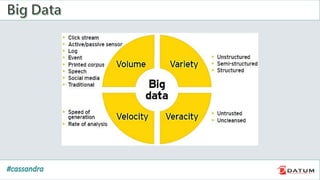
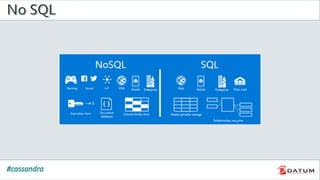
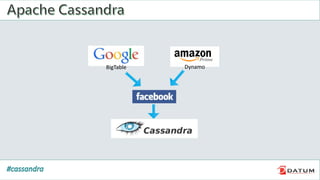
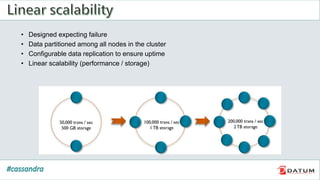
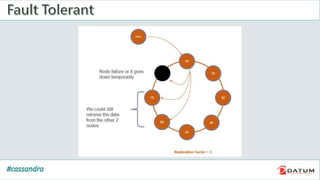
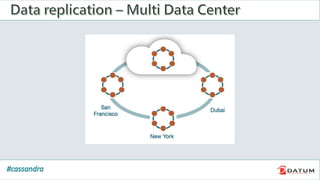
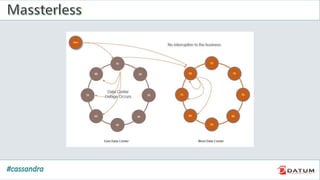
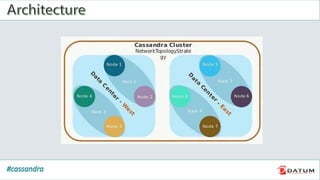
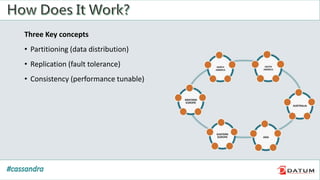
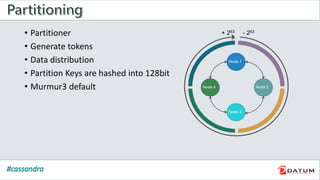
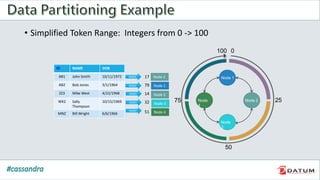
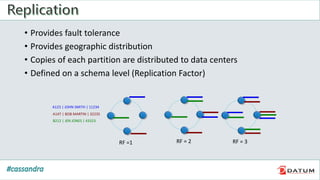
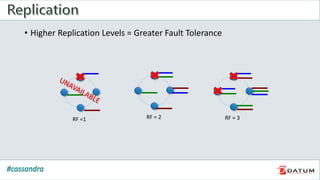
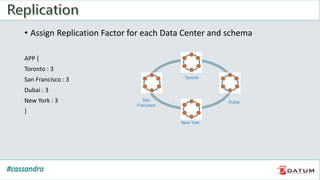
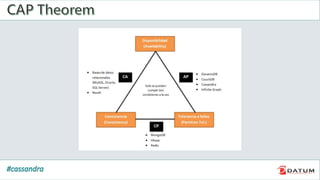
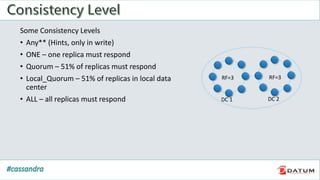
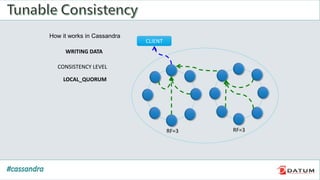
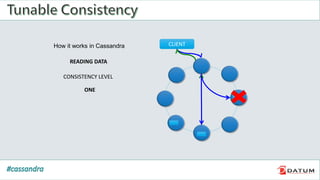
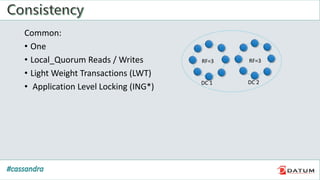
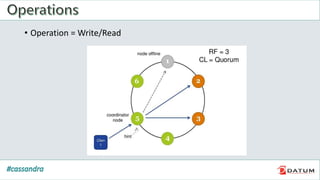
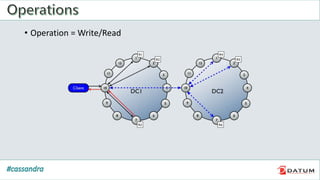
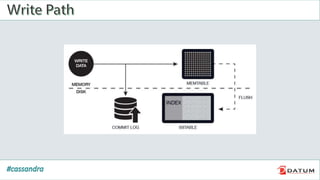
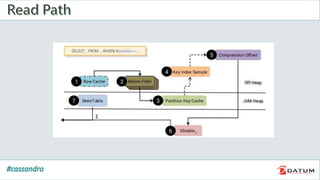
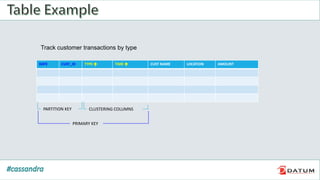
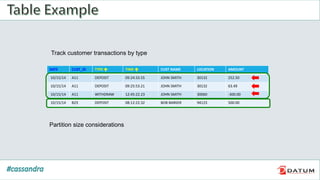
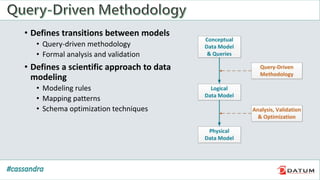
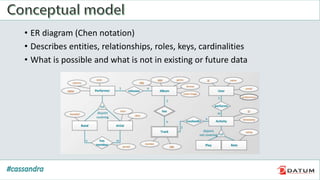
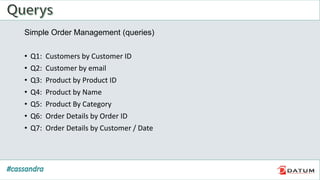
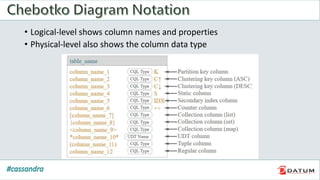
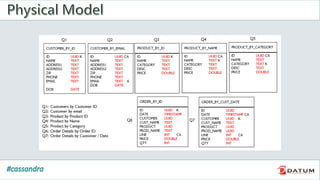
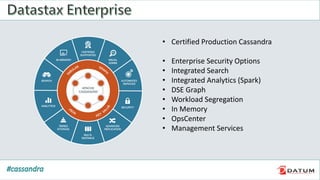
Apache Cassandra is an open source, distributed, decentralized, scalable, highly available, fault-tolerant, and tunably consistent database. It is based on Amazon's Dynamo and Google's Bigtable models. Cassandra provides linear scalability, high availability with no single points of failure, and tunable consistency. It uses a distributed data model across a cluster with configurable replication for fault tolerance.