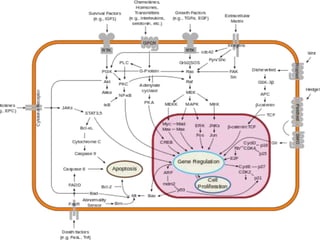
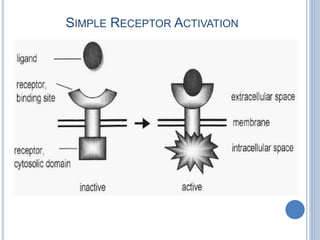
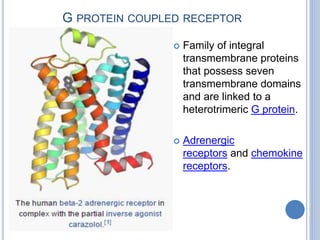
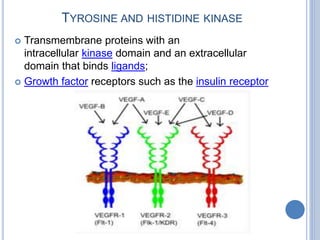
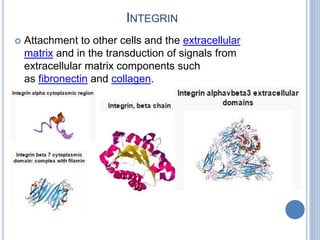
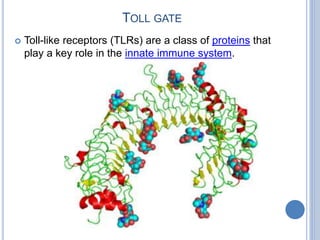
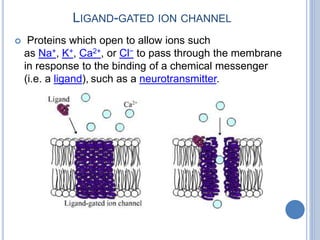
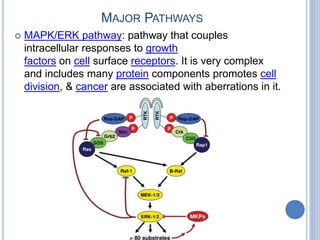
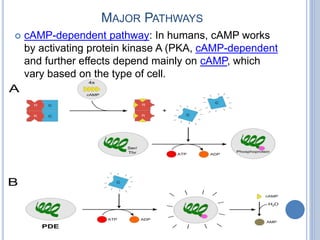
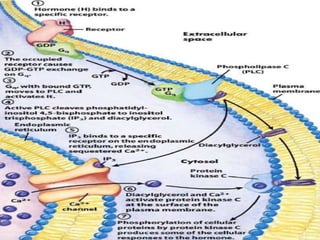
This document provides an overview of signal transduction. It begins with defining signal transduction as the process by which extracellular signaling molecules activate cell surface or intracellular receptors, triggering a biochemical chain reaction that results in a cellular response. The document then discusses the history of studying signal transduction, examples of environmental stimuli, types of receptors, second messengers, cellular responses, and major signaling pathways involved in signal transduction like the MAPK/ERK, cAMP-dependent, and IP3/DAG pathways.