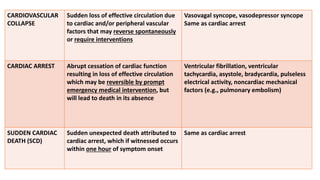
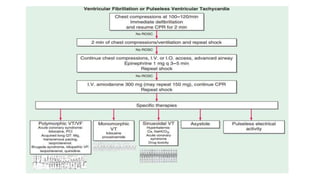
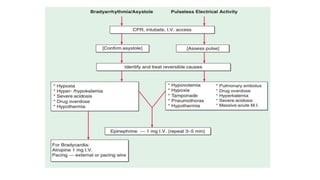
1) Cardiac arrest is the abrupt cessation of cardiac function leading to loss of circulation unless reversed by emergency intervention. It can be caused by conditions like ventricular fibrillation, asystole or mechanical issues.
2) Most cardiac arrests occur outside hospitals and fewer than 10% of patients survive after attempted resuscitation. Survival rates are lower for black Americans and higher for Asian populations.
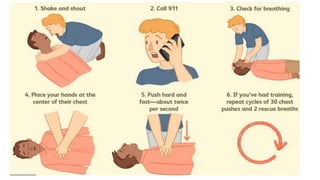
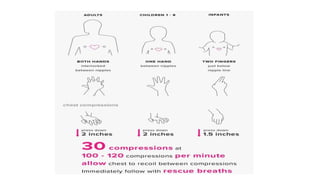
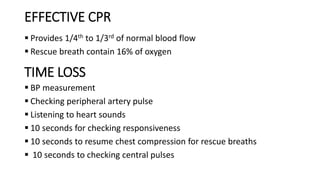
3) The chain of survival for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest includes early CPR, defibrillation if needed, advanced medical services and post-cardiac arrest care. Effective CPR provides some blood flow until further treatment.