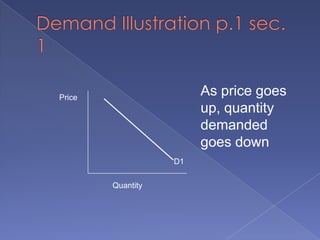
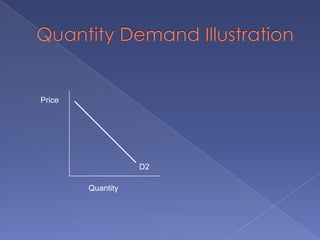
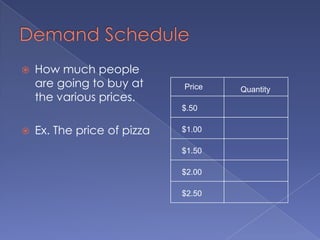
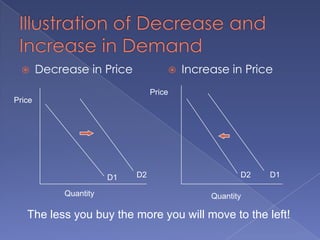
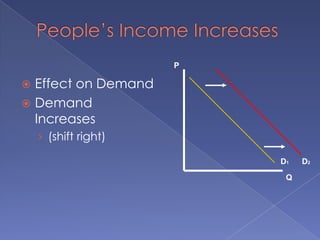
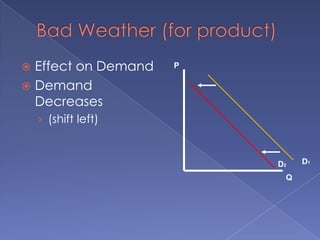
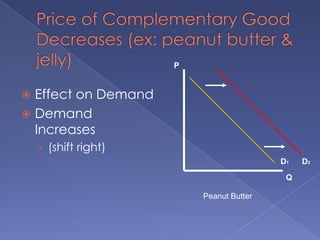
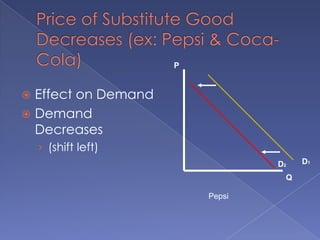
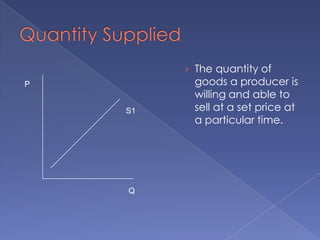
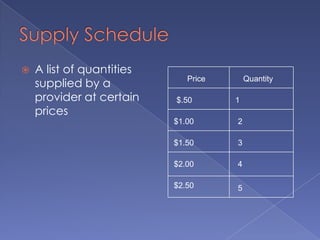
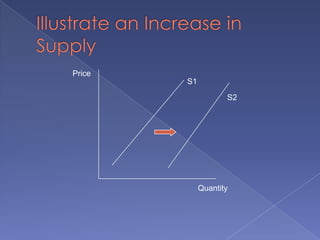
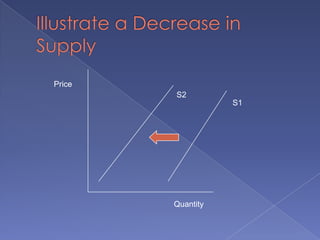
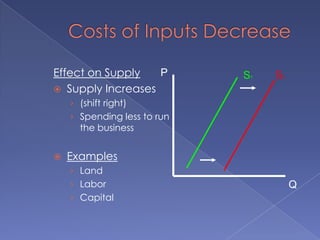
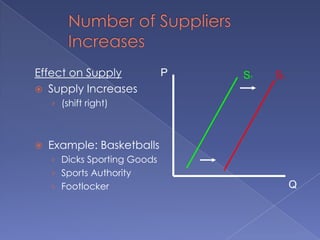
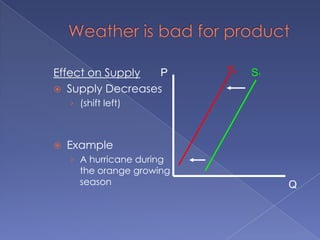
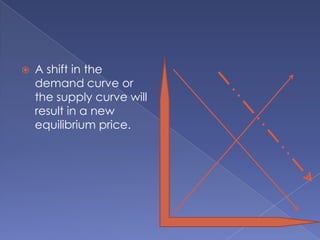
The document discusses the concepts of supply and demand. It defines key terms like demand, quantity demanded, demand schedules, the law of demand, elasticity of demand, supply, quantity supplied, supply schedules, and the law of supply. It explains how demand and supply interact to determine equilibrium price and quantity in a market. When demand or supply changes, there is a new equilibrium. The document provides examples of how factors like input costs, number of suppliers, or weather can impact supply.