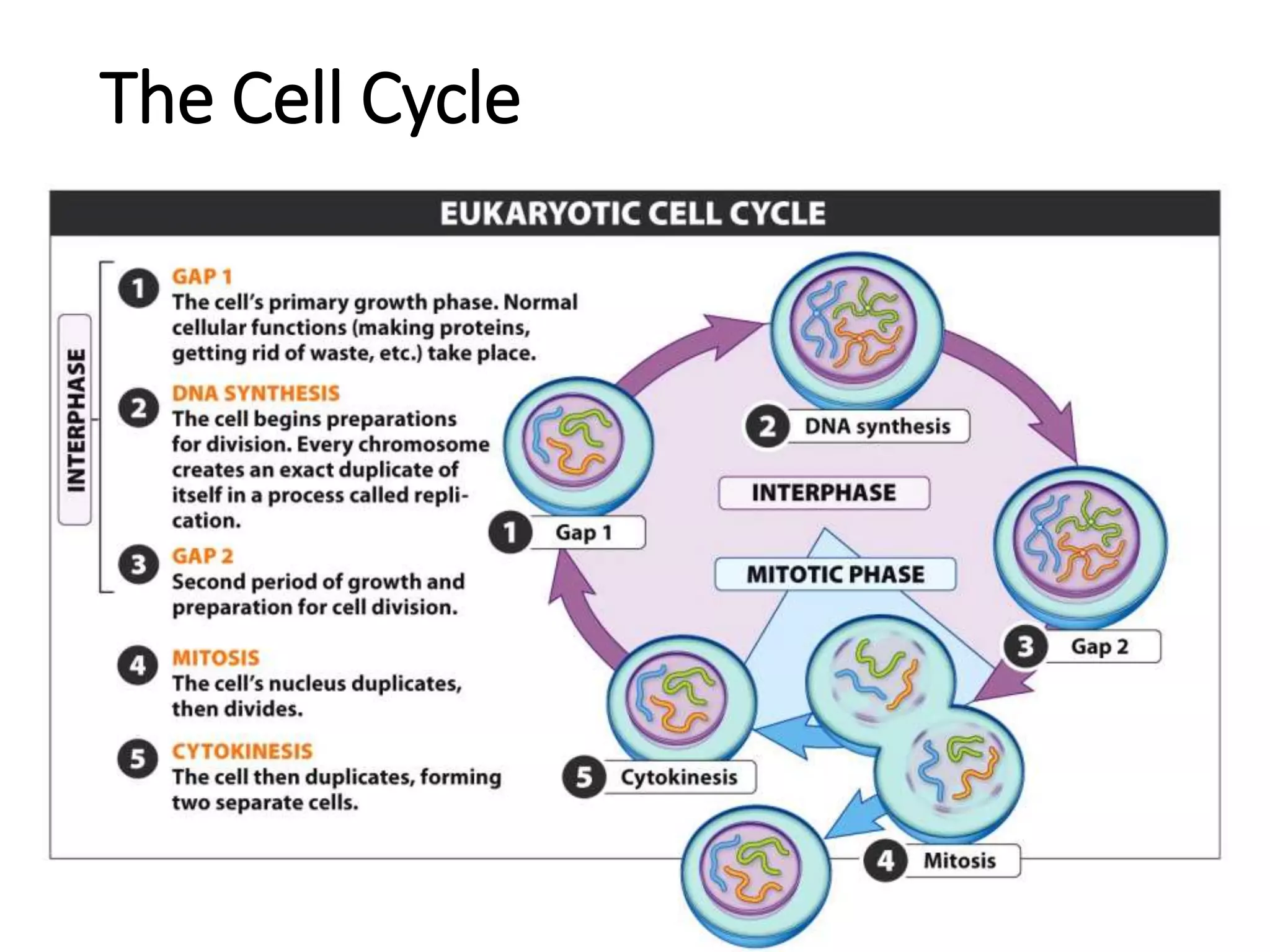
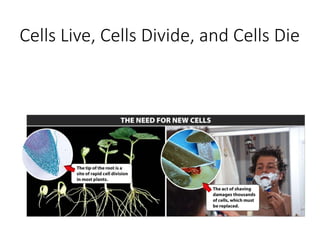
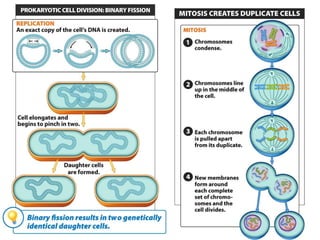
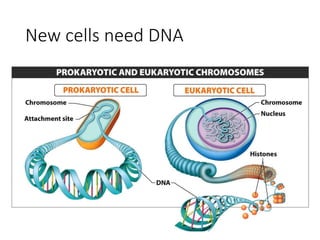
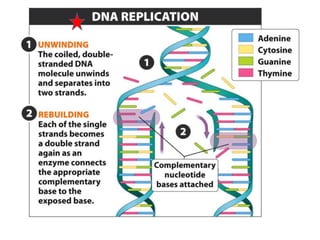
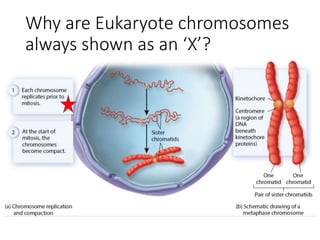
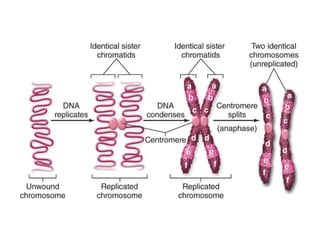
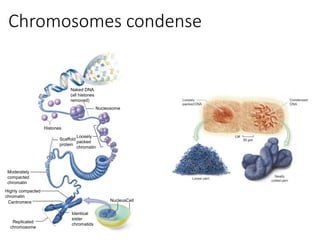
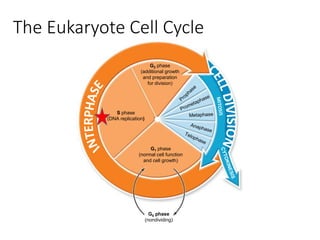
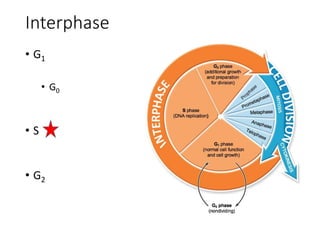
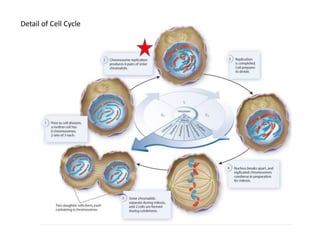
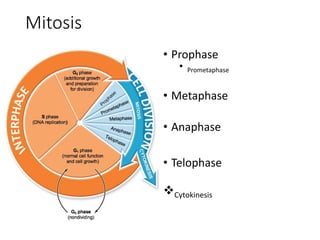
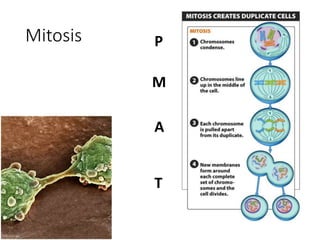
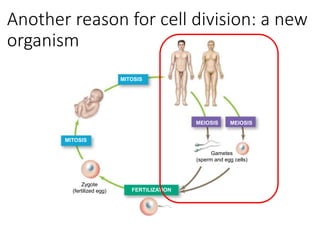
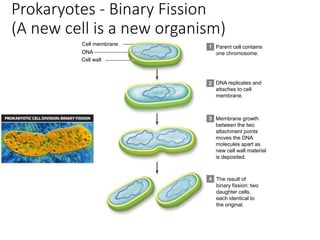
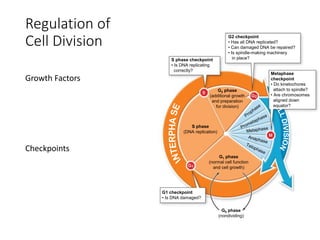
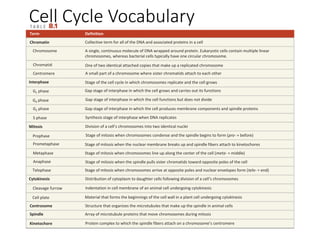
Eukaryotic cell chromosomes are always shown as an 'X' shape because during cell division, the duplicated chromosomes condense and their two identical copies, called sister chromatids, attach together at the centromere. The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and DNA replicates, and cell division via mitosis, where the duplicated chromosomes separate into two daughter cells. Mitosis is made up of prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, culminating in cytokinesis which divides the cytoplasm.