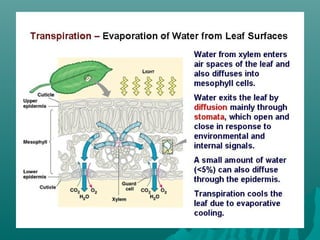
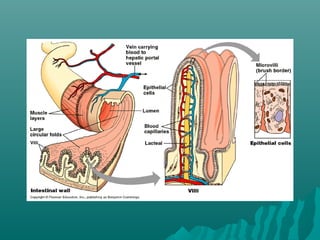
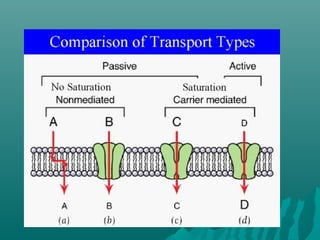
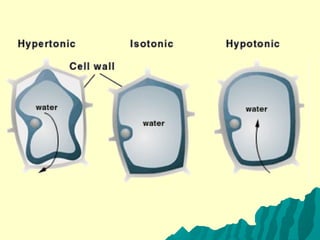
The plasma membrane controls the movement of substances into and out of cells using transport proteins and is selectively permeable, allowing some molecules to pass through more easily than others. Cell membranes use passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion requiring transport proteins, and active transport using energy to regulate the flow of nutrients, waste, and other molecules into and out of cells. The fluid mosaic model describes cell membranes as a phospholipid bilayer with various embedded proteins that can move laterally within the membrane.