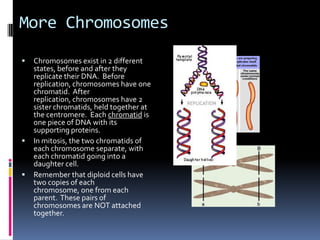
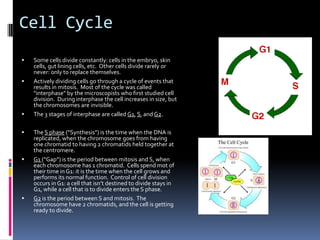
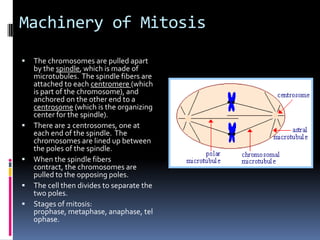
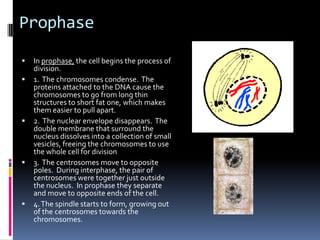
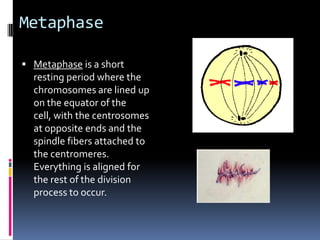
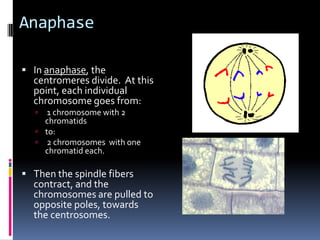
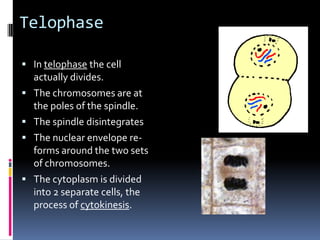
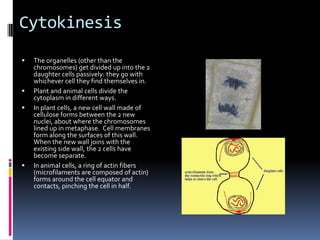
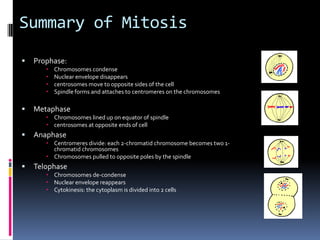
Mitosis is the process of normal cell division where the parent cell divides into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. It involves several stages - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. During prophase, chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, chromosomes line up along the center of the cell. In anaphase, chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles. In telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms and cytokinesis occurs to separate the cell contents. Mitosis ensures genetic inheritance and growth and replacement of cells.