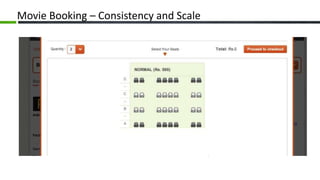
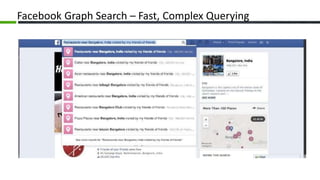
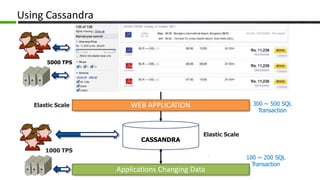
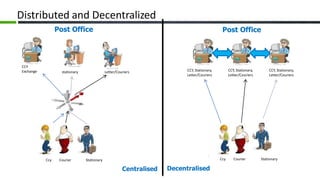
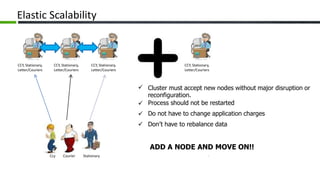
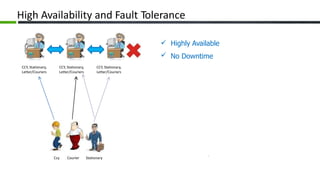
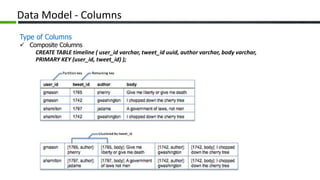
The document provides an overview of Apache Cassandra, a distributed NoSQL database, highlighting its features such as tunable consistency, elastic scalability, and high availability. It discusses use cases, including e-commerce and travel booking, while contrasting the data model of Cassandra with traditional relational databases. Additionally, it covers the design principles of Cassandra including data structure and operational efficiency, stressing the importance of its architecture for handling large volumes of data.