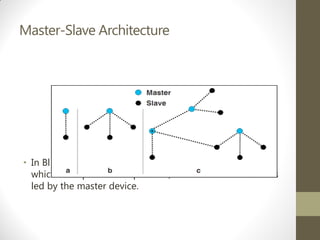
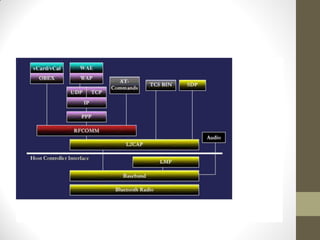
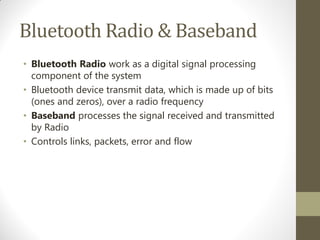
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances. It allows devices such as phones, laptops, headphones, and other portable devices to connect to each other and establish ad-hoc networks. Bluetooth operates in the unlicensed ISM band between 2.4-2.48 GHz using frequency hopping to prevent interference. Devices connect in a master-slave topology where one device is the master and up to seven can connect as slaves in a piconet. Bluetooth uses protocols like L2CAP, RFCOMM, and OBEX to transfer data and supports profiles for services like file transfer, synchronization, and telephony. Security in Bluetooth includes authentication, authorization, and encryption at different security levels.