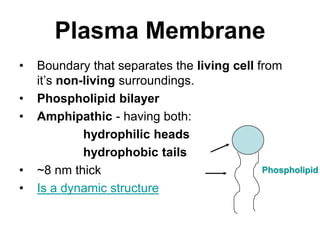
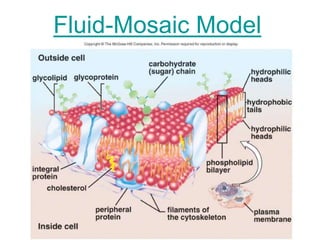
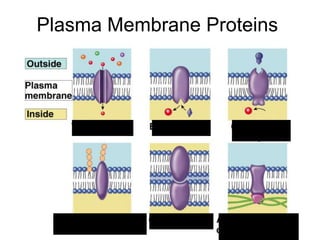
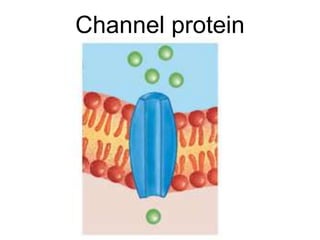
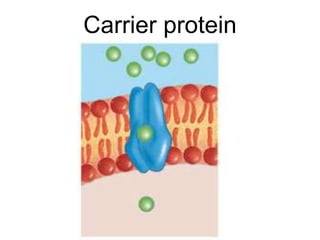
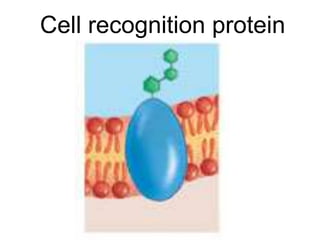
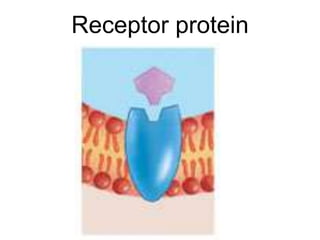
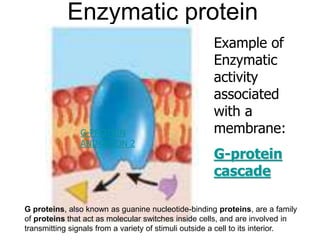
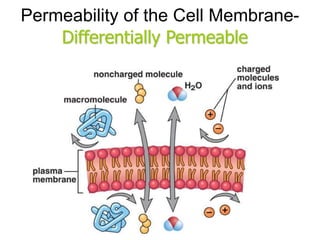
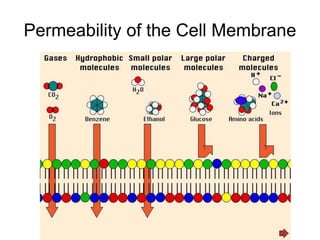
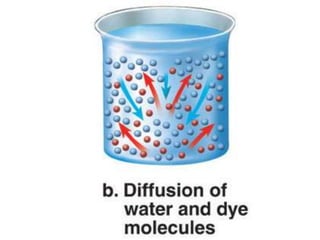
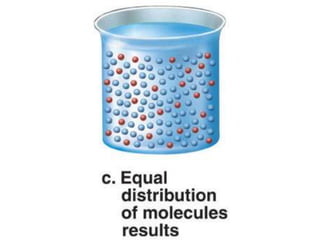
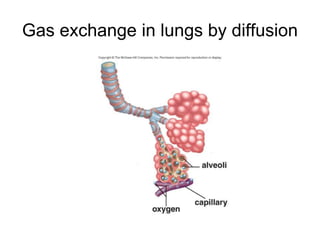
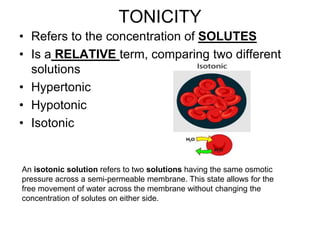
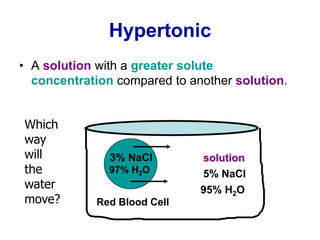
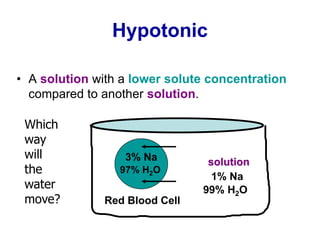
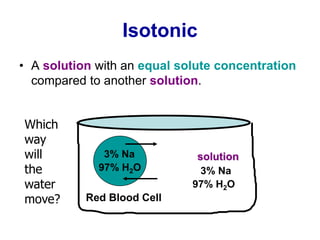
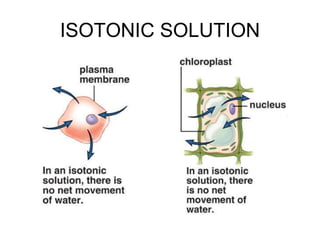
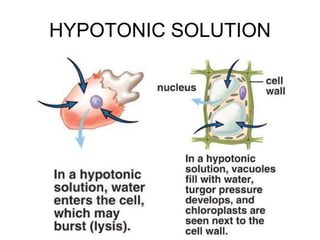
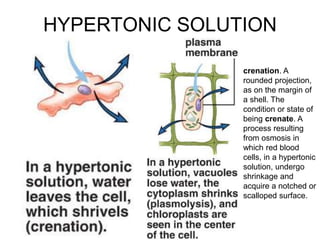
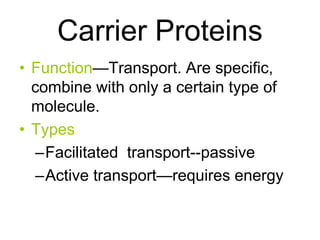
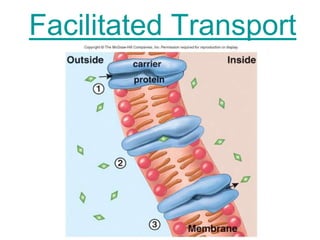
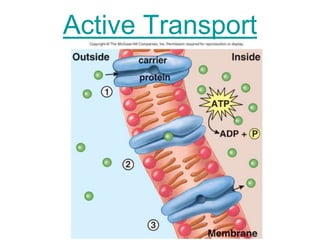
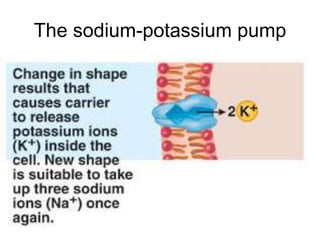
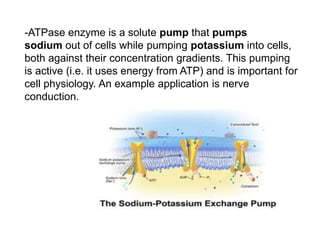
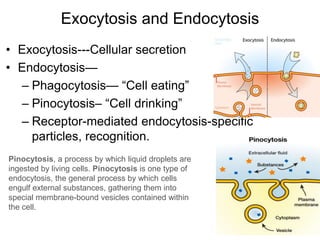
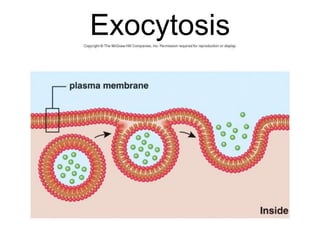
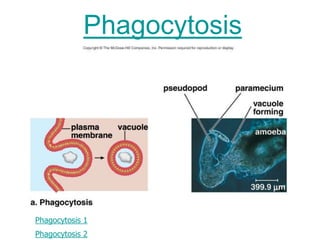
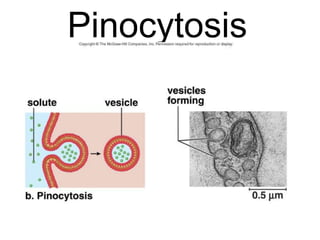
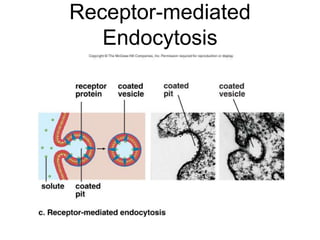
The document discusses the structure and functions of the plasma membrane. It describes the plasma membrane as a phospholipid bilayer composed of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails arranged in a fluid mosaic structure. The membrane contains various proteins that facilitate transport, act as receptors, or perform other functions. The document outlines different types of membrane transport including diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, bulk transport, and active transport.