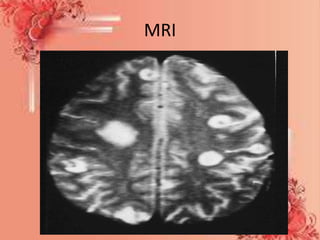
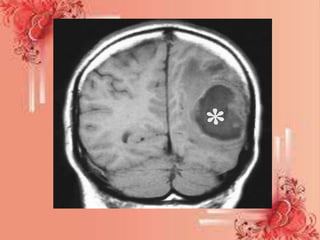
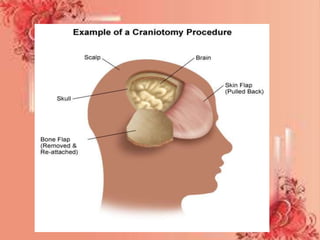
A brain abscess is a rare, life-threatening infection within the brain tissue that develops from a local or remote infection source. Common causes include ear, dental, sinus, or lung infections. Symptoms include severe headache, nausea, vomiting, and neurological deficits. Diagnosis involves imaging scans like MRI or CT scan to detect pockets of infected material. Treatment requires long-term antibiotics and potentially surgical drainage or resection of the abscess. Complications can include increased intracranial pressure, neurological damage, or disability if not properly treated.