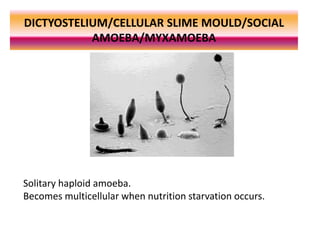
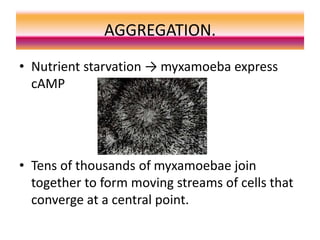
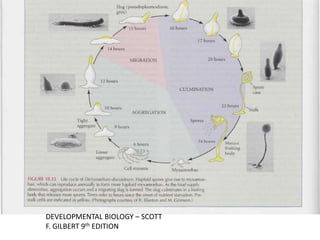
The document summarizes the life cycle and cellular aggregation and differentiation process of Dictyostelium, a social amoeba. It has three stages: aggregation, migration, and culmination. During aggregation, thousands of solitary amoeba join together in streams in response to cyclic AMP signals. They migrate as a slug and the prestalk and prespore cells sort out, with prestalk cells becoming the stalk and prespore cells becoming spores. In culmination, the migrating slug forms a fruiting body with a stalk holding aloft a sorus of spores. The cells differentiate into their final fates depending on the stage of their cell cycle during starvation.