1) Cefazolin is a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections including bone, respiratory, skin, urinary tract, and surgical site infections.
2) It is administered via intravenous or intramuscular injection, with dosages varying based on the infection severity and the patient's age, renal function, and other factors.
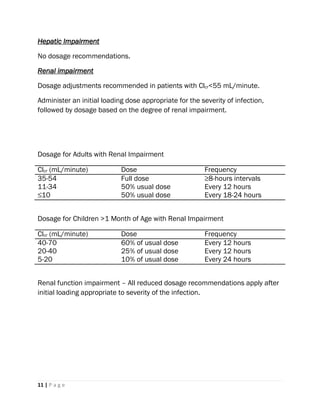
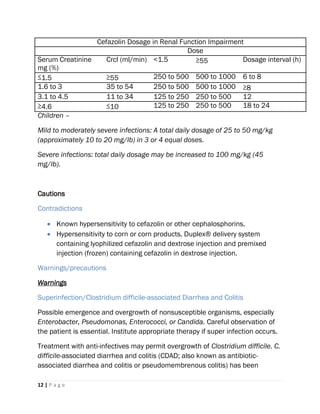
3) Special precautions are outlined for patients with renal impairment, as dosage must be adjusted based on creatinine clearance to avoid toxicity.