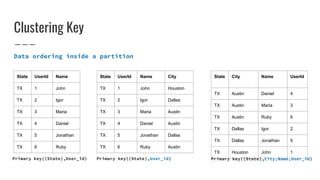
This document provides an overview of Cassandra concepts including its distributed architecture, data distribution and replication, tunable consistency, data modeling using schemas and primary keys, and querying data using the Cassandra Query Language (CQL). Key points covered include Cassandra's peer-to-peer node architecture, replication strategies, consistency levels, data structures like tables and columns, primary keys for partitioning and clustering data, and limitations of CQL compared to SQL.