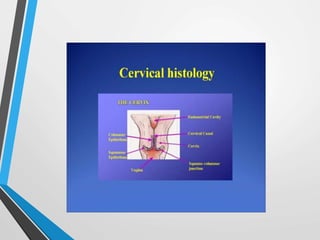
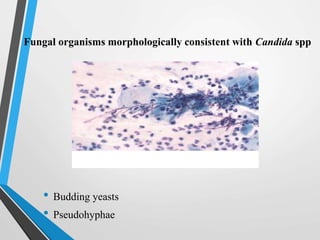
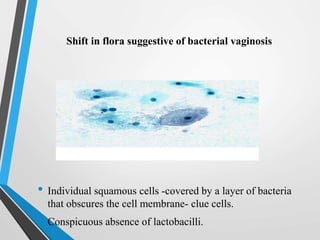
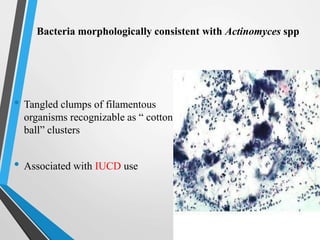
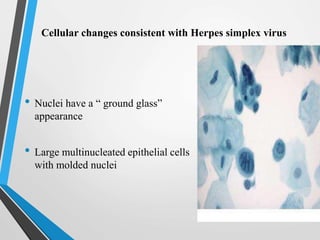
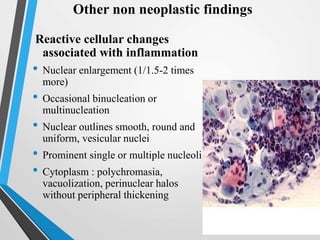
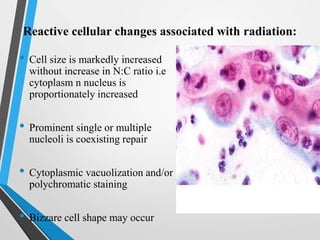
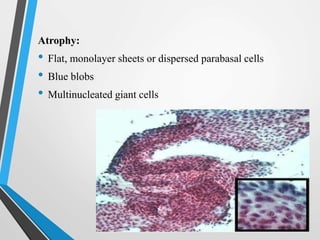
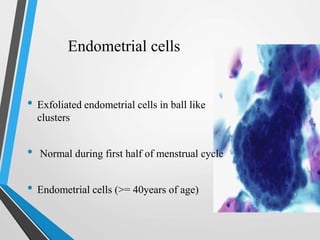
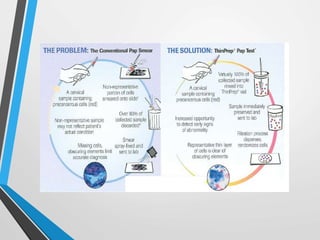
- Cervical cytology, also known as the Pap test, is a screening test used to detect cervical cancer and precancerous conditions. It was introduced in the 1940s by Dr. George Papanicolaou.
- Screening guidelines recommend starting Pap tests at age 21, with testing every 3 years from ages 21-29 and every 5 years with co-testing from ages 30-65. Screening can stop at age 65 if previous results were normal.
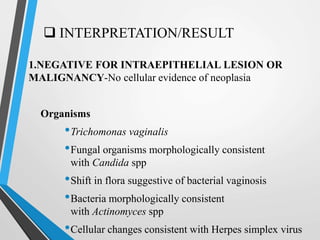
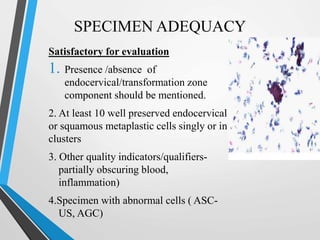
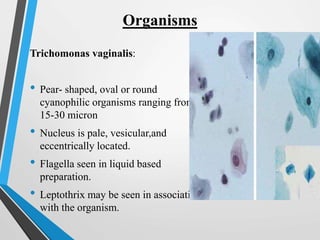
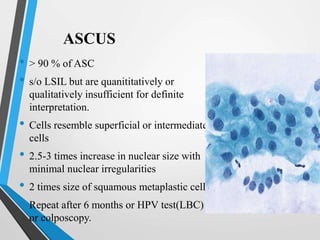
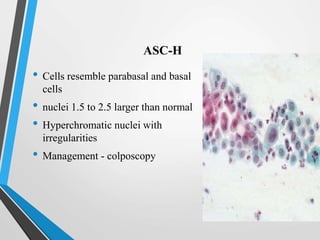
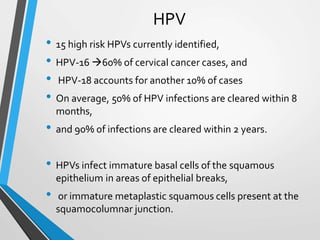
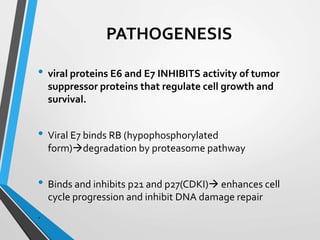
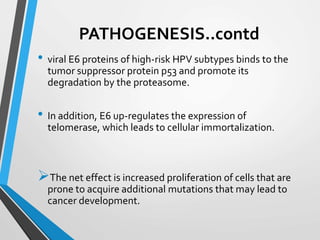
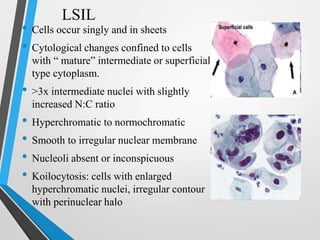
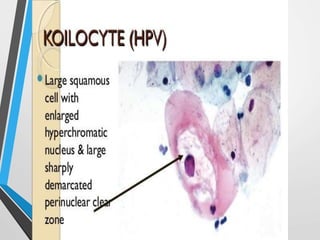
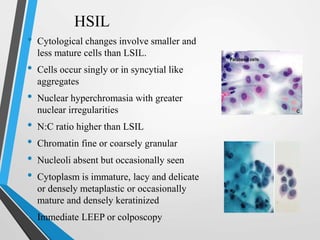
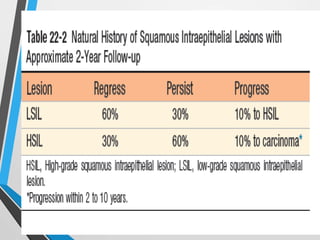
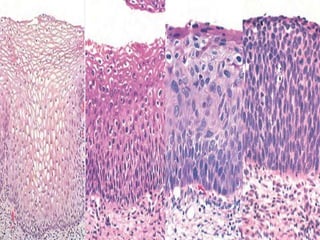
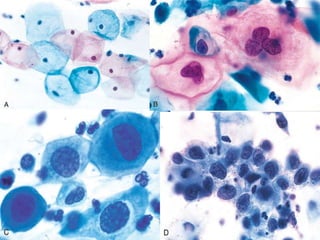
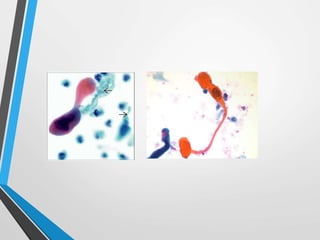
- The Bethesda System provides a standardized terminology for reporting cervical cytology results and categorizes findings as negative, atypical squamous cells, low-grade or high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, or cancer. Management depends on