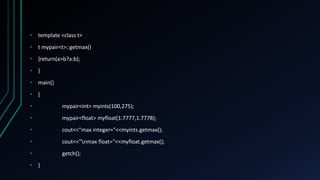
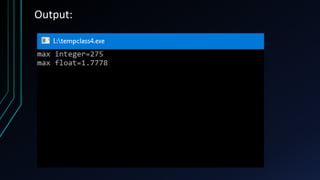
This document discusses templates in C++. Templates allow functions and classes to operate on different data types in a generic way. Function templates define functions that can accept different data types as parameters. Class templates define classes that can work with different types. Examples are provided to demonstrate function and class templates, including defining a max function and pair class that work for both integer and float data types. Templates support generic programming and allow reusable software components to handle different types in a single framework.