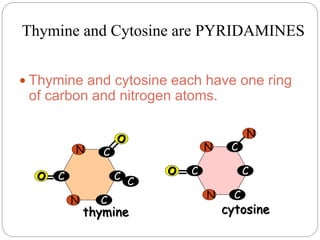
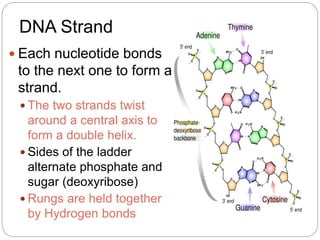
DNA contains the genetic instructions that determine traits in living organisms. It is found in the form of a double helix composed of two strands of nucleotides bonded together. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, sugar (deoxyribose), and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine. The base pairing rule dictates that adenine bonds only with thymine and cytosine bonds only with guanine. DNA replicates semi-conservatively prior to cell division to produce two identical copies of the original DNA molecule. It uses messenger RNA to transport its genetic instructions to ribosomes for protein production.