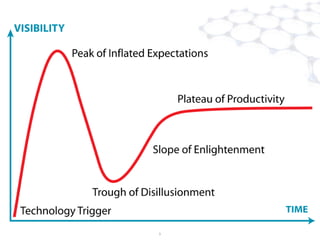
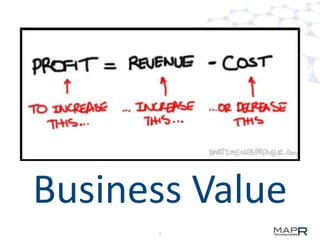
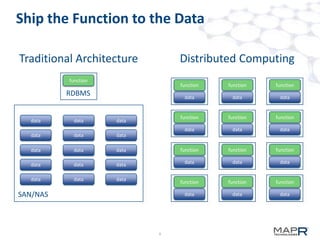
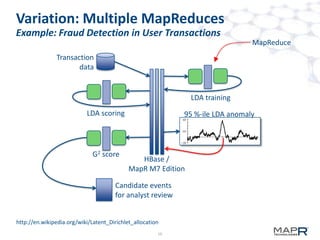
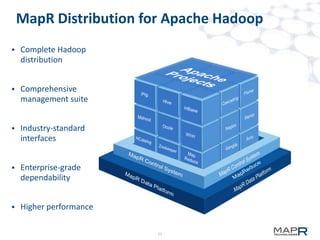
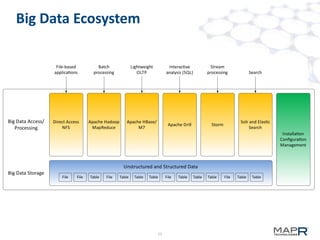
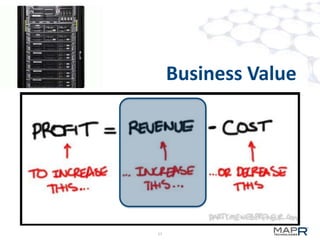
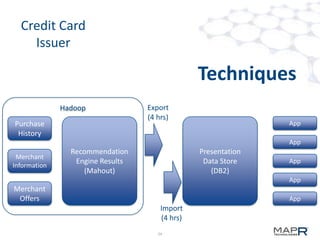
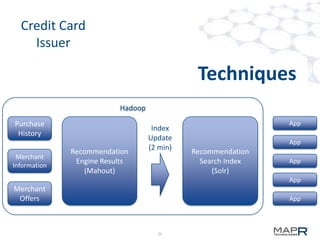
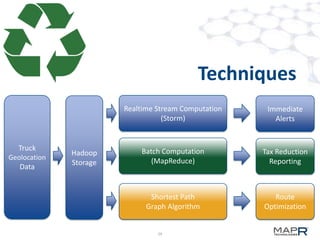
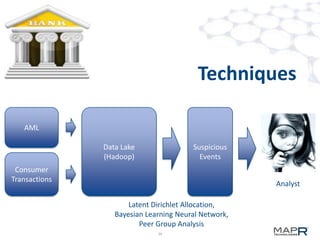
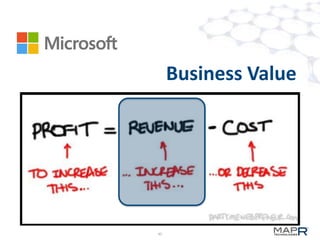
The document discusses the application of big data in various industries, presenting use cases such as telecommunications, fraud detection, and credit card transactions. It emphasizes the evolution of tools and processing methods like Hadoop, MapReduce, and machine learning techniques for extracting business value from data. Examples highlight proactive monitoring and pattern recognition to drive efficiency and insights in diverse sectors.