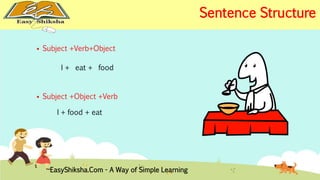
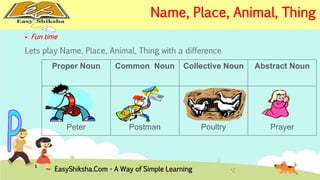
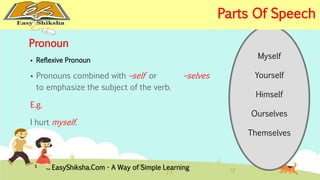
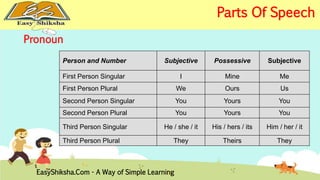
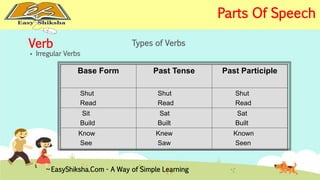
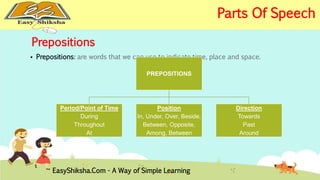
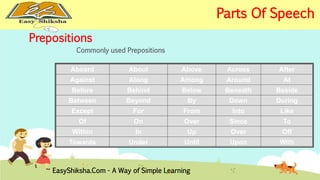
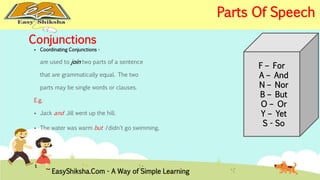
The document provides an overview of basic grammar concepts, including sentence structure, parts of speech such as nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It includes definitions, examples, and types of each part of speech to aid in English language learning. The content is designed to enhance understanding and fluency in English communication.