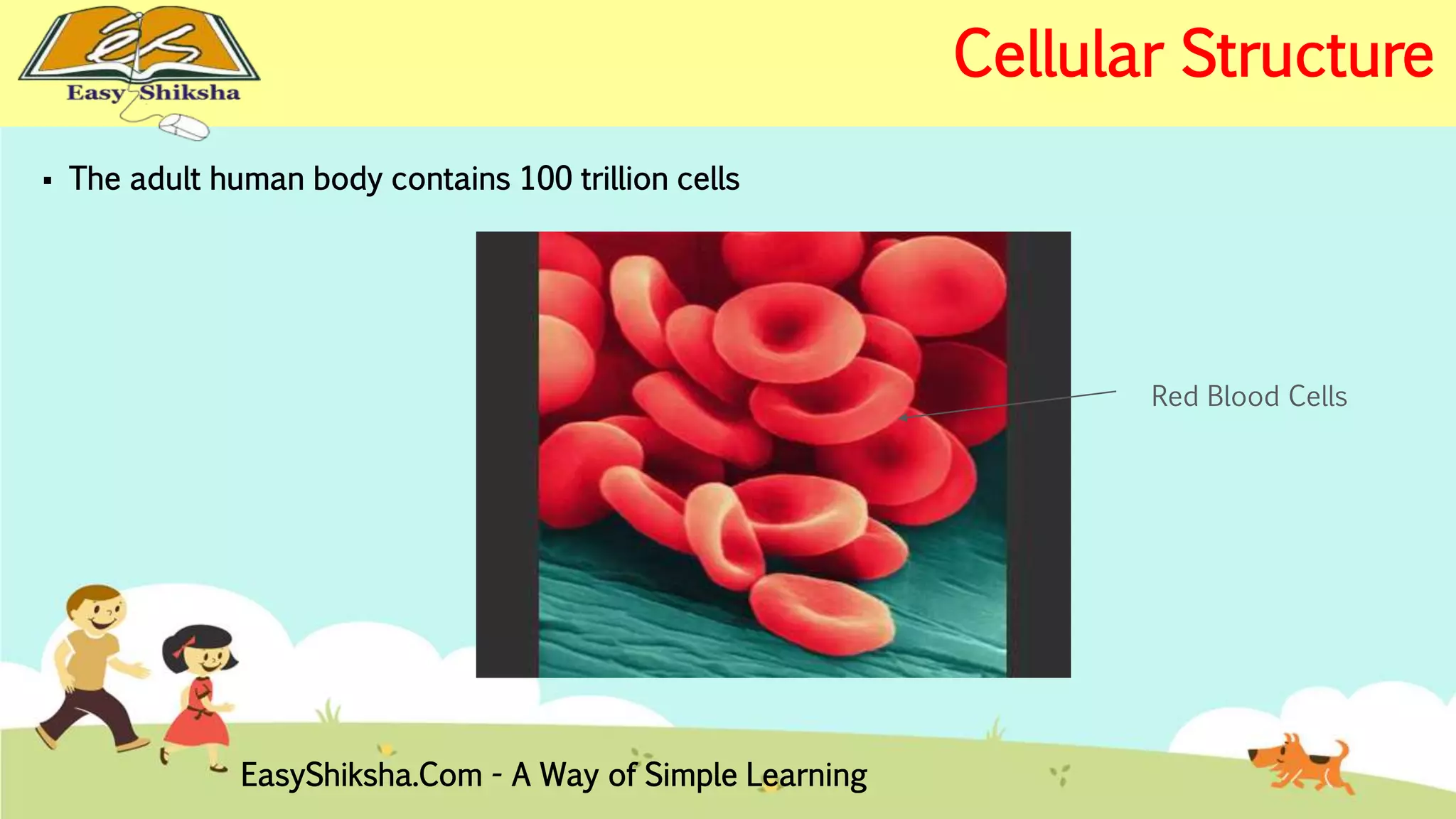
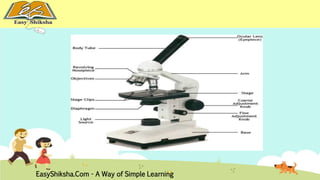
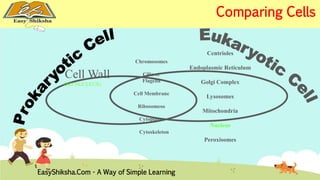
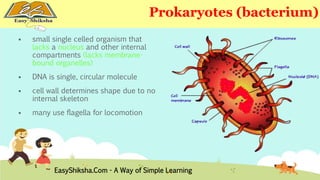
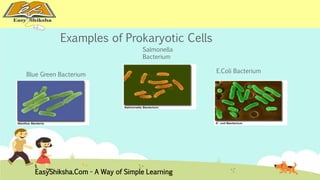
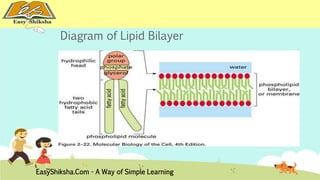
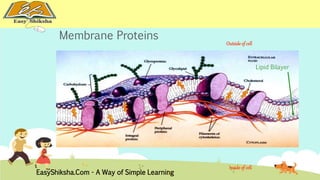
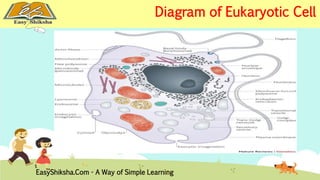
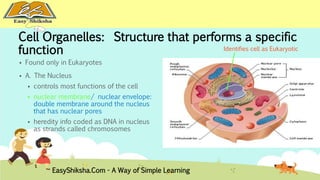
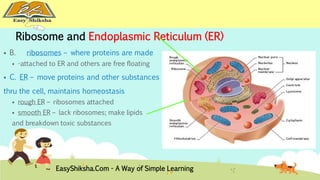
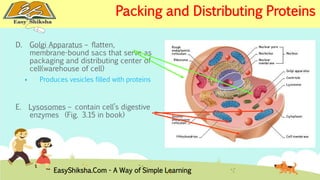
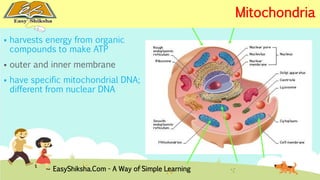
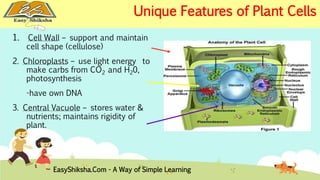
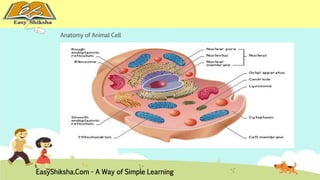
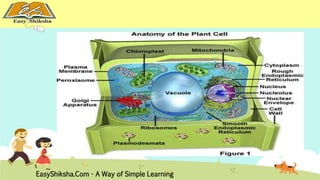
The document discusses the structure and types of cells, highlighting the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It details cell theory, the function and organization of cellular components, and the importance of cell size and surface area in biological efficiency. Furthermore, it explains various microscopy techniques to observe cells and describes unique features of plant cells.