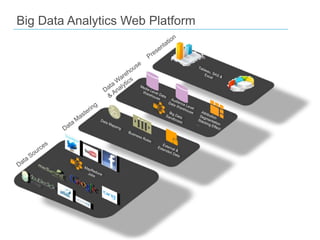
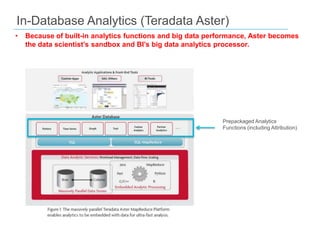
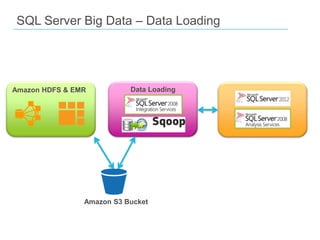
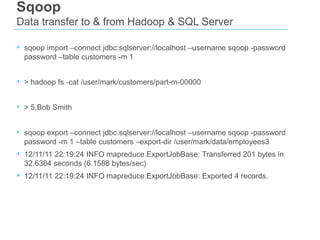
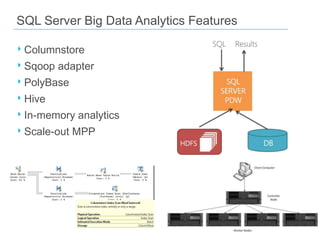
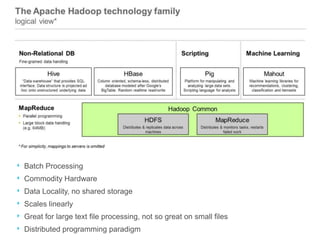
This document discusses big data and SQL Server. It covers what big data is, the Hadoop environment, big data analytics, and how SQL Server fits into the big data world. It describes using Sqoop to load data between Hadoop and SQL Server, and SQL Server features for big data analytics like columnstore and PolyBase. The document concludes that a big data analytics approach is needed for massive, variable data, and that SQL Server 2012 supports this with features like columnstore and tabular SSAS.



![MapReduce Framework (Map)
using Microsoft.Hadoop.MapReduce;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
public class TotalHitsForPageMap : MapperBase
{
public override void Map(string inputLine, MapperContext context)
{
context.Log(inputLine);
var parts = Regex.Split(inputLine, "s+");
if (parts.Length != expected) //only take records with all values
{
return;
}
context.EmitKeyValue(parts[pagePos], hit);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phillycodecampnov2012-bigdatawithsqlserver-markkromer-002-121116231215-phpapp02/85/Big-Data-with-SQL-Server-5-320.jpg)