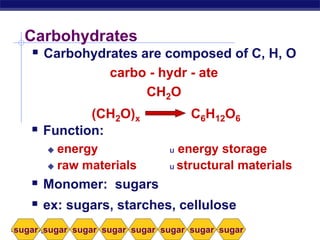
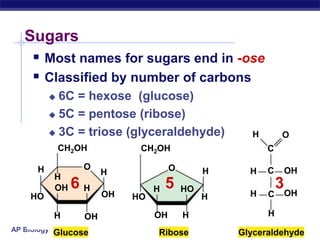
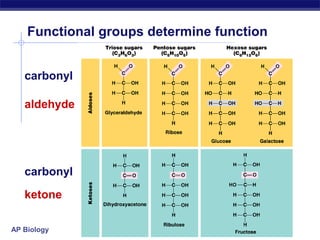
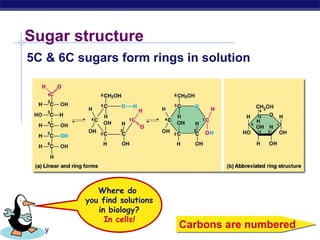
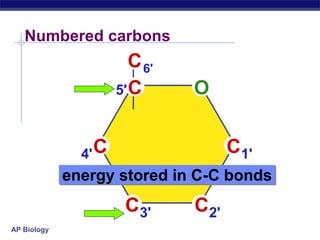
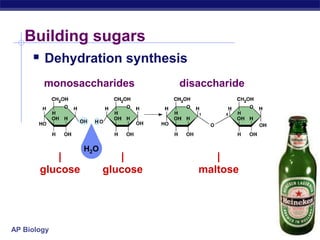
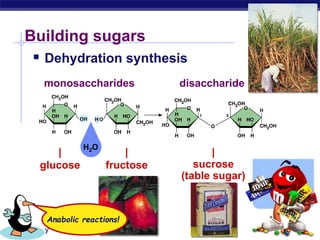
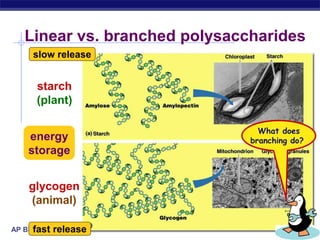
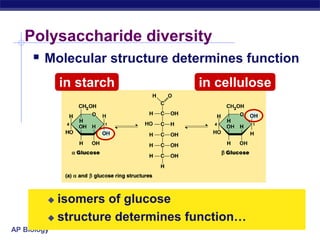
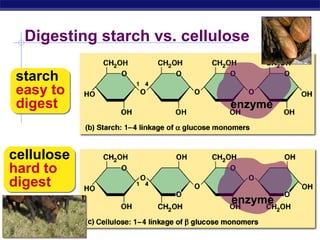
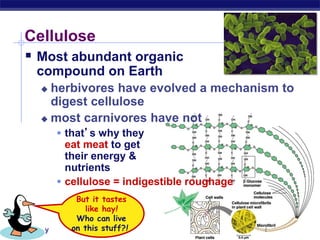
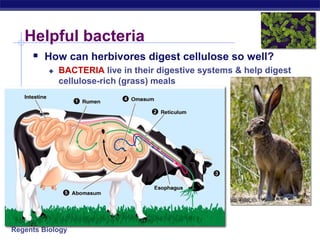
This document discusses carbohydrates, including their structure, function, classification, and digestion. It notes that carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They function to store energy and act as structural materials. Monosaccharides like glucose are the monomers that make up disaccharides like sucrose and polysaccharides like starch and cellulose. While starch can be easily digested, cellulose is difficult to digest for many organisms. Herbivores have evolved with bacteria in their digestive systems that help break down cellulose.