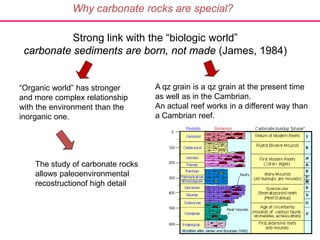
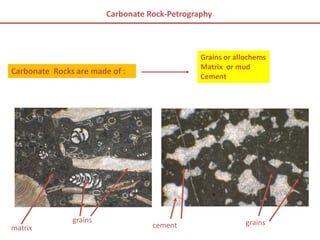
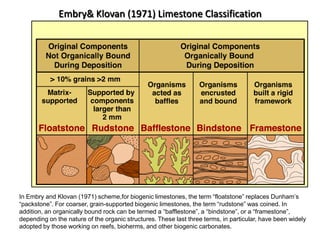
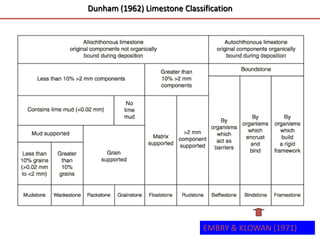
Carbonate rocks are special because they have a strong link to biological processes. Carbonate sediments are formed biologically rather than through inorganic processes. The composition of carbonate rocks can provide precise information about the depositional environment, unlike siliciclastic rocks. Carbonates can form through various processes, including mechanical deposition, chemical precipitation, and in situ growth. They are classified based on their grain composition, matrix, and cement using ternary diagrams and schemes from Dunham and Folk.