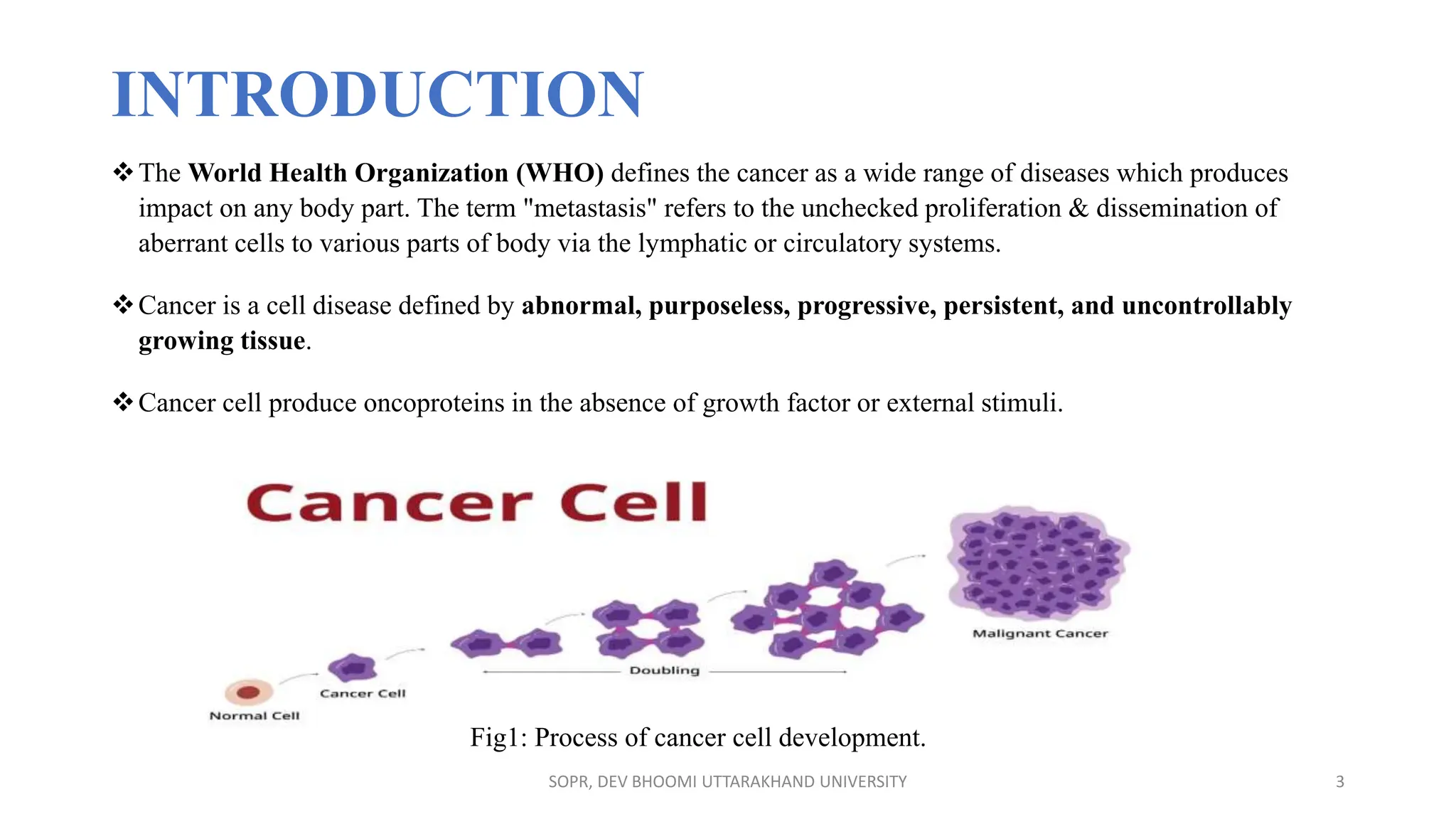
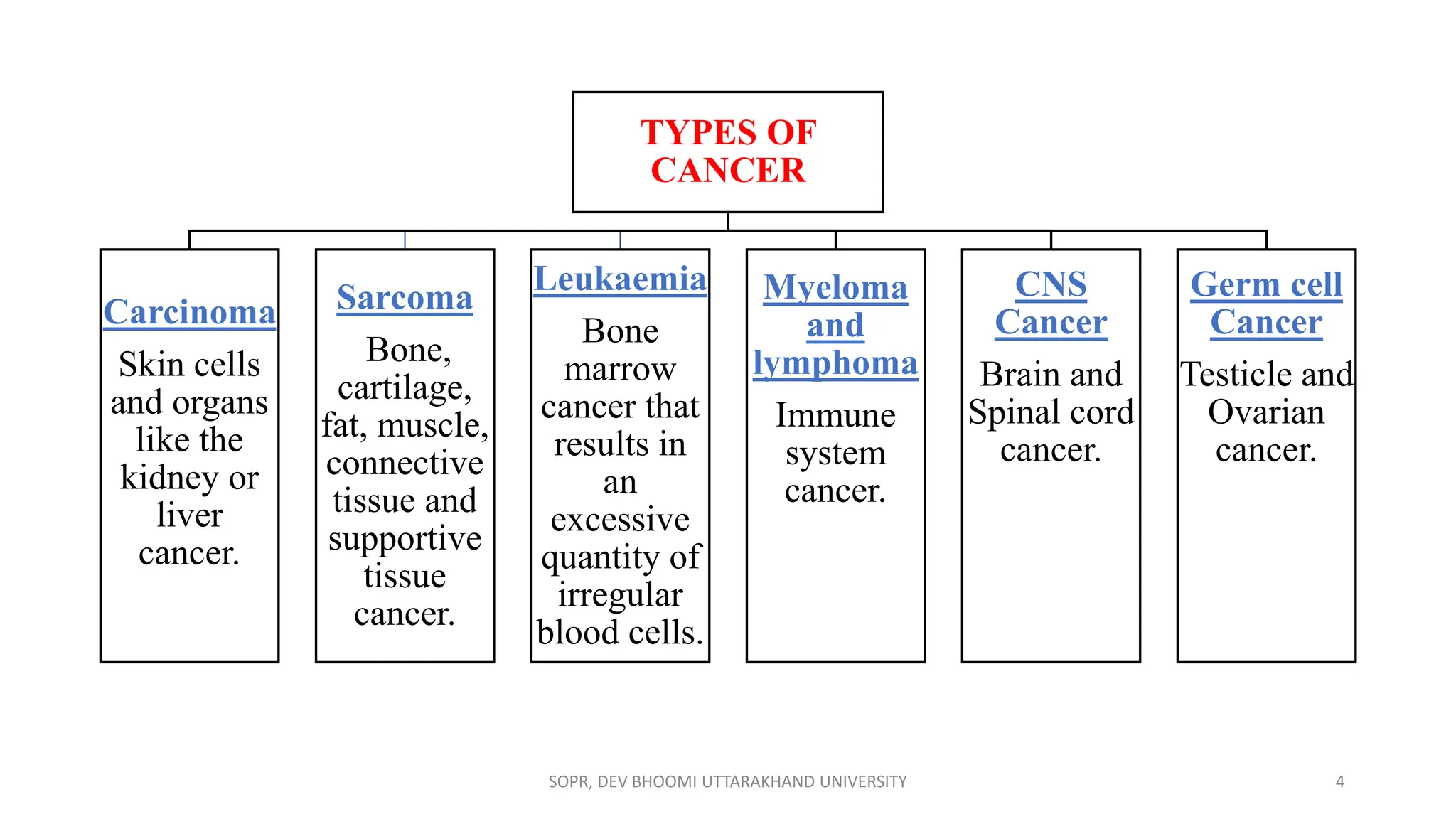
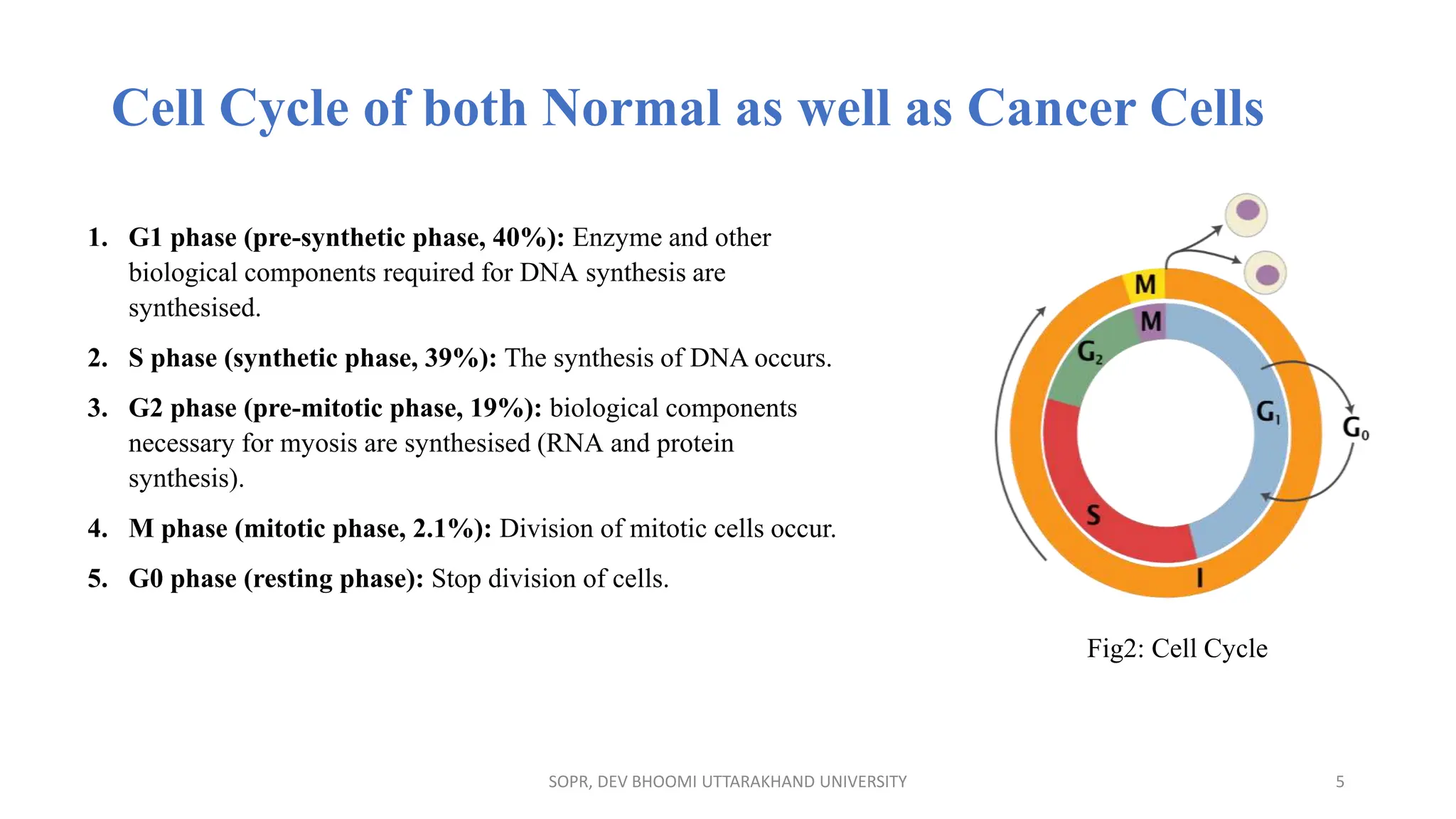
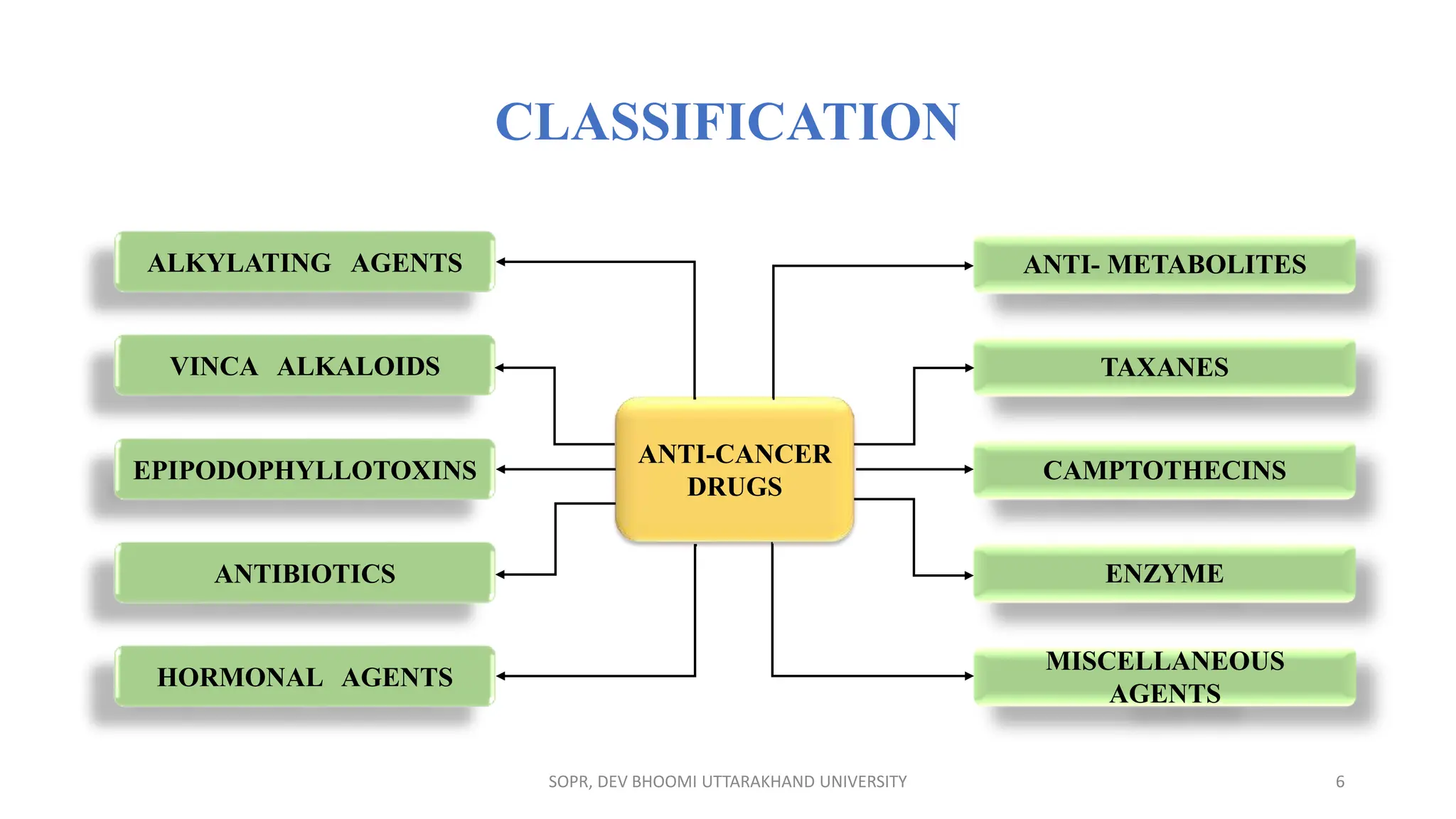
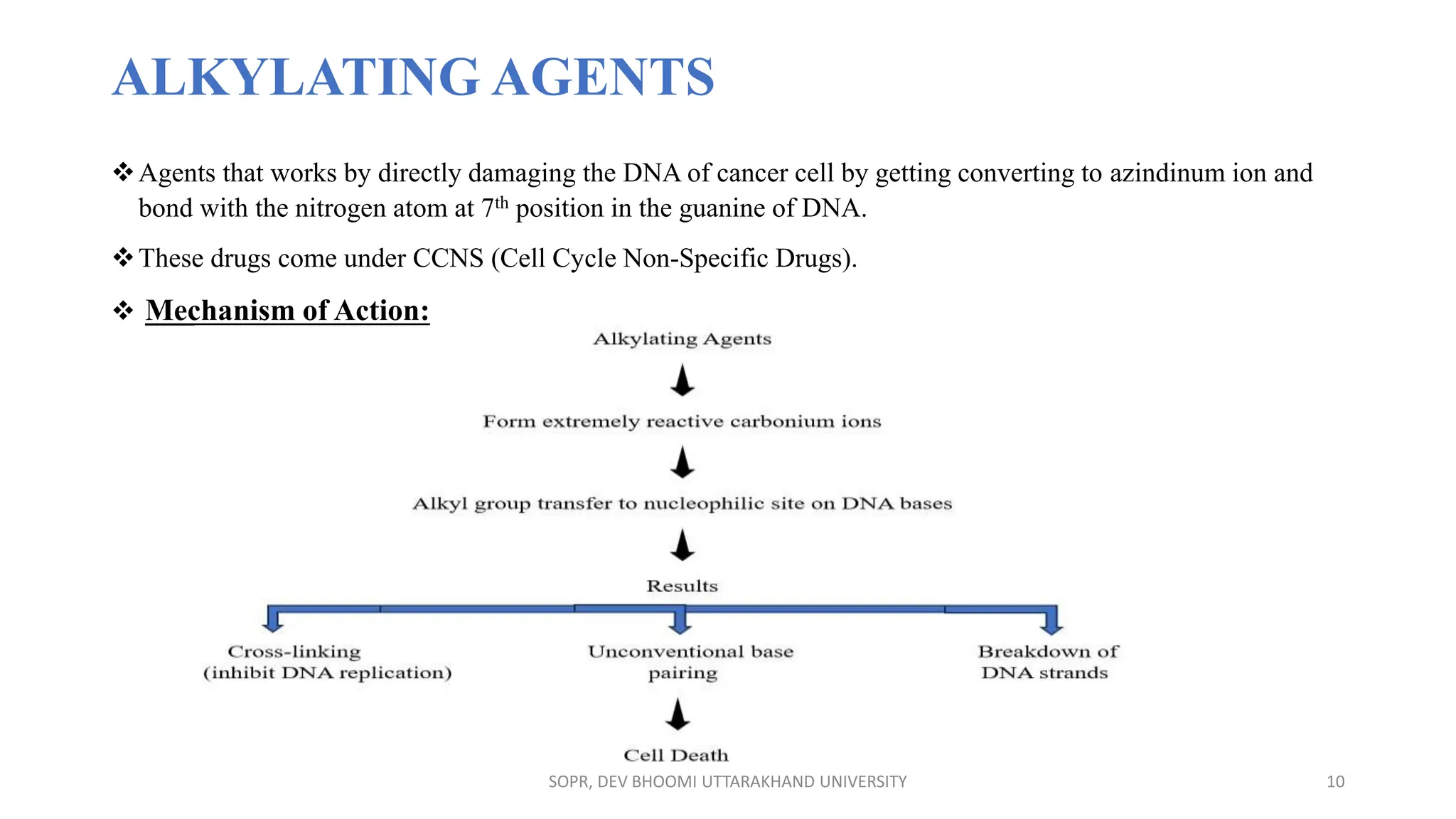
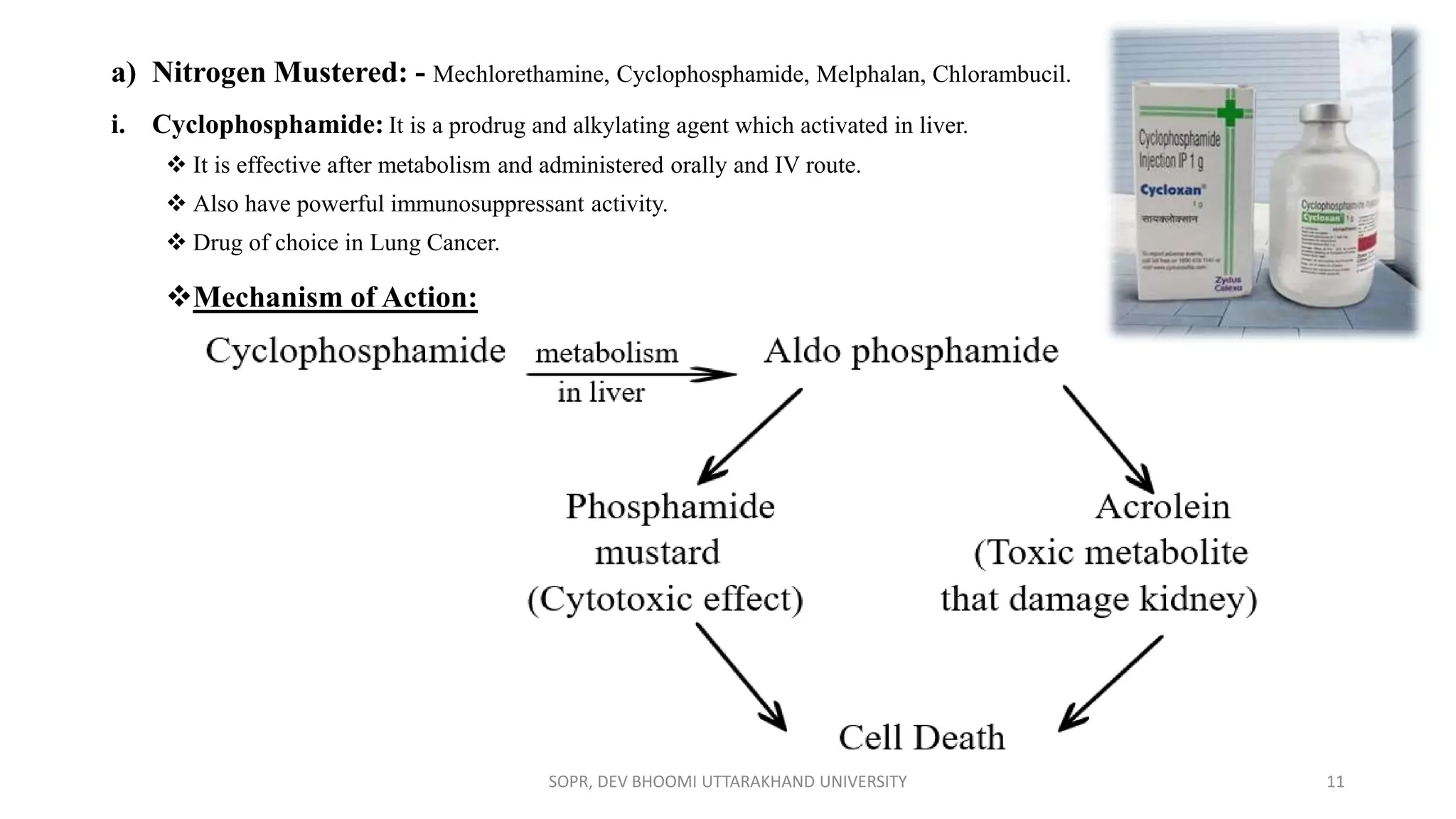
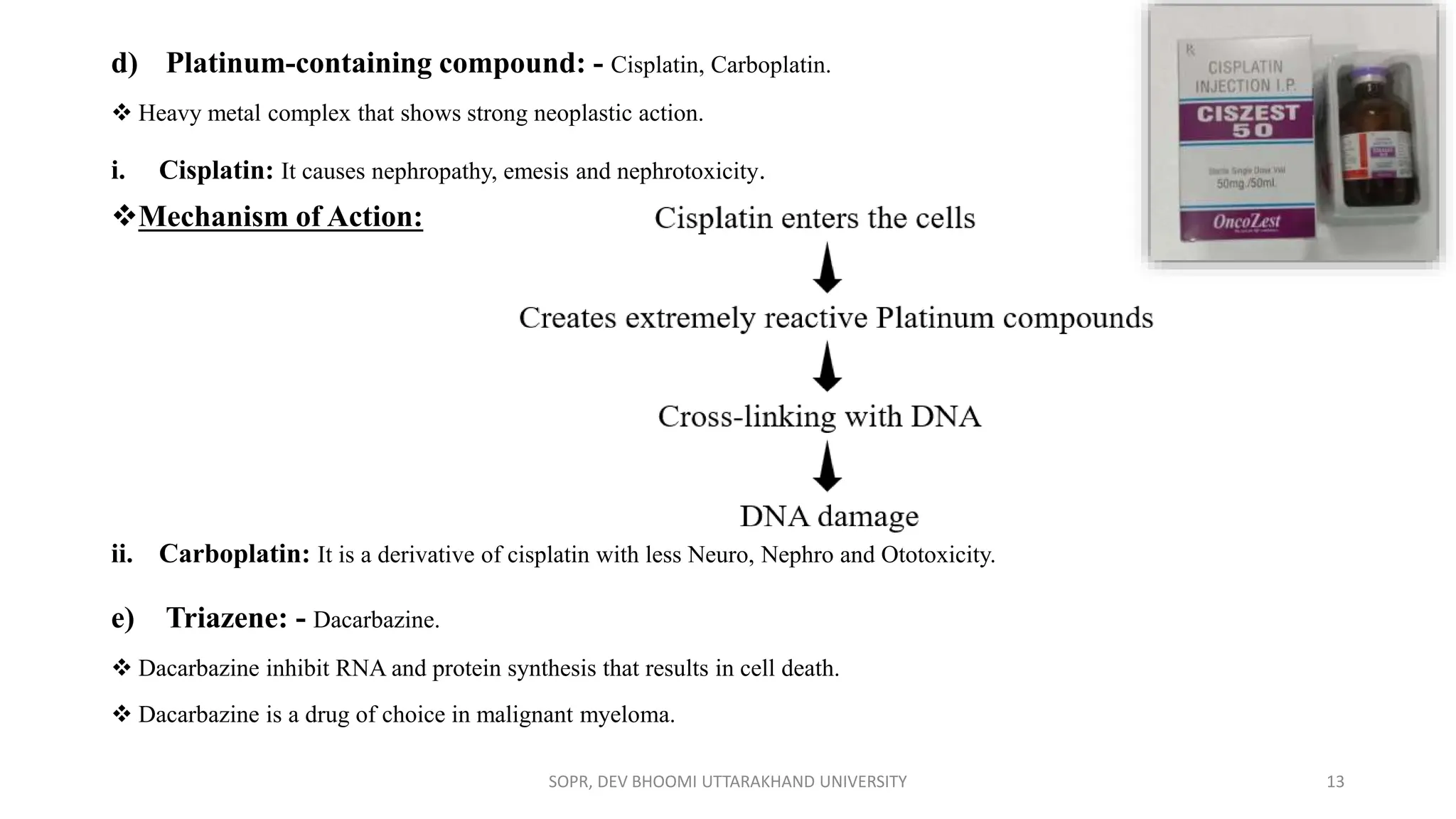
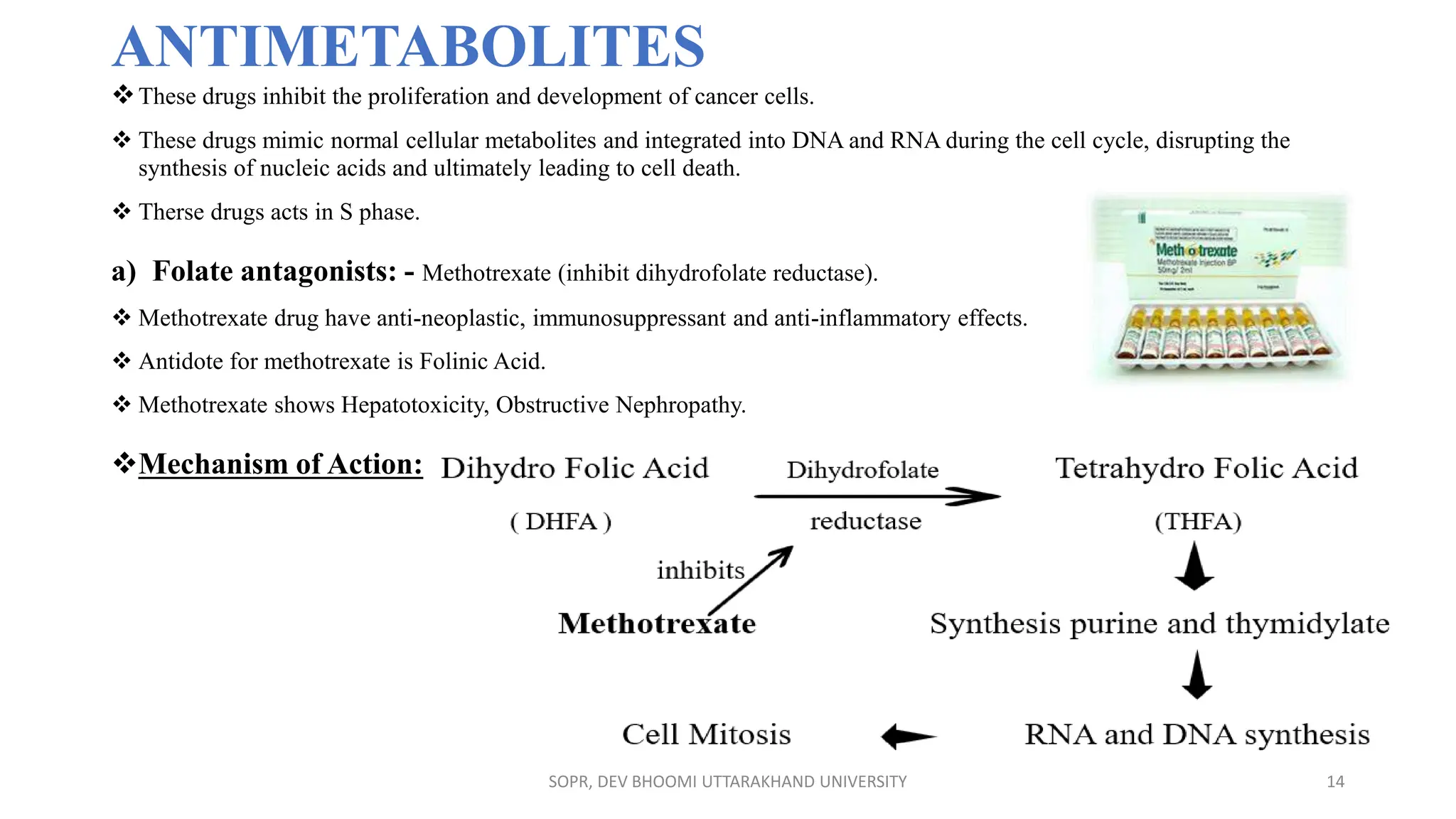
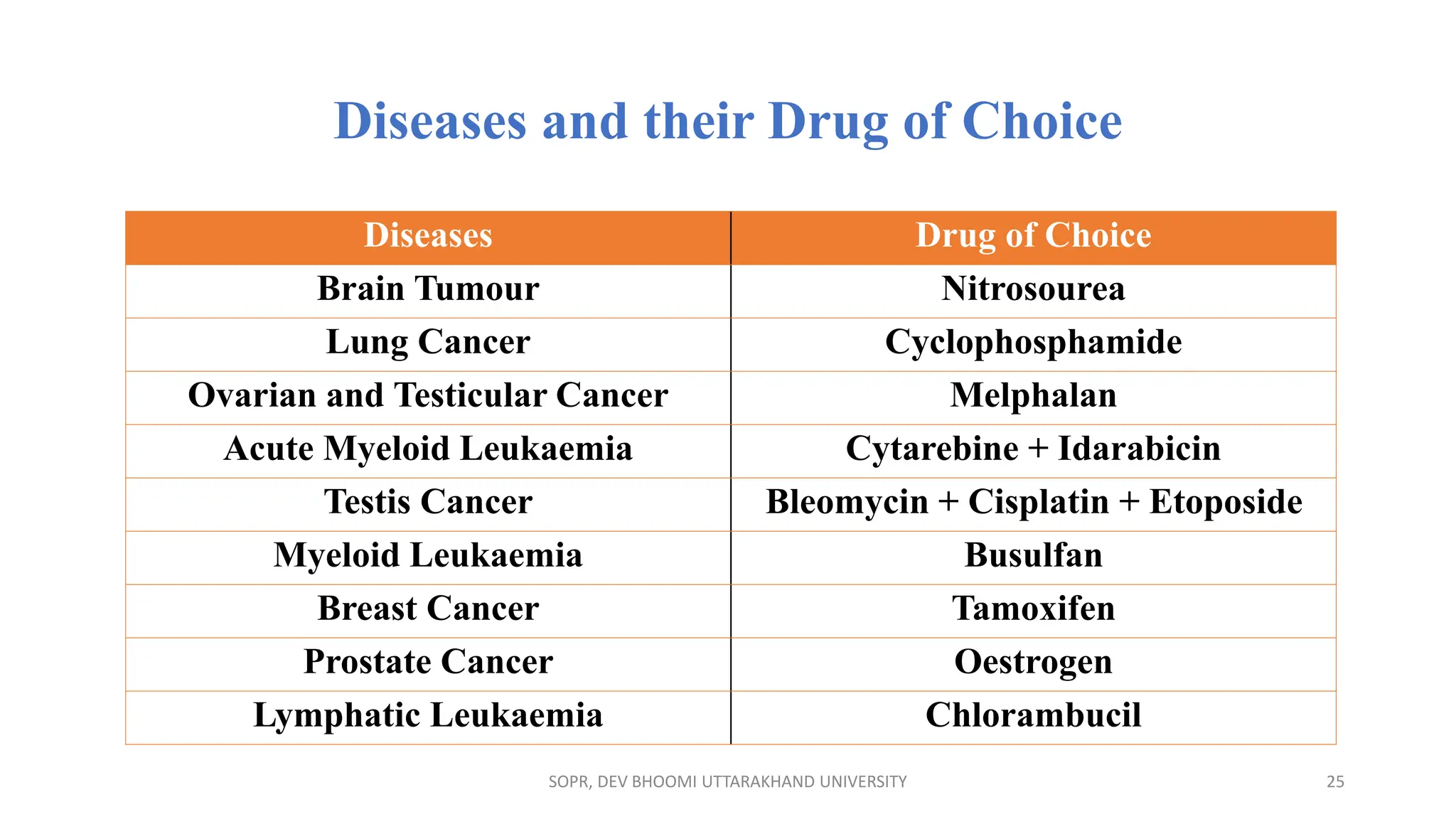
The document provides an overview of various anti-cancer drugs, their classifications, mechanisms of action, and specific applications for different types of cancer. It discusses different categories of cancer and the respective drug choices for treatment, including cell cycle-specific and non-specific agents. Key drug classes include alkylating agents, antimetabolites, vinca alkaloids, and hormonal agents, along with their mechanisms and side effects.