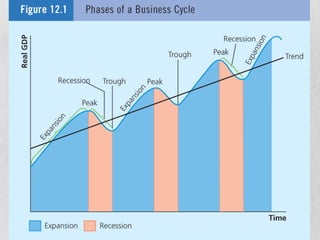
The document discusses the business cycle, which refers to alternating periods of economic expansion and contraction. It identifies key phases like booms, busts, peaks and troughs. It then examines various causes of economic fluctuations, such as changes in consumption, inventories, government spending, expectations, interest rates, and supply shocks. Finally, it outlines different indicators that are used to forecast business cycles, including leading, coincidental, and lagging indicators.