1. The document provides information about carbohydrates from a student named Tushar Bharat Harde who is studying Plant Physiology and Biochemistry.
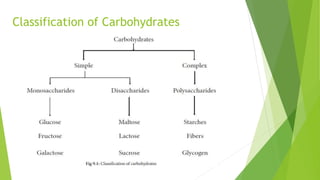
2. It defines carbohydrates and lists common sources like potatoes, maize, milk, popcorn and bread. It then classifies carbohydrates into simple carbohydrates like sugars and complex carbohydrates.
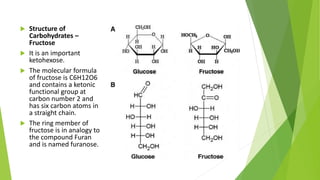
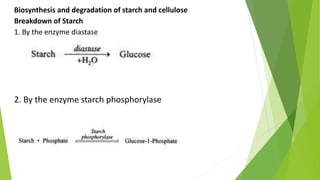
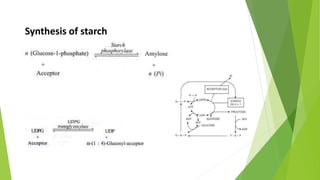
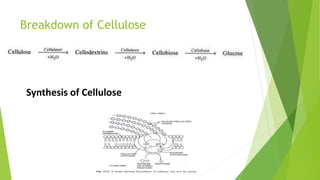
3. Carbohydrates are further classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. Examples of each like glucose, sucrose, starch and cellulose are provided along with their structures and properties.