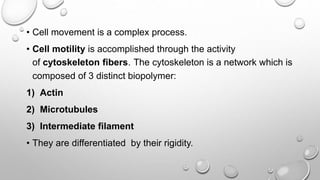
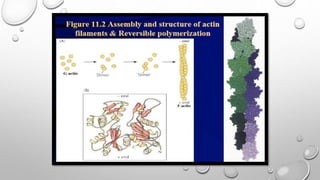
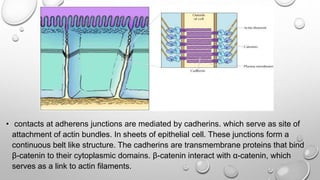
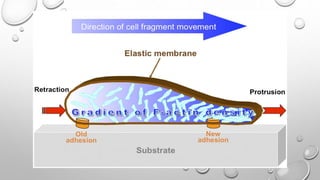
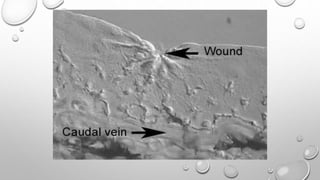
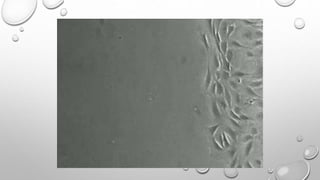
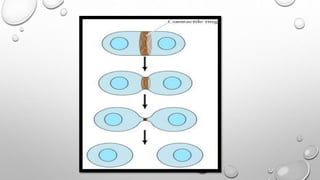
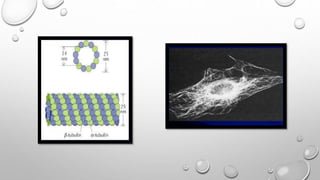
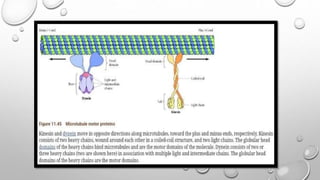
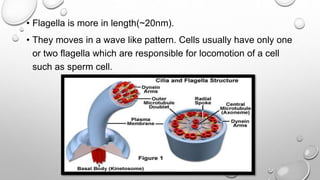
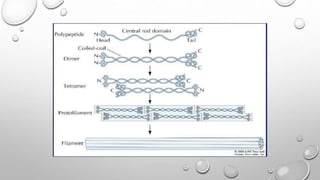
Cell movement is accomplished through the cytoskeleton, which is composed of three main types of fibers: actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. Actin filaments interact with motor proteins like myosin to generate movement and play roles in cell adhesion, crawling, and contraction. Microtubules and their motor proteins kinesin and dynein facilitate intracellular transport and movement of cilia and flagella. Intermediate filaments provide structural support to cells but are not involved in motility. The three fiber types work together with associated proteins to control cell shape, division, transport, and movement.