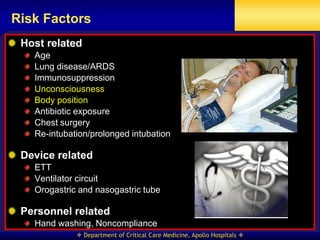
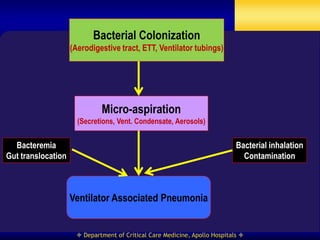
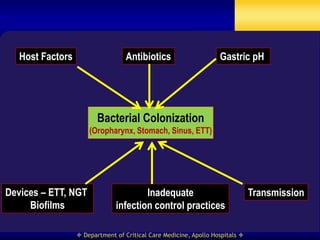
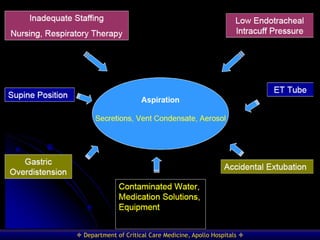
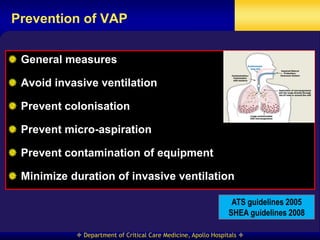
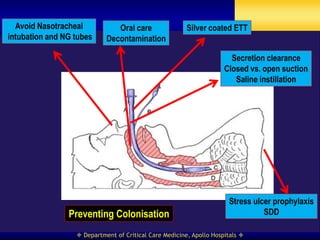
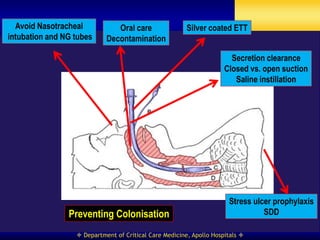
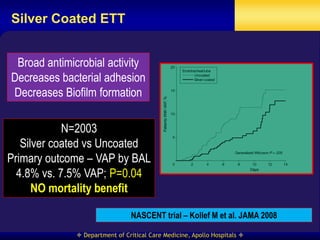
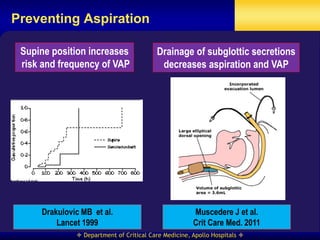
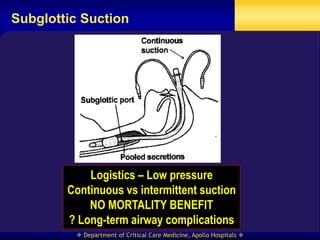
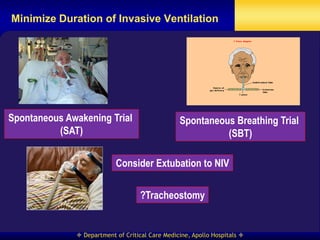
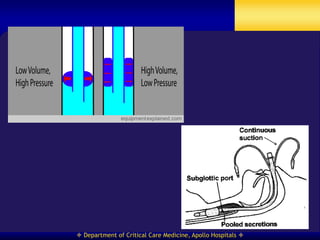
This document discusses strategies for preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) in intubated patients. It defines VAP and reviews risk factors such as prolonged intubation. Preventative measures include following infection control guidelines, using oral antiseptics to reduce bacterial colonization, maintaining head of bed elevation and cuff pressure to prevent aspiration, and minimizing the duration of mechanical ventilation when possible. Adhering closely to bundles that incorporate these various preventative strategies can help reduce the incidence of VAP.