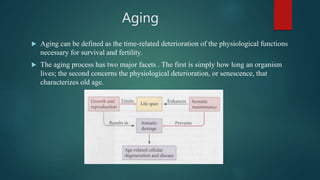
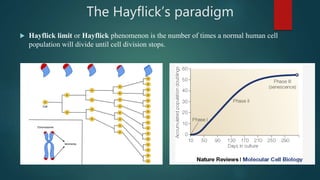
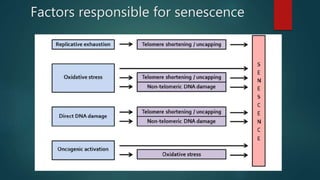
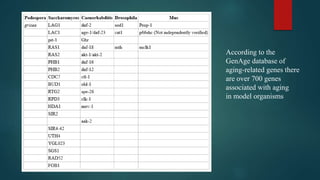
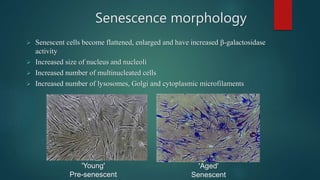
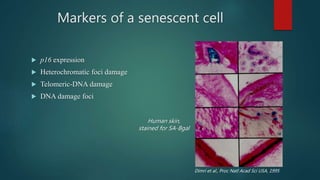
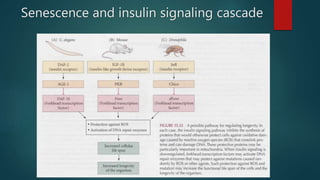
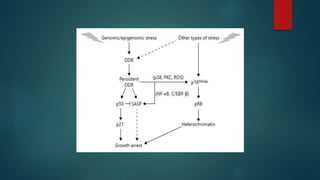
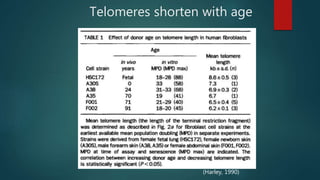
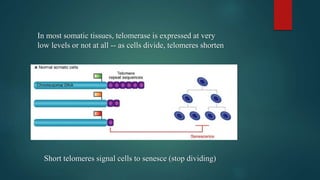
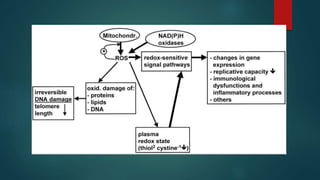
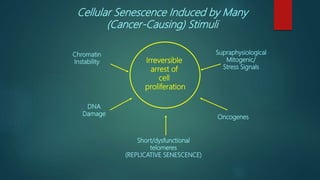
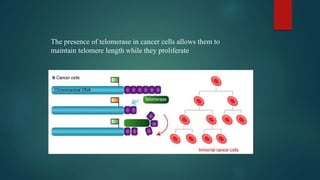
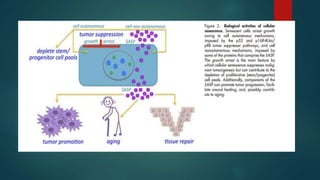
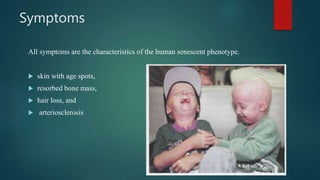
The document discusses aging as a time-related deterioration of physiological functions, detailing two main theories: programmed theories linked to biological clocks and stochastic theories identifying cumulative environmental damage. Senescence, characterized by the irreversible loss of cellular function, is associated with increased age, affecting various tissues and linked to genes responsible for aging such as p53 and klotho. The document also connects cellular senescence to cancer suppression and highlights conditions such as progeria as related to aging processes.