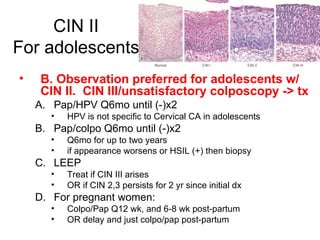
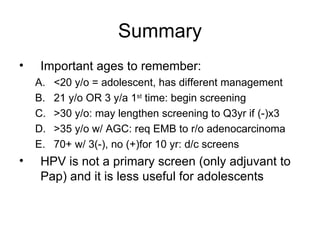
This document provides guidelines for cervical cancer screening and management of abnormal findings according to the 2007 ASCCP guidelines. Key points include: initiating screening at age 21 or 3 years after first sexual intercourse; transitioning to every 3 year screening after age 30 with 3 normal annual pap smears; diagnostic excisional procedure is recommended for CIN II or III in adults but observation is preferred for adolescents; and endometrial biopsy is recommended for women over 35 with atypical glandular cells to evaluate for endometrial cancer.