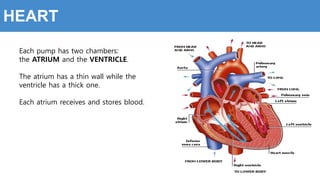
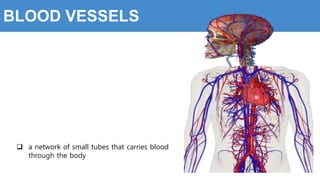
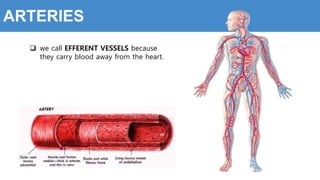
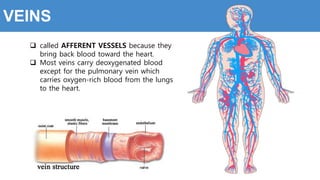
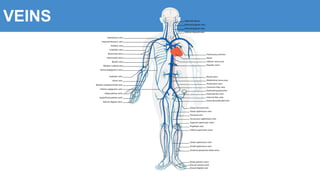
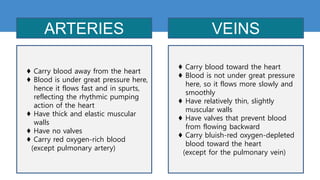
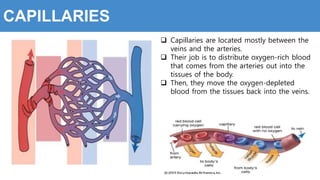
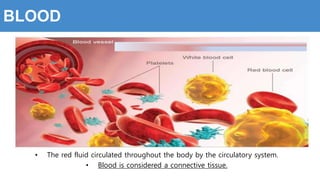
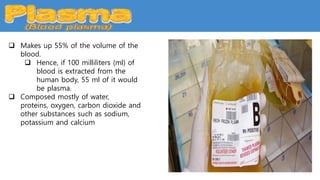
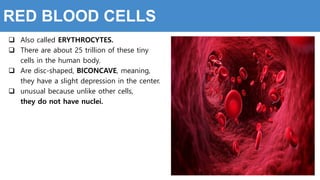
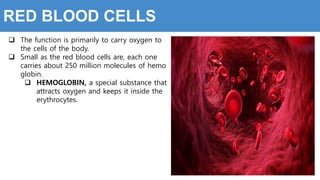
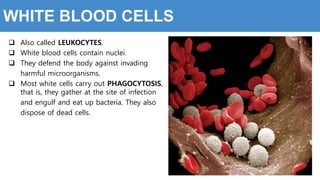
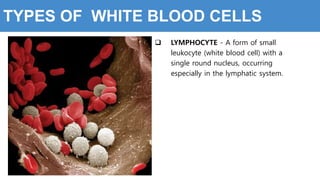
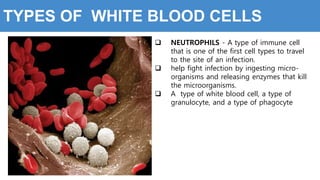
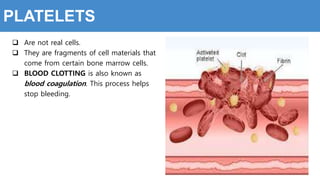
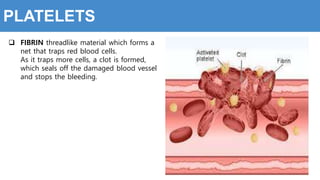
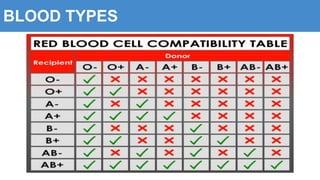
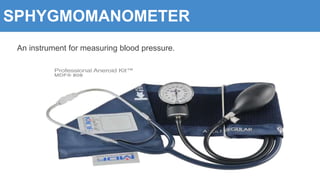
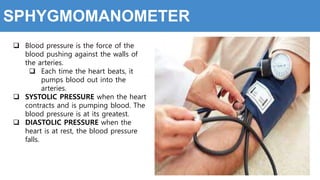
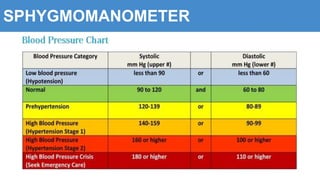
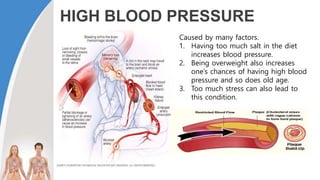
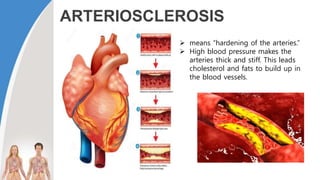
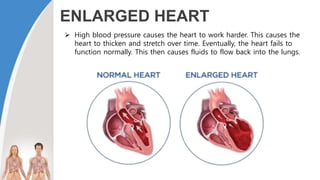
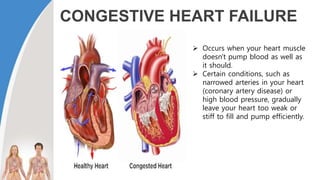
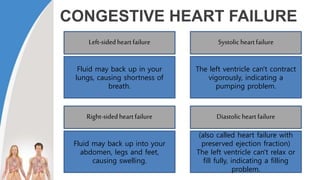
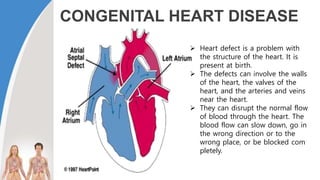
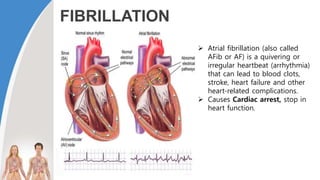
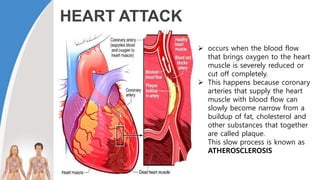
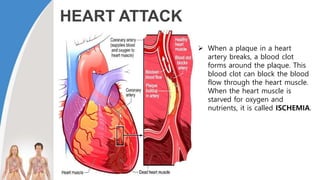
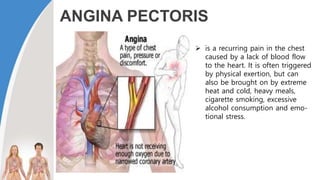
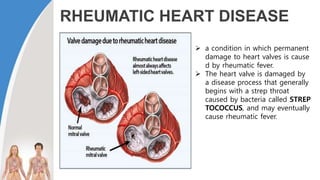
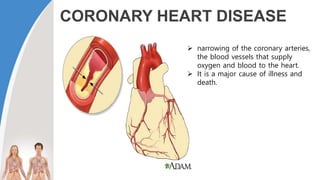
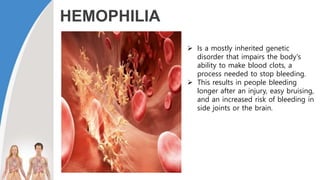
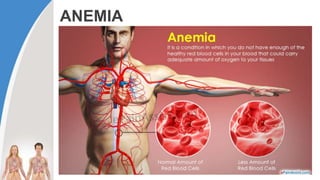
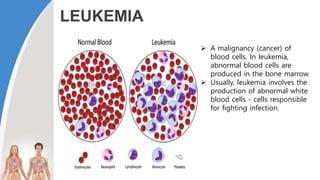
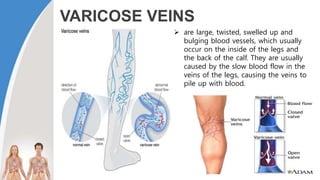
This document provides information about the circulatory system and diseases that can affect it. It begins by defining parts of the circulatory system like the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. It then discusses blood components such as plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The document also covers blood pressure, blood types, and diseases including high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, enlarged heart, congestive heart failure, congenital heart disease, fibrillation, heart attack, angina pectororis, and rheumatic heart disease.