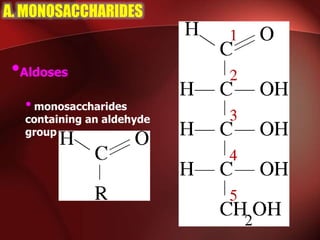
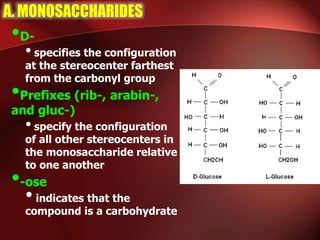
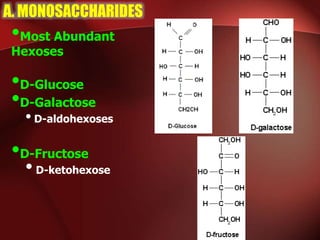
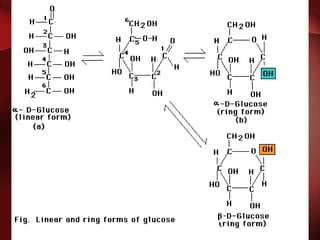
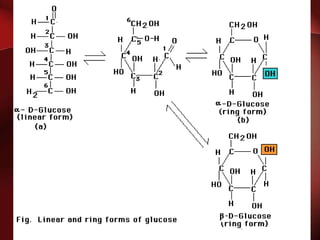
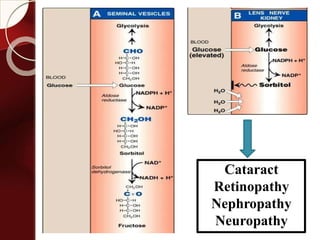
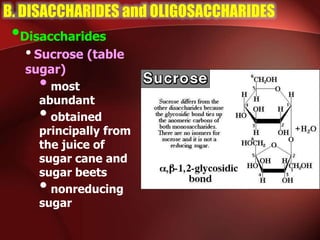
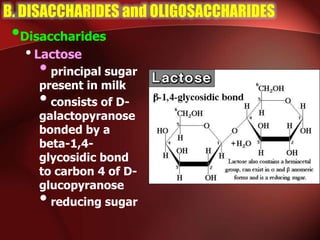
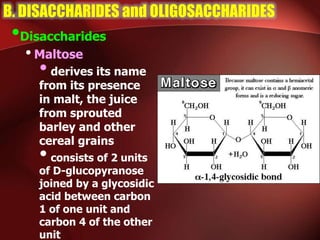
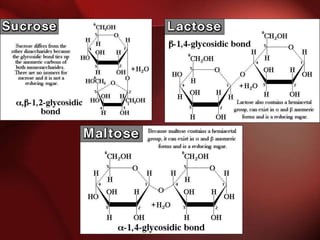
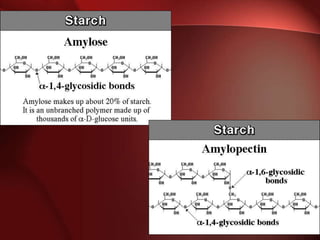
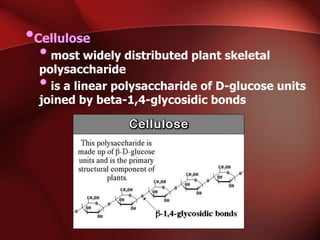
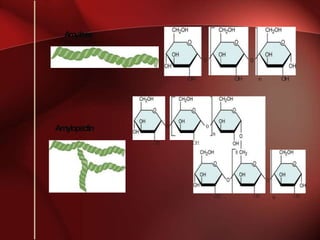
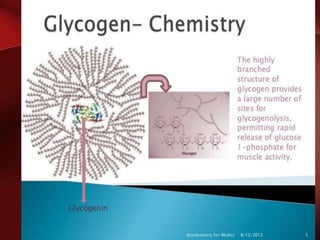
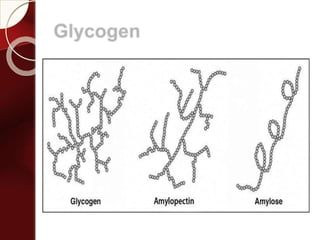
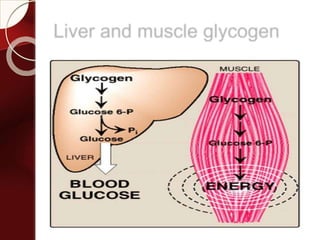
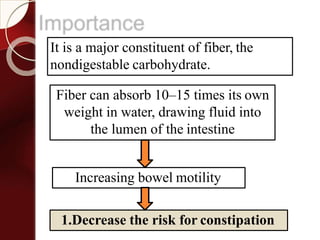
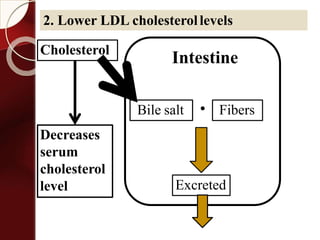
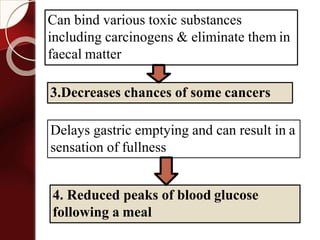
Carbohydrates are the most abundant organic compounds in plants. They act as storehouses of chemical energy and components of supportive structures. There are four main types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose are formed from two monosaccharide units. Polysaccharides including starch, glycogen, and cellulose are long chains of monosaccharide units and serve as energy storage. Carbohydrates undergo various reactions including formation of glycosides, esters, and reduction to alcohols.







































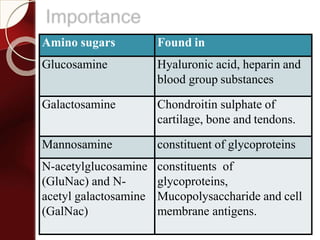
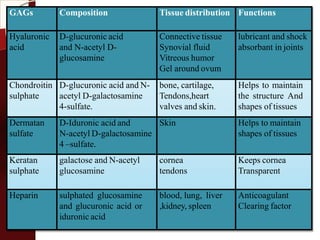
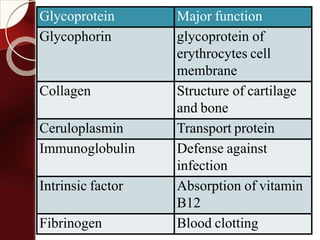
![Mucopolysaccharide
glycosaminoglycans(GAGs)
[acidic sugar–amino sugar]n.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbohydrates-160430124448/85/Carbohydrates-67-320.jpg)