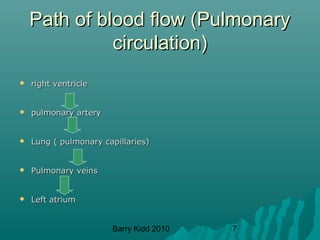
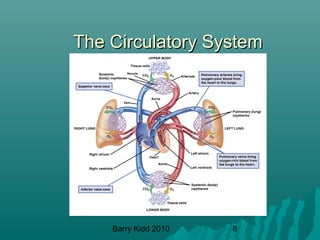
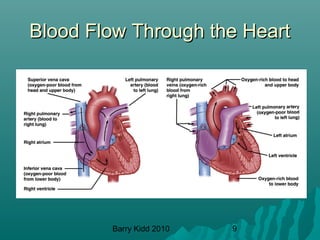
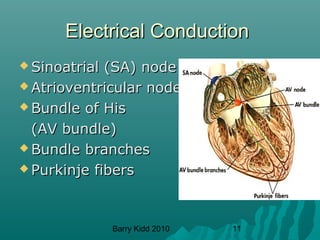
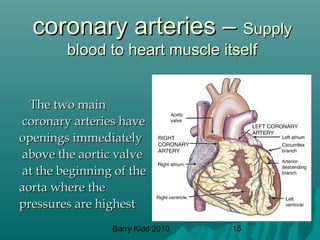
The document describes the cardiovascular system and cardiovascular emergencies. It discusses the components of the cardiovascular system including the heart, vessels, and blood. It describes the pathways of blood flow through the systemic and pulmonary circulations. It then covers abnormal heart conditions like angina, myocardial infarction, and congestive heart failure. It also discusses vascular emergencies such as atherosclerosis, thrombus, embolism, and aneurysm.