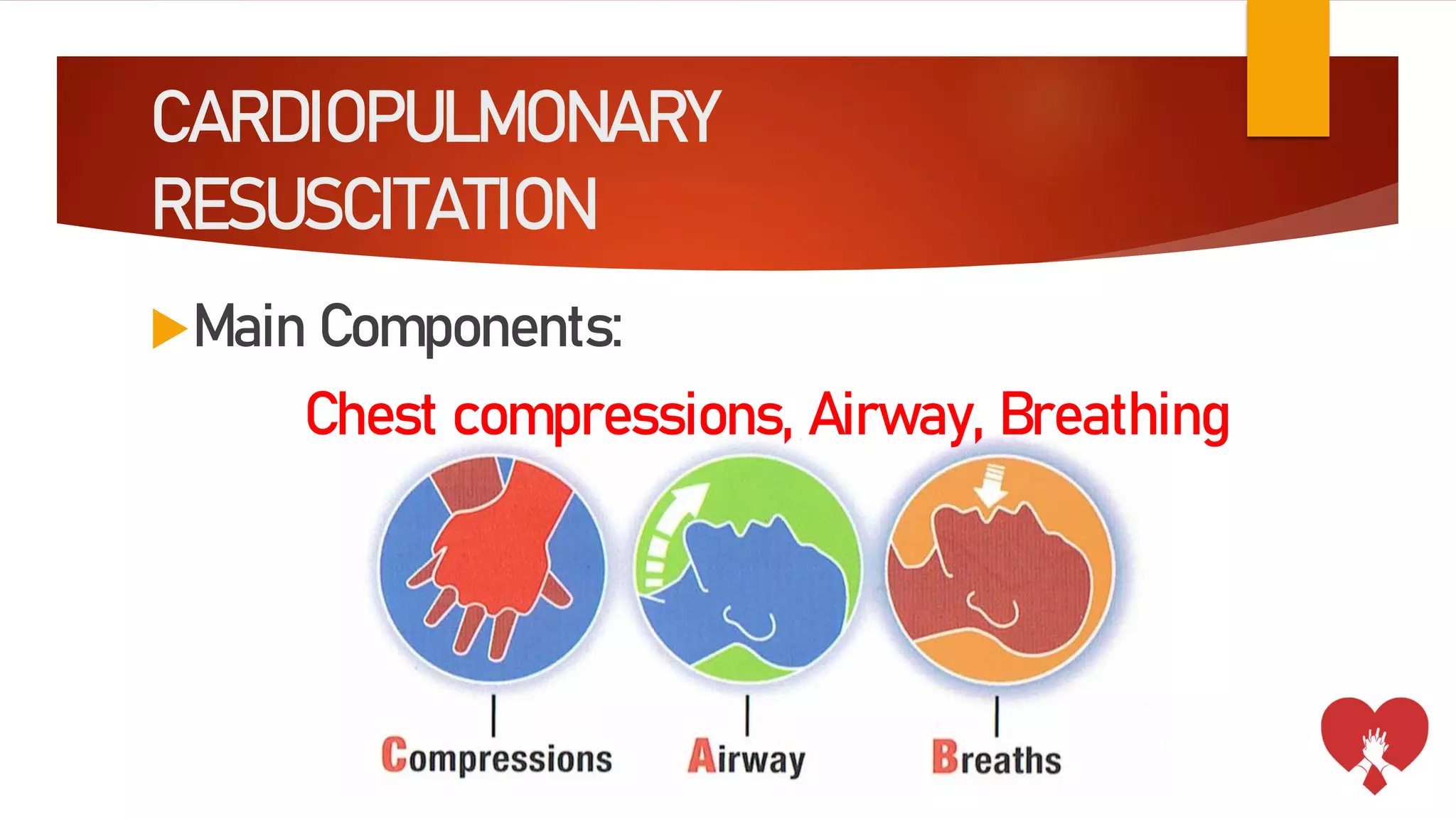
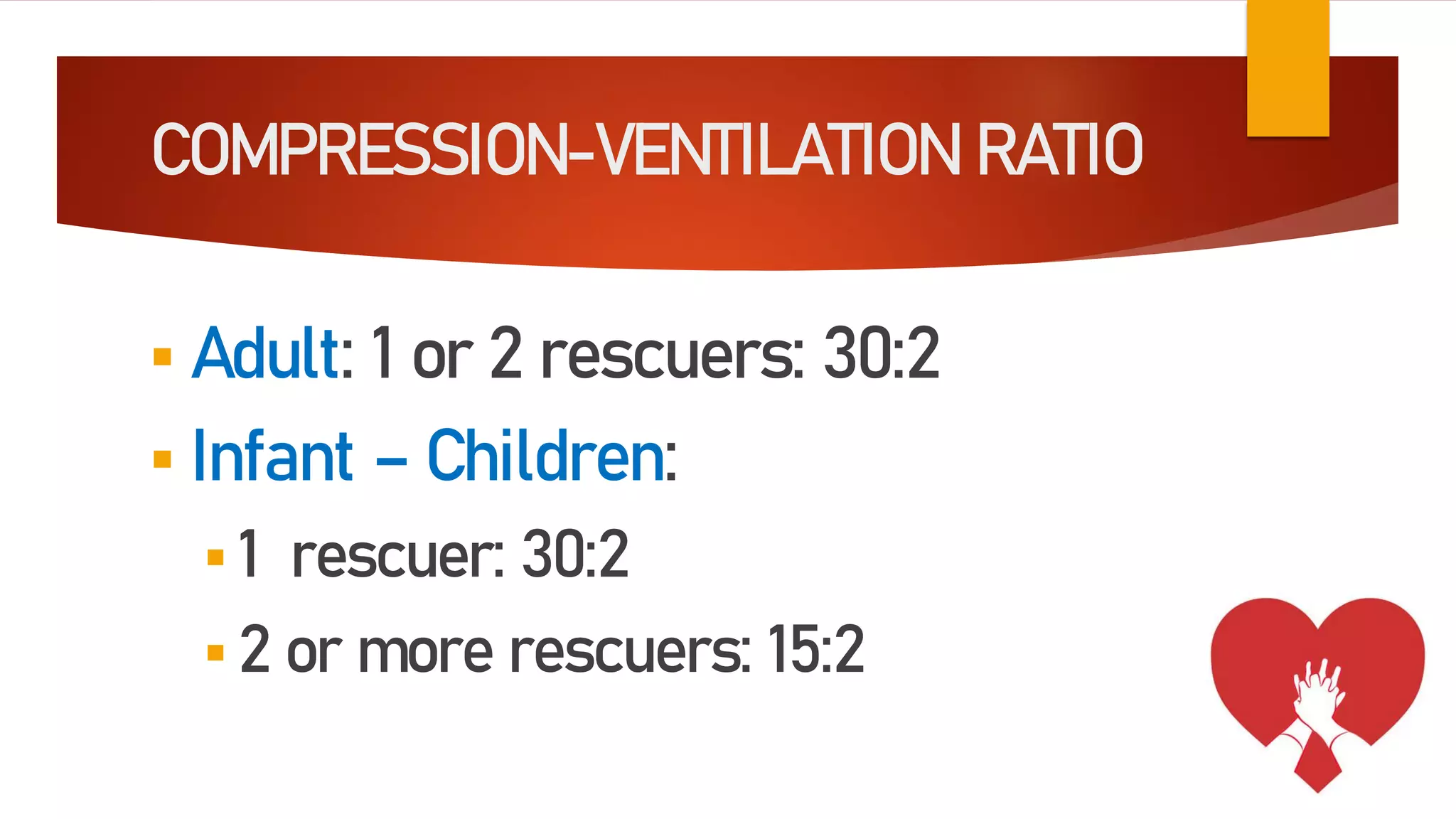
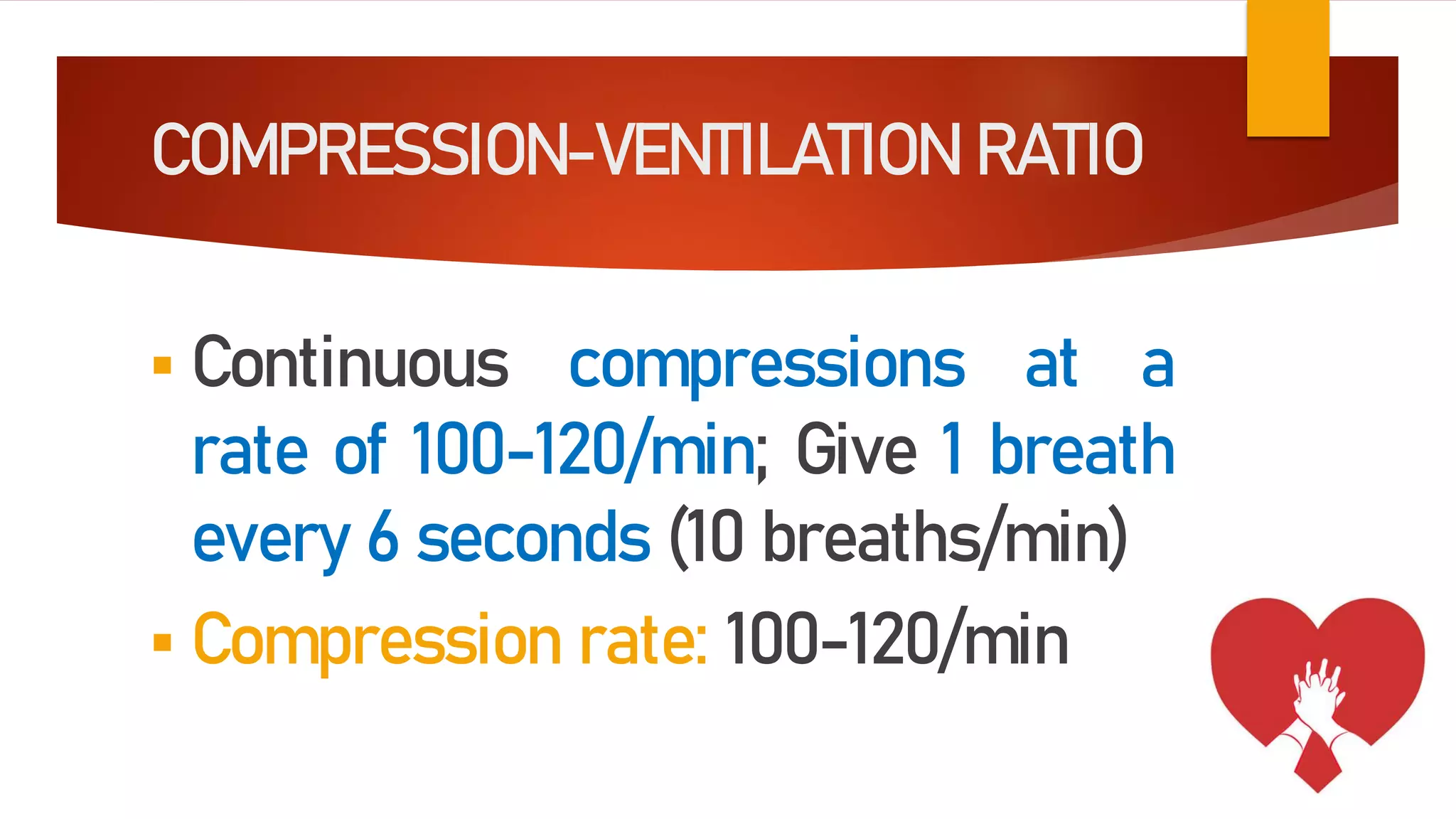
This document outlines the key aspects of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) including its objectives, components, signs of cardiac arrest, and the cardiac arrest algorithm. CPR involves chest compressions and ventilations to manually circulate blood and oxygenate tissues when someone's heart is not pumping effectively. The cardiac arrest algorithm details the steps to take including assessing breathing and pulse, beginning CPR with 30 chest compressions and 2 breaths, using an AED if available, and continuing CPR until emergency responders arrive or the victim starts moving. High-quality CPR is critical to survival and involves pushing hard and fast at the proper rate and depth along with limiting interruptions.