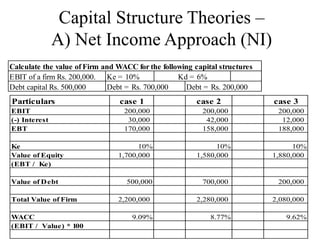
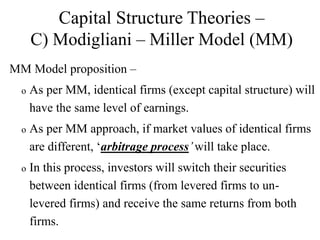
This document discusses capital structure and various capital structure theories. It begins by defining capital structure and explaining that the objective is to maximize shareholder wealth through an optimal capital structure design. It then covers key considerations in capital structure planning like return, cost, risk and control. Several capital structure theories are explained - the Net Income Approach proposes higher debt increases value, while the Net Operating Income Approach says value is independent of structure. The Modigliani-Miller model supports the latter. The Traditional Approach finds an optimal structure where cost is minimum and value maximum. Formulas and an example are provided.







![Capital Structure Theories –
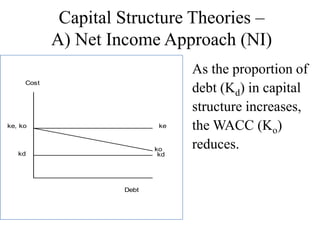
A) Net Income Approach (NI)
Net Income approach proposes that there is a definite
relationship between capital structure and value of the firm.
The capital structure of a firm influences its cost of capital
(WACC), and thus directly affects the value of the firm.
NI approach assumptions –
o NI approach assumes that a continuous increase in debt does
not affect the risk perception of investors.
o Cost of debt (Kd) is less than cost of equity (Ke) [i.e. Kd < Ke ]
o Corporate income taxes do not exist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockiiigroup4-140721044356-phpapp02/85/capital-structure-8-320.jpg)