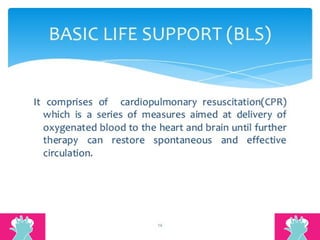
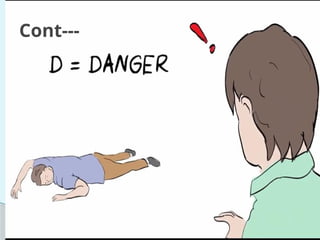
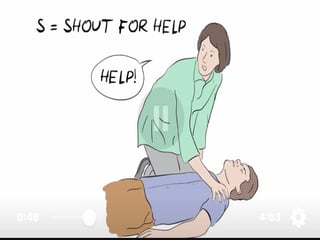
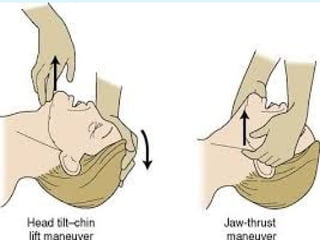
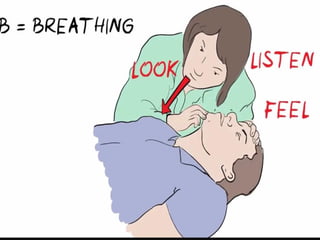
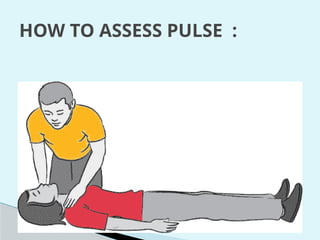
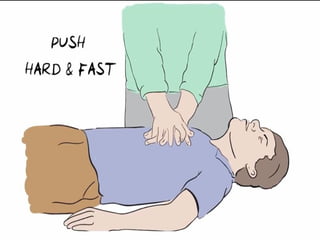
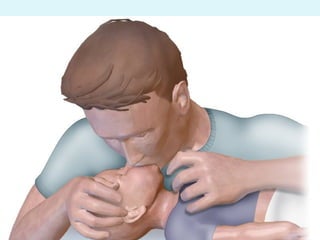
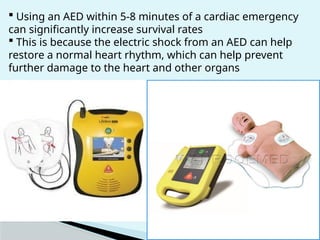
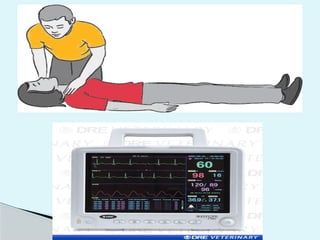
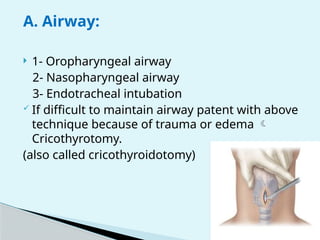
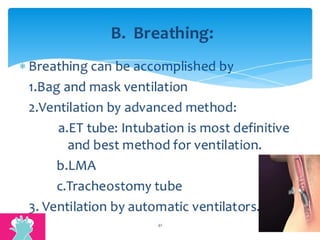
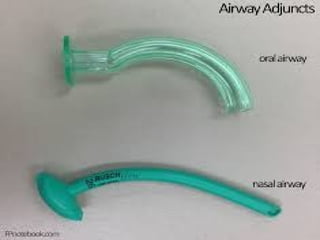
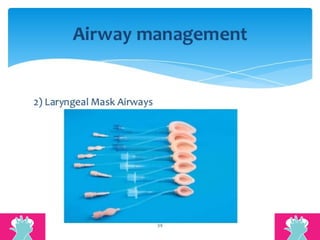
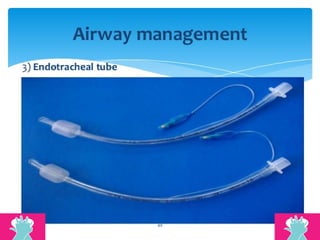
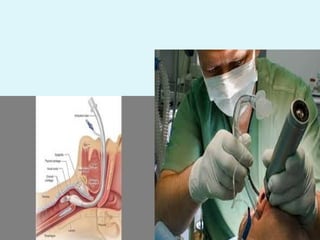
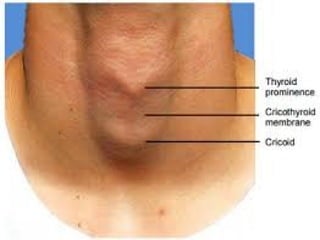
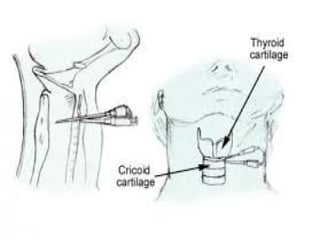
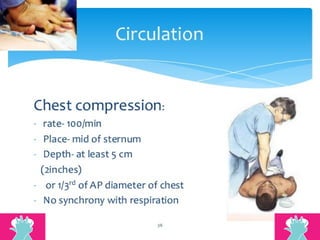
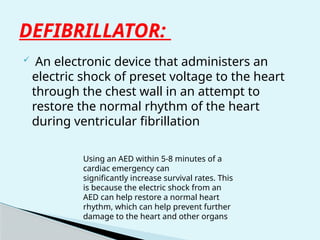
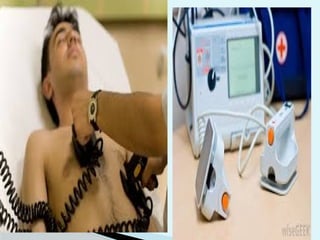
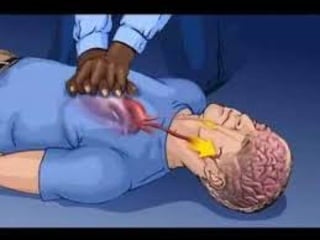
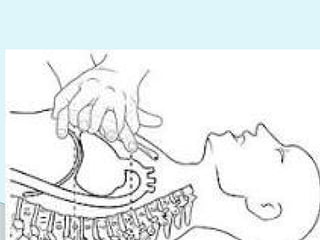
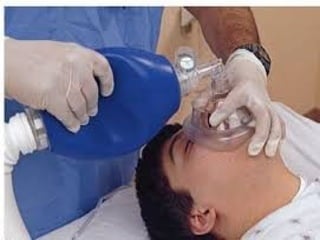
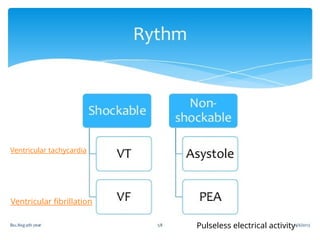
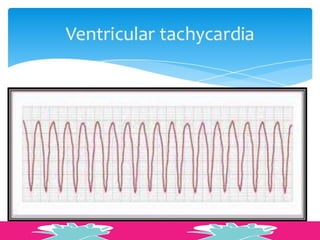
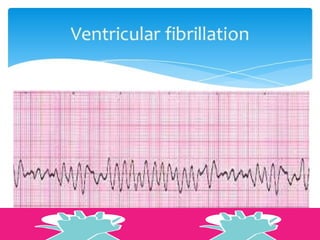
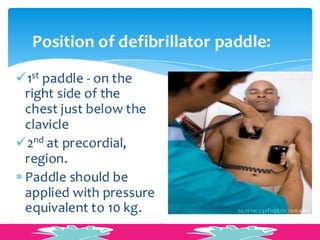
This document outlines the protocols for Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Life Support (ALS) in emergency situations, including recognizing cardiac arrest and administering CPR, defibrillation, and medication management. It details reversible causes of cardiac arrest, techniques for airway management, and the importance of post-resuscitation care to address brain and cardiac dysfunctions. The document emphasizes the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) and various life-support measures to improve survival rates in cardiac emergencies.