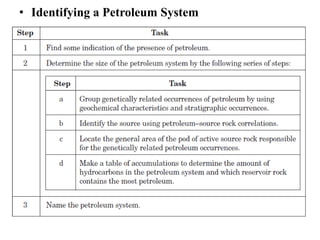
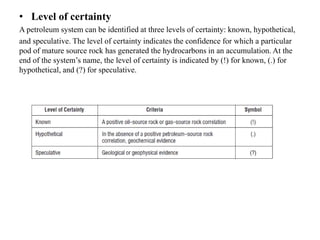
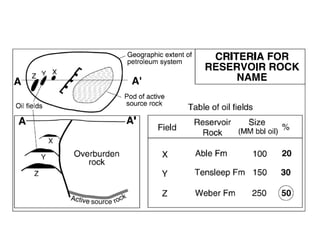
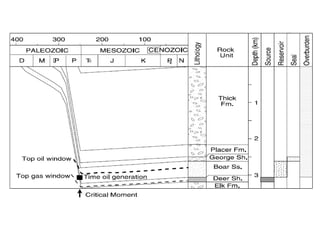
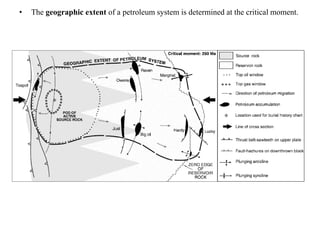
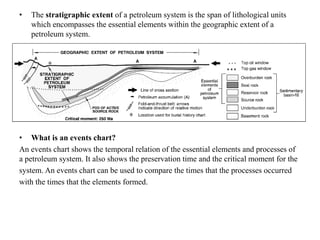
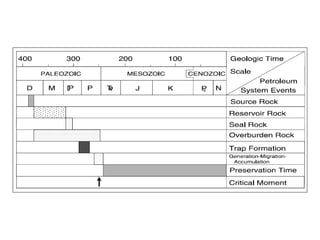
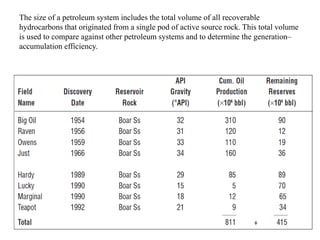
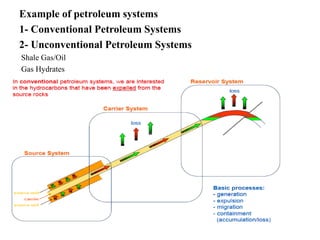
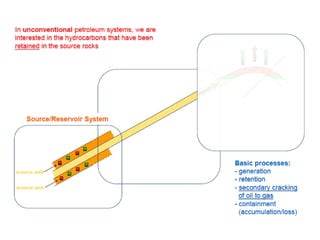
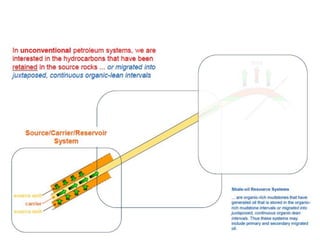
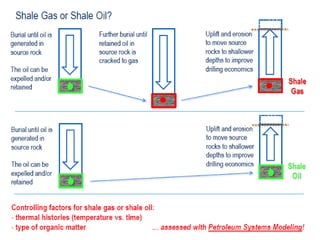
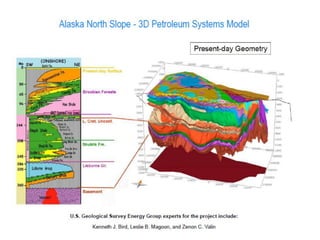
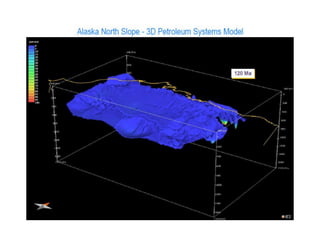
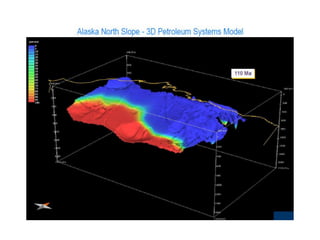
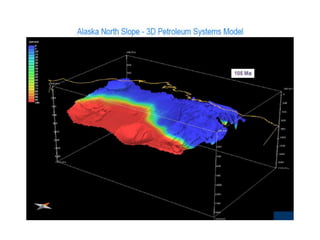
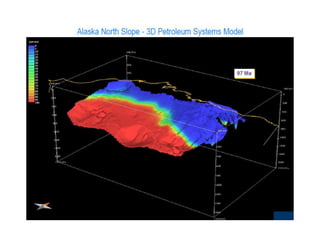
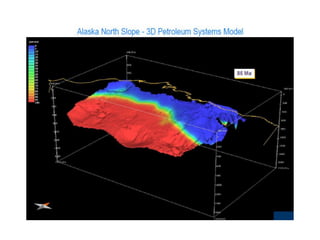
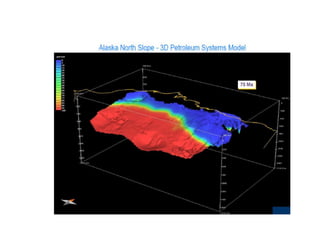
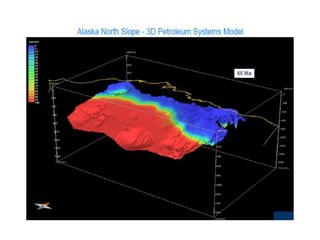
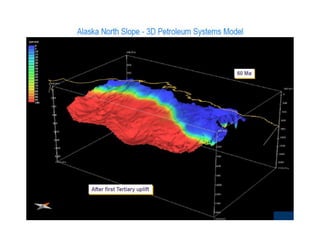
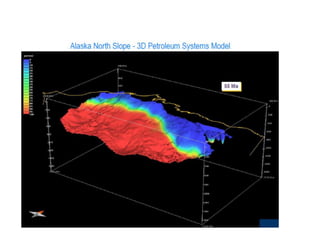
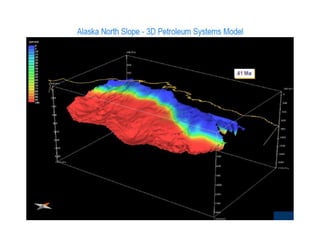
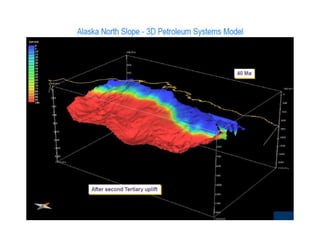
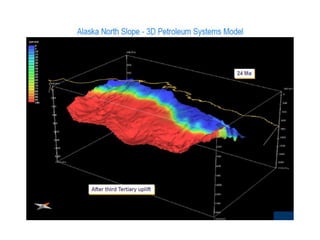
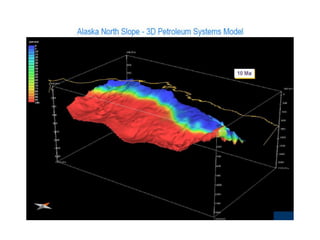
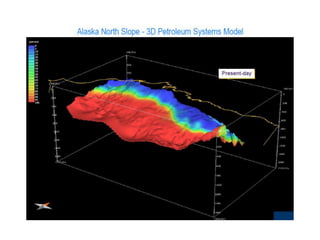
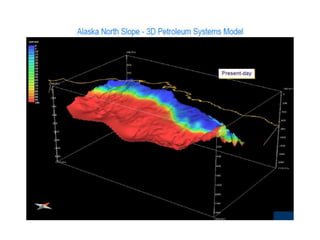
A petroleum system encompasses a source rock and all related oil and gas accumulations. It includes essential geologic elements and processes for oil and gas formation, including the source rock, reservoir rock, seal rock, overburden rock, trap formation, and hydrocarbon generation, migration, and accumulation. A petroleum system is identified by naming the source rock, largest reservoir rock, and level of certainty. It has a geographic, stratigraphic, and temporal extent defined by the critical moment of hydrocarbon formation. An events chart illustrates the temporal relationship between a system's essential elements and processes.