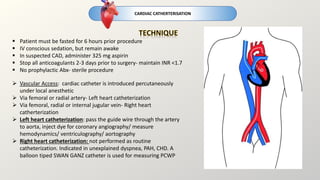
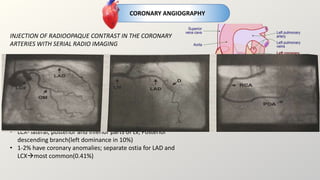
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure where a catheter is inserted into the heart via arteries or veins to perform diagnostic testing or interventions. It can be used to assess heart structure and function through angiography, assess blood flow and pressures, and treat conditions like coronary artery disease. Potential risks include bleeding, infection, arrhythmias, and contrast-induced kidney injury. Post-procedure care involves bed rest, monitoring for complications, and follow up. Other cardiac tests discussed include radionuclide imaging, electrophysiology studies, and coronary angiography.