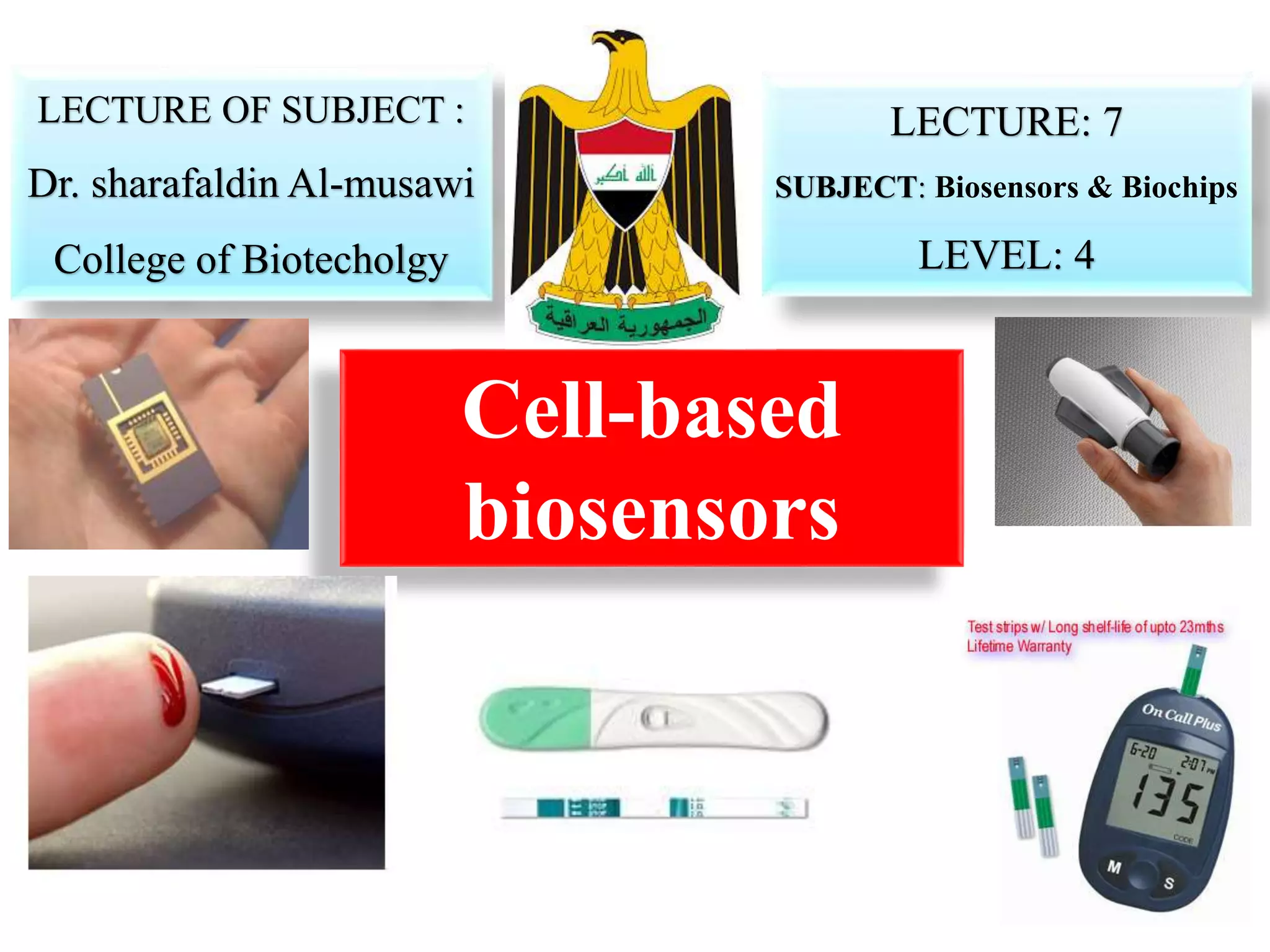
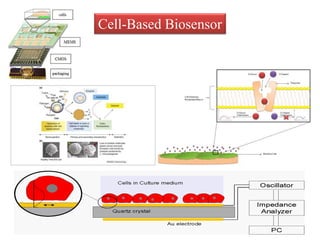
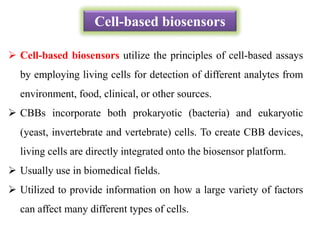
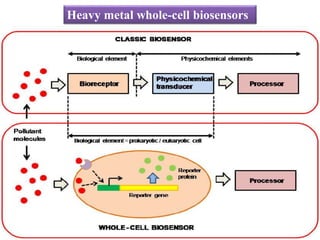
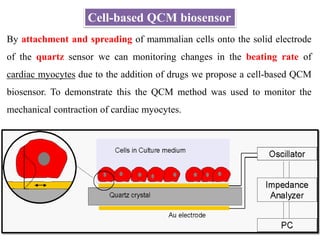
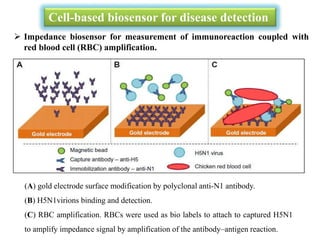
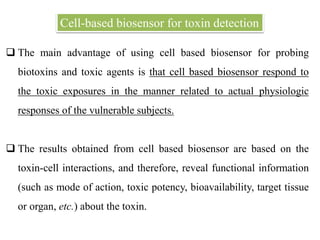
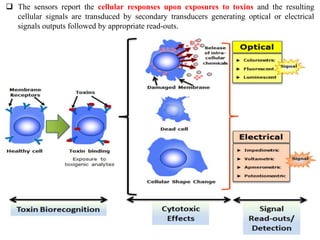
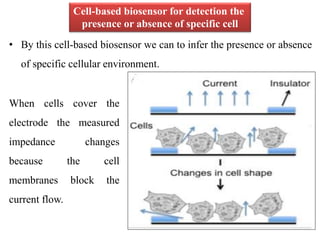
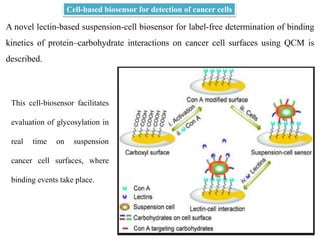
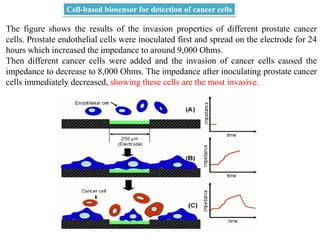
Cell-based biosensors utilize living cells integrated onto a biosensor platform to detect analytes. They can use both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells from bacteria to mammalian cells. One example is a cell-based quartz crystal microbalance biosensor that monitors the beating rate of cardiac myocytes to detect drugs. Cell-based biosensors can also detect diseases by measuring immunoreactions amplified by cells, and detect toxins by measuring the cellular responses to exposures. They provide information about toxin mode of action and effects related to actual physiological responses.