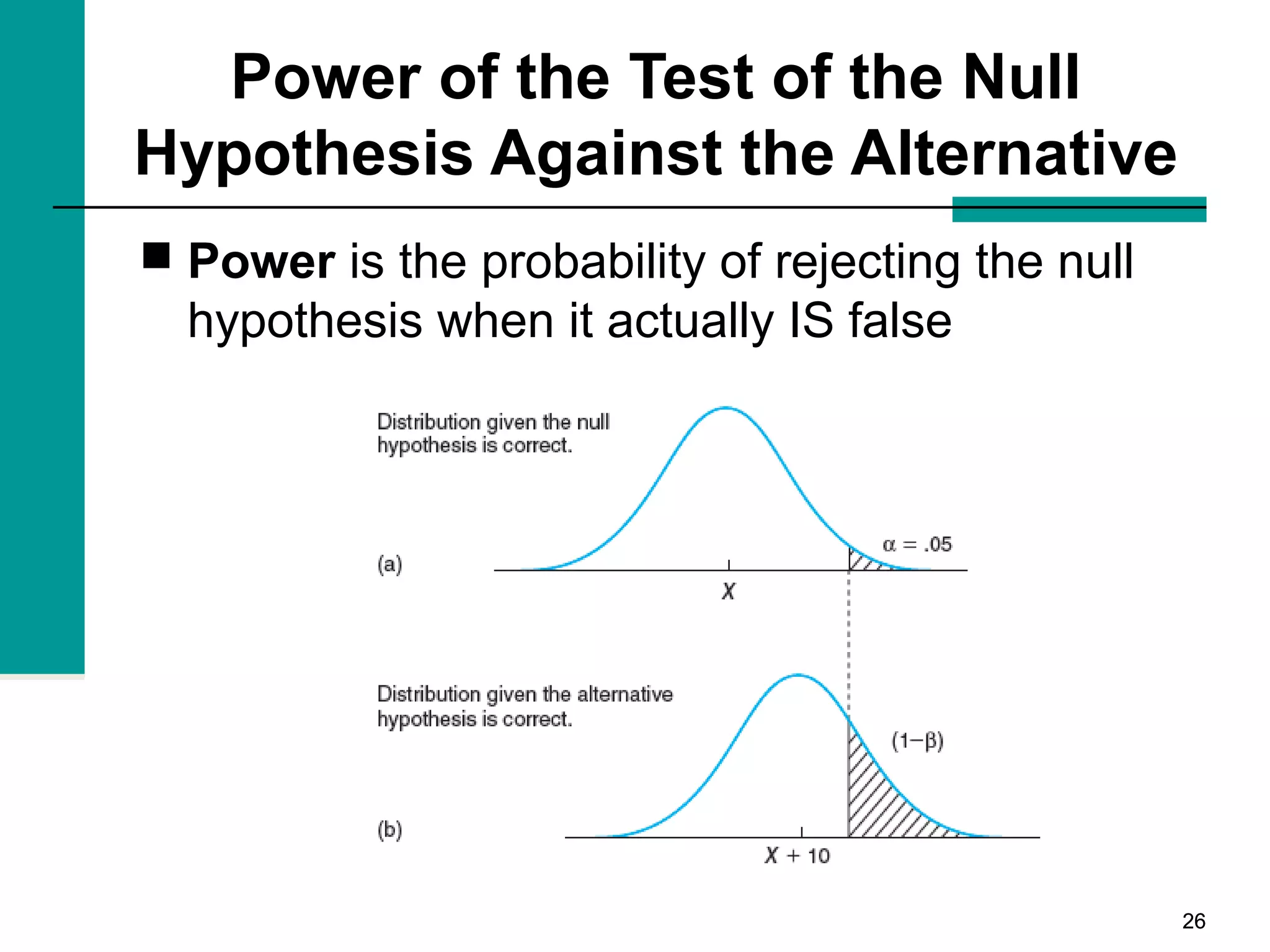
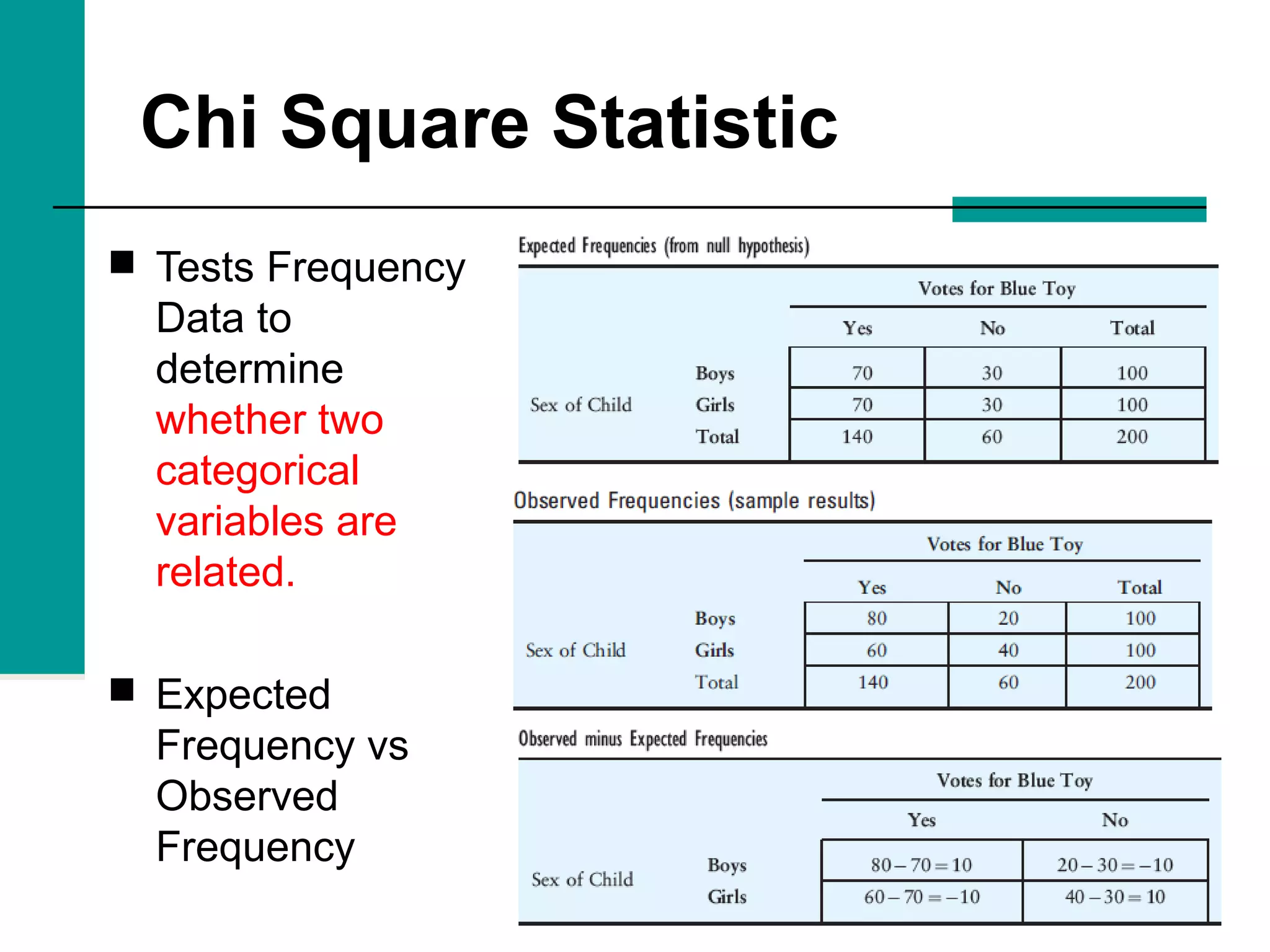
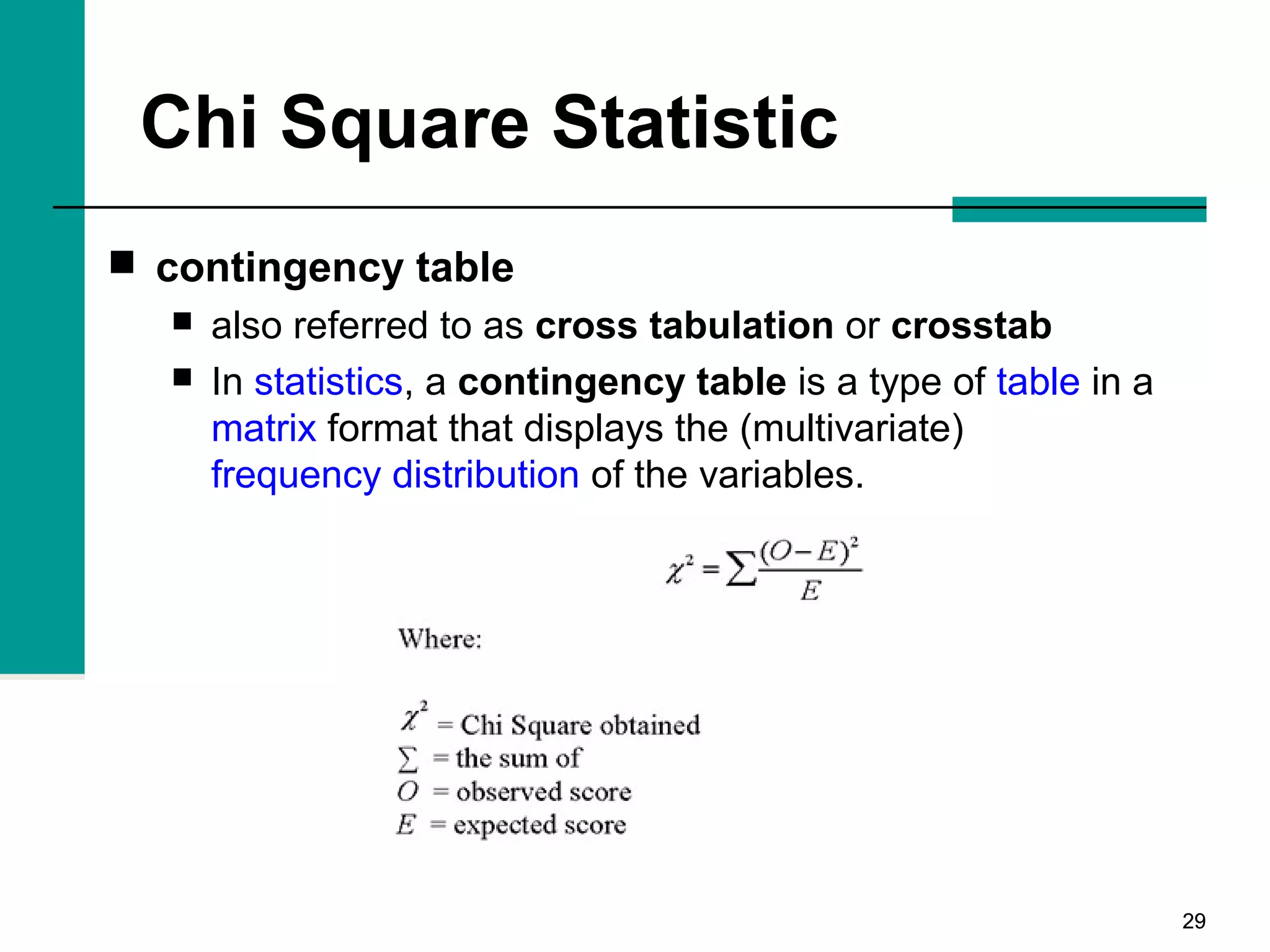
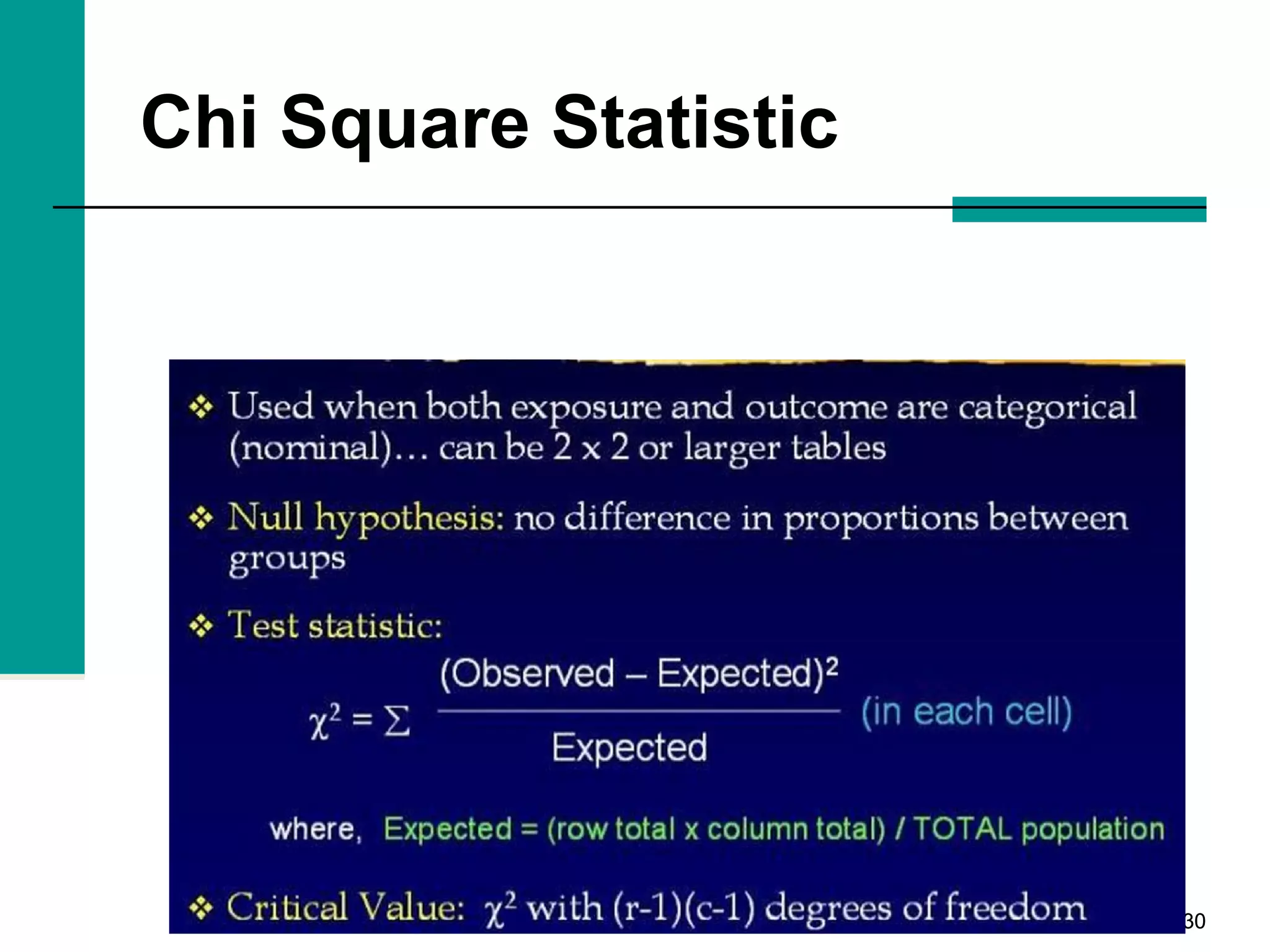
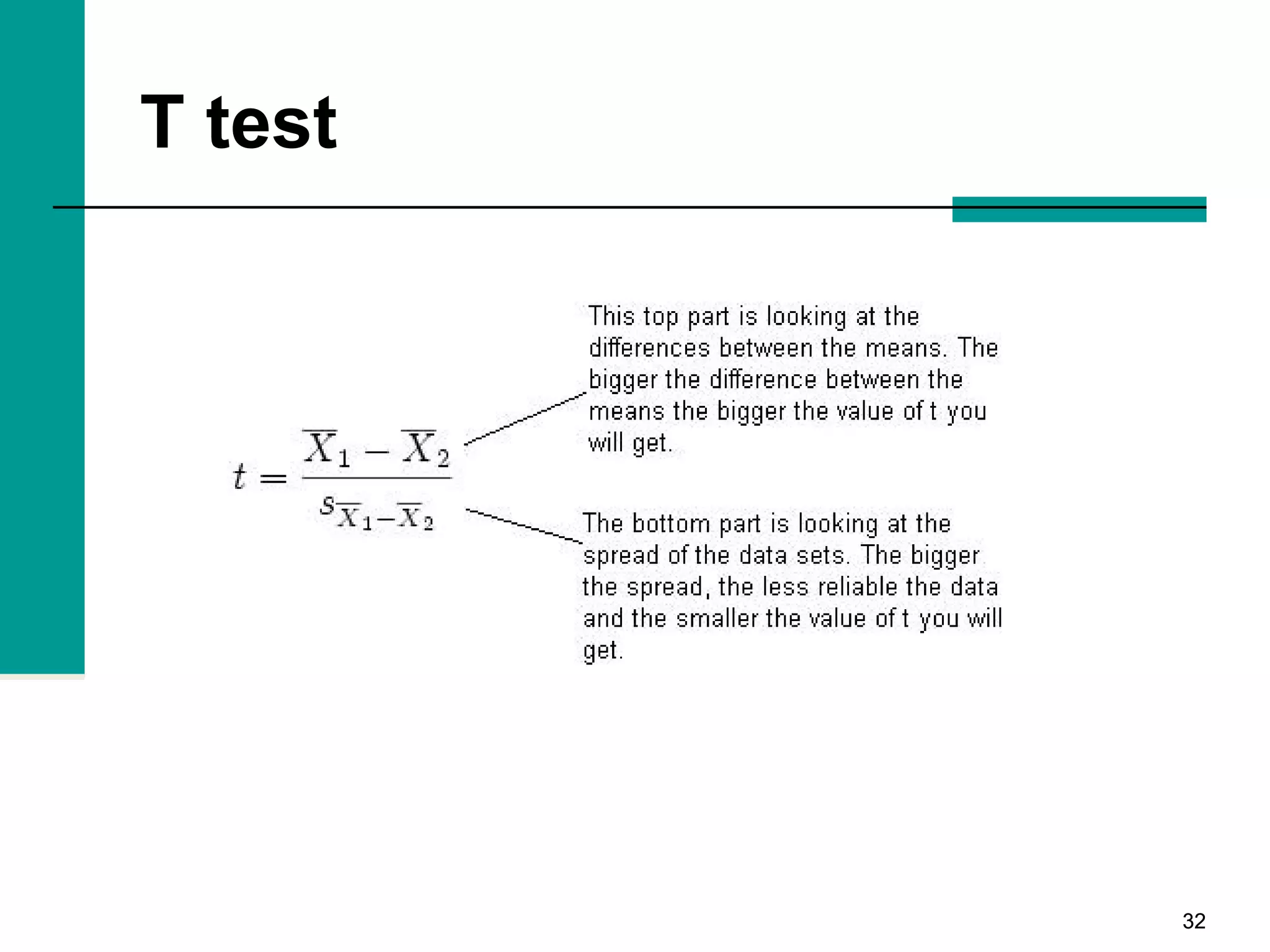
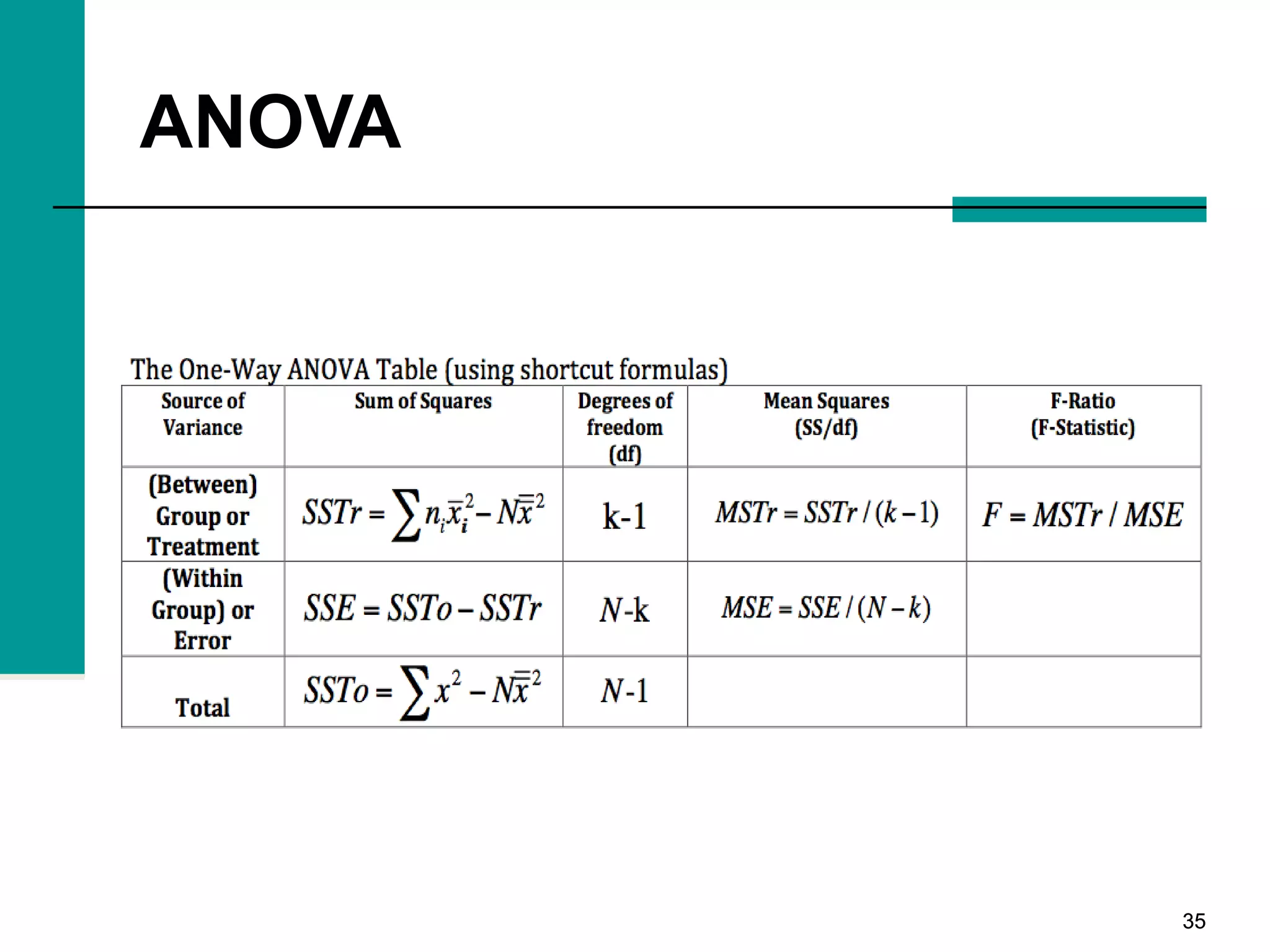
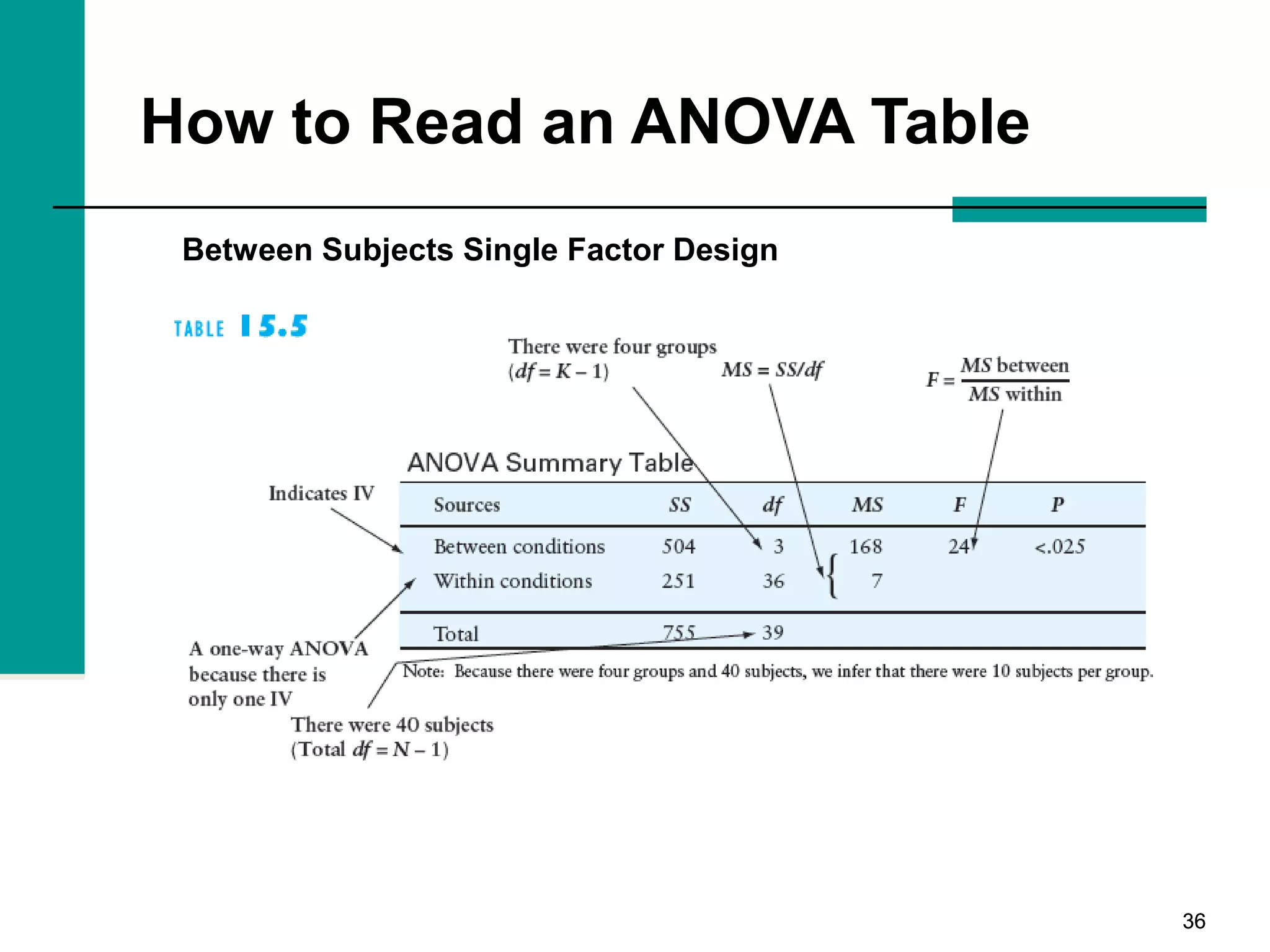
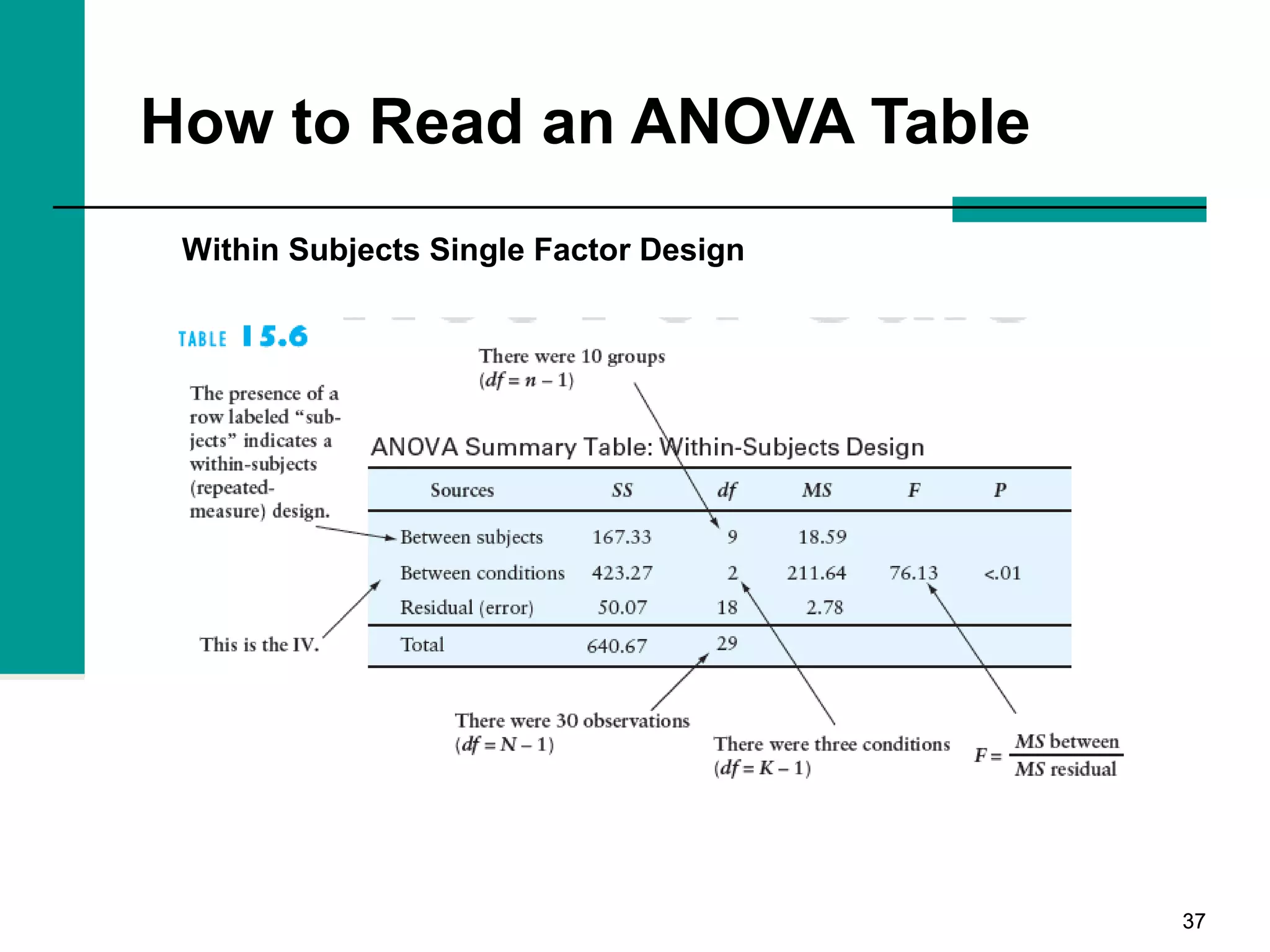
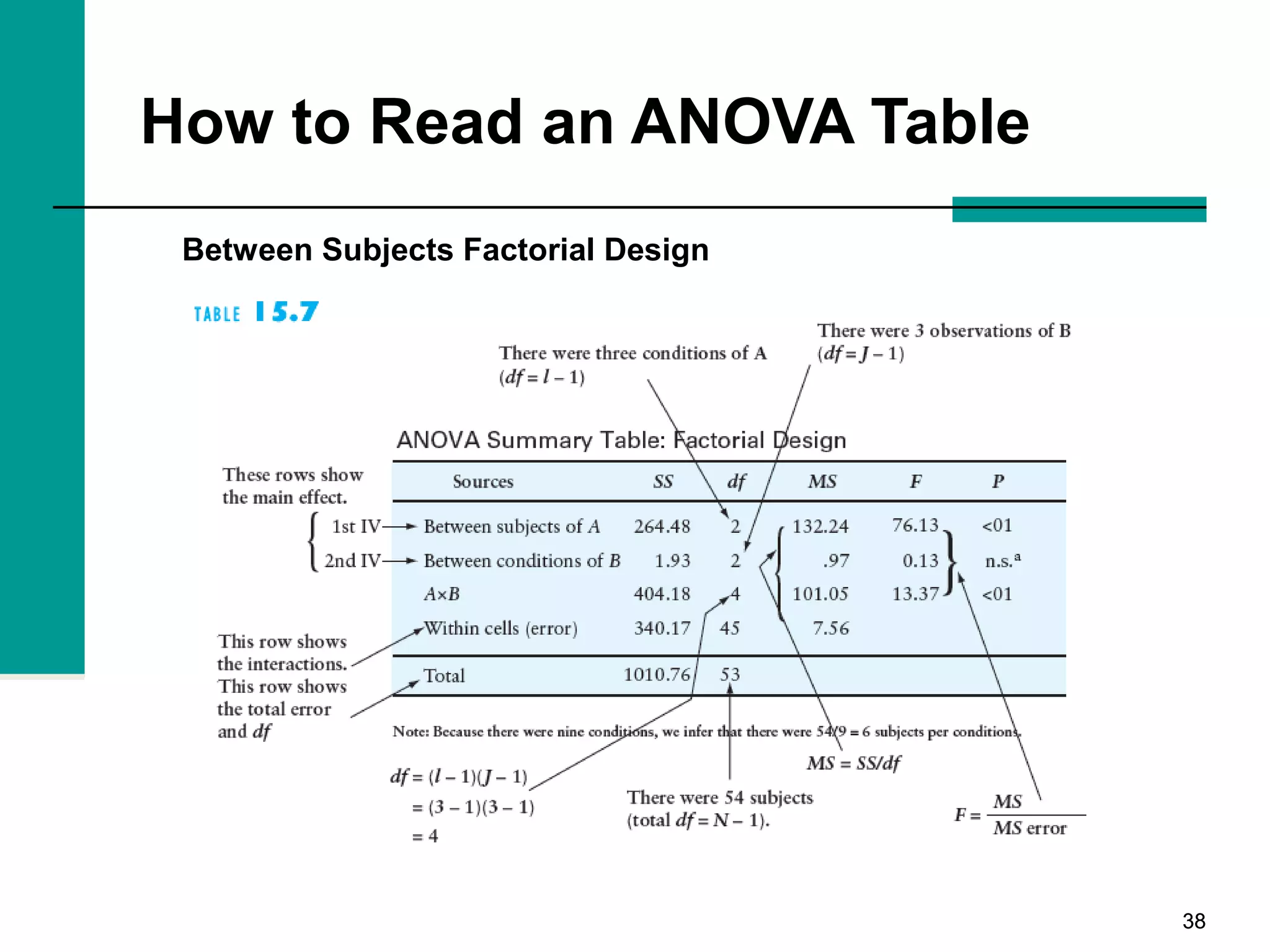
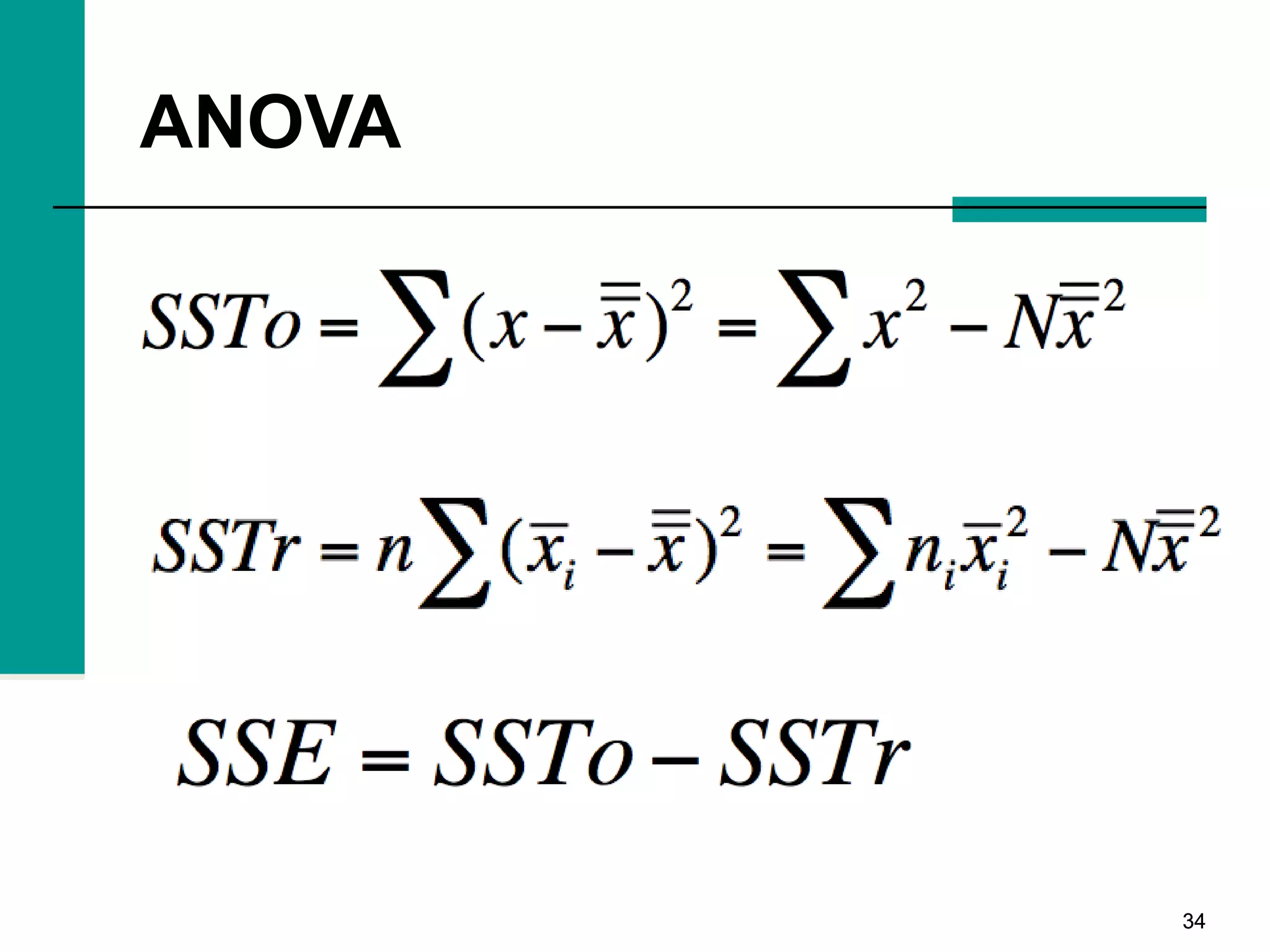This document discusses key concepts in inferential statistics, including sampling distributions, hypothesis testing, significance, effect size, power, chi-square tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and t-tests. It explains that inferential statistics are used to draw conclusions about populations based on samples, and covers topics like the standard error of the mean, properties of sampling distributions, null and alternative hypotheses, one-tailed and two-tailed tests, and how to interpret ANOVA tables.