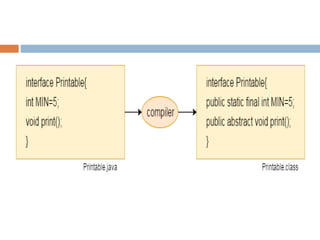
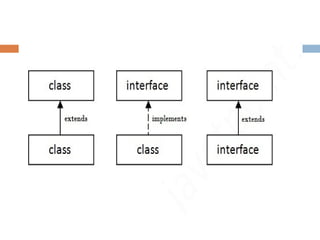
An interface in Java serves as a blueprint for classes and is key to achieving abstraction and multiple inheritance, containing only static constants and abstract methods. It cannot be instantiated, similar to an abstract class, and allows for the implementation of multiple inheritance without ambiguity. Since Java 8, interfaces can include default and static methods with method bodies.







![public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.print();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-11-320.jpg)

![class TestInterface
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Drawable d=new Circle();
d.draw();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-13-320.jpg)


![class TestInterface
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bank b=new SBI();
System.out.println("ROI: "+b.rateOfInterest());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-16-320.jpg)




![public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-21-320.jpg)



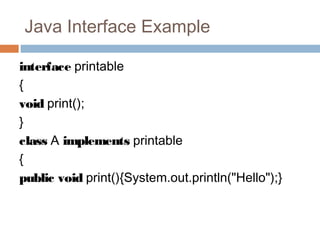
![• class A implements Printable, Showable
• {
• public void print()
• {
• System.out.println("Hello");
• }
• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• A obj = new A();
• obj.print();
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-25-320.jpg)




![public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-30-320.jpg)



![class A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Drawable d=new Rectangle();
d.draw();
d.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-34-320.jpg)


![class A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Drawable d=new Rectangle();
d.draw();
System.out.println(Drawable.cube(3));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfaceinjava-170702034507/85/Interface-in-java-37-320.jpg)