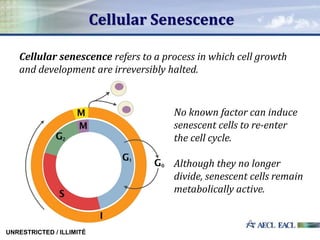
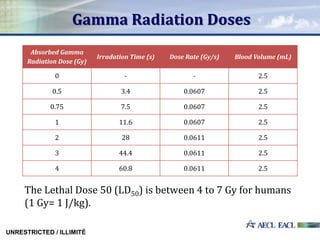
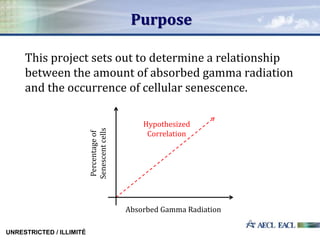
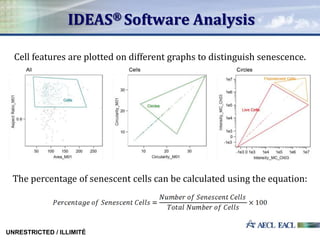
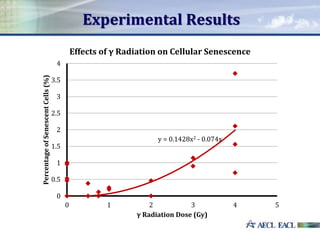
This study investigated the relationship between absorbed gamma radiation dose and cellular senescence in lymphocytes. Lymphocytes were isolated from human blood samples and exposed to varying doses of gamma radiation from 0 to 4 Gy. The samples were then analyzed using flow cytometry and p16 biomarker staining to determine the percentage of senescent cells at each radiation level. The results showed a positive quadratic correlation between radiation dose and senescence. This research establishes a foundation for using cellular senescence analysis to determine an individual's original radiation exposure level.