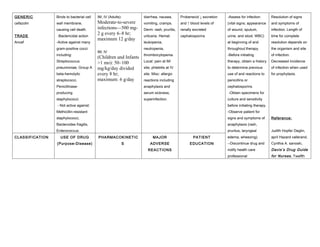
Cefazolin is a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat infections caused by susceptible bacteria. It works by binding to bacterial cell walls and causing cell death. The typical therapeutic dose for adults is 500 mg to 2 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 6-8 hours, up to a maximum of 12 g per day. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions. Major adverse reactions include seizures at high doses and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of infection resolution and adverse drug reactions.