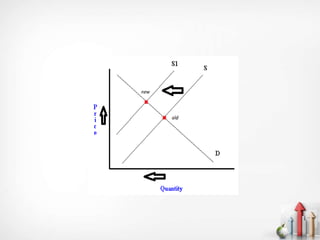
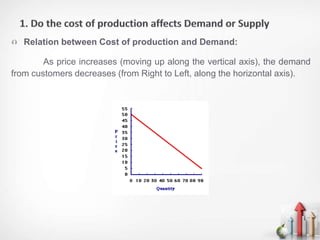
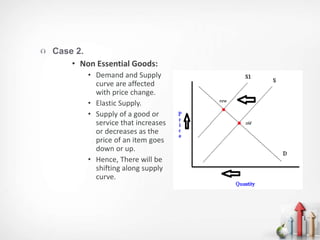
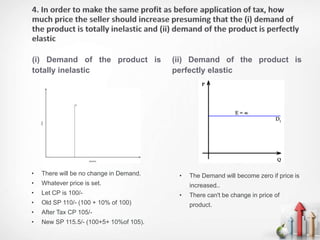
The document discusses the relationship between the cost of production and demand, distinguishing between essential and non-essential goods. For essential goods, demand remains inelastic despite production cost increases, while non-essential goods exhibit elastic demand, leading to decreased demand as costs rise. Additionally, factors such as price sensitivity, income levels, consumer preferences, competition, and future price expectations significantly influence overall demand.