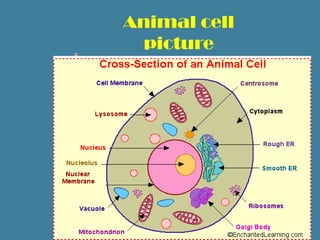
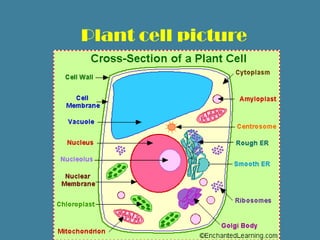
There are two main types of cells: eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Cells are microscopic structures that are the basic unit of life. Animal cells contain organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Plant cells also contain these organelles as well as additional structures like chloroplasts, cell walls, and vacuoles for storage. Both animal and plant cells have semipermeable membranes that regulate what enters and exits the cell and internal components that perform specific functions to keep the cell alive.






![Ribosome
• These are the parts that mainly contain RNA[ribonucleic acids].
Ribosomes are those parts that are responsible for production of
proteins in plants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellspowerpoint-120906135926-phpapp01/85/Cells-power-point-8-320.jpg)














![Sources
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/animal-cell
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/plant-cell-parts
My Dad
My Mom
My Brother David [a scientist]
Google images
Enchantedlearning.com
Dictionary.com ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellspowerpoint-120906135926-phpapp01/85/Cells-power-point-25-320.jpg)