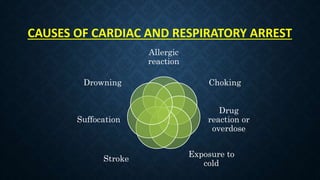
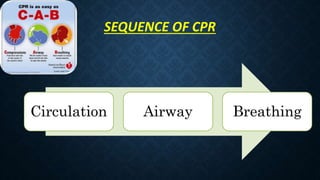
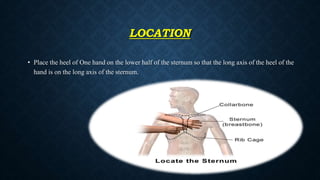
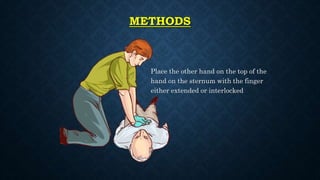
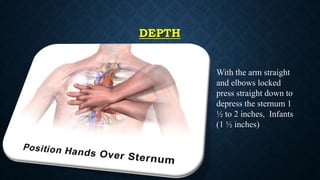
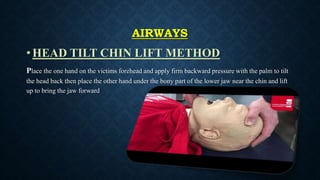
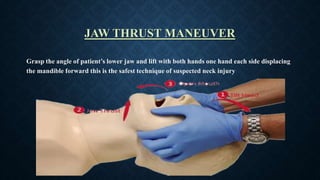
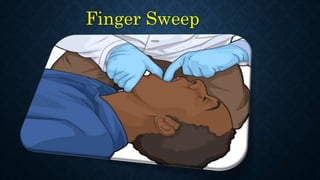
The document outlines life-saving emergency procedures including CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation), BLS (basic life support), and ACLS (advanced cardiac life support) for treating cardiac and respiratory arrest. It details indications for use, assessment methods, and the specific techniques for performing CPR, including compression, airway management, and ventilation. Additionally, it addresses complications and the use of medications during CPR to enhance patient outcomes.