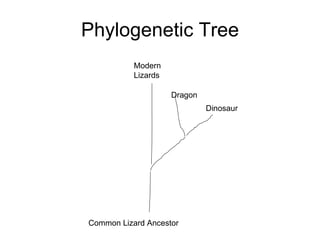
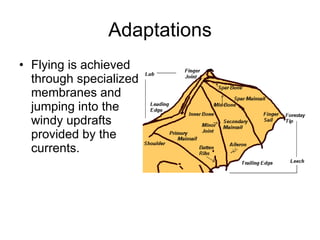
The document discusses the evolutionary lineage and biological characteristics of dragons, linking them to modern reptiles like dinosaurs and crocodiles. It highlights adaptations for survival, including flying mechanisms and predatory features, as well as the dragons' extinction due to habitat loss and human activities. This decline was exacerbated by genetic inbreeding as their populations diminished, ultimately leading to their extinction.